
Geodesy is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's geometric shape, orientation in space and gravitational field. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivalent measurements for other planets. Geodynamical phenomena include crustal motion, tides and polar motion, which can be studied by designing global and national control networks, applying space and terrestrial techniques and relying on datums and coordinate systems.

In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north–south position of a point on the Earth's surface. Latitude is an angle which ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the poles. Lines of constant latitude, or parallels, run east–west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude is used together with longitude to specify the precise location of features on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term latitude should be taken to be the geodetic latitude as defined below. Briefly, geodetic latitude at a point is the angle formed by the vector perpendicular to the ellipsoidal surface from that point, and the equatorial plane. Also defined are six auxiliary latitudes which are used in special applications.

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.

The World Geodetic System (WGS) is a standard for use in cartography, geodesy, and satellite navigation including GPS. This standard includes the definition of the coordinate system's fundamental and derived constants, the ellipsoidal (normal) Earth Gravitational Model (EGM), a description of the associated World Magnetic Model (WMM), and a current list of local datum transformations.

The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system is a system of geographic grid references used in Great Britain, distinct from latitude and longitude. It is often called British National Grid (BNG).
In geodesy, conversion among different geographic coordinate systems is made necessary by the different geographic coordinate systems in use across the world and over time. Coordinate conversion is composed of a number of different types of conversion: format change of geographic coordinates, conversion of coordinate systems, or transformation to different geodetic datums. Geographic coordinate conversion has applications in cartography, surveying, navigation and geographic information systems.

In geodesy, a reference ellipsoid is a mathematically defined surface that approximates the geoid, the truer figure of the Earth, or other planetary body. Because of their relative simplicity, reference ellipsoids are used as a preferred surface on which geodetic network computations are performed and point coordinates such as latitude, longitude, and elevation are defined.

A geodetic datum or geodetic system is a coordinate system, and a set of reference points, used to locate places on the Earth. An approximate definition of sea level is the datum WGS 84, an ellipsoid, whereas a more accurate definition is Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008), using at least 2,159 spherical harmonics. Other datums are defined for other areas or at other times; ED50 was defined in 1950 over Europe and differs from WGS 84 by a few hundred meters depending on where in Europe you look. Mars has no oceans and so no sea level, but at least two martian datums have been used to locate places there.

The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface . The term elevation is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while altitude or geopotential height is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and depth is used for points below the surface.

A Lambert conformal conic projection (LCC) is a conic map projection used for aeronautical charts, portions of the State Plane Coordinate System, and many national and regional mapping systems. It is one of seven projections introduced by Johann Heinrich Lambert in his 1772 publication Anmerkungen und Zusätze zur Entwerfung der Land- und Himmelscharten.

A spatial reference system (SRS) or coordinate reference system (CRS) is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems. Spatial reference systems are defined by the OGC's Simple Feature Access using well-known text representation of coordinate reference systems, and support has been implemented by several standards-based geographic information systems. Spatial reference systems can be referred to using a SRID integer, including EPSG codes defined by the International Association of Oil and Gas Producers. It is specified in ISO 19111:2007 Geographic information—Spatial referencing by coordinates, prepared by ISO/TC 211, also published as OGC Abstract Specification, Topic 2: Spatial referencing by coordinate.
Georeferencing means that the internal coordinate system of a map or aerial photo image can be related to a ground system of geographic coordinates. The relevant coordinate transforms are typically stored within the image file, though there are many possible mechanisms for implementing georeferencing. The most visible effect of georeferencing is that display software can show ground coordinates and also measure ground distances and areas. In other words, Georeferencing means to associate something with locations in physical space. The term is commonly used in the geographic information systems field to describe the process of associating a physical map or raster image of a map with spatial locations. Georeferencing may be applied to any kind of object or structure that can be related to a geographical location, such as points of interest, roads, places, bridges, or buildings.
The International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP) is the petroleum industry's global forum in which members identify and share best practices to achieve improvements in health, safety, the environment, security, social responsibility, engineering and operations.
The State Plane Coordinate System is a set of 124 geographic zones or coordinate systems designed for specific regions of the United States. Each state contains one or more state plane zones, the boundaries of which usually follow county lines. There are 110 zones in the contiguous US, with 10 more in Alaska, 5 in Hawaii, and one for Puerto Rico and US Virgin Islands. The system is widely used for geographic data by state and local governments. Its popularity is due to at least two factors. First, it uses a simple Cartesian coordinate system to specify locations rather than a more complex spherical coordinate system. By using the Cartesian coordinate system's simple XY coordinates, "plane surveying" methods can be used, speeding up and simplifying calculations. Second, the system is highly accurate within each zone. Outside a specific state plane zone accuracy rapidly declines, thus the system is not useful for regional or national mapping.
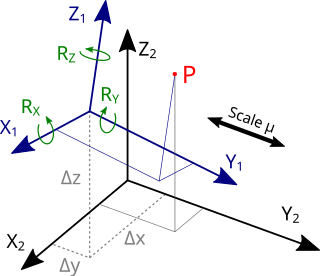
The Helmert transformation is a transformation method within a three-dimensional space. It is frequently used in geodesy to produce distortion-free transformations from one datum to another. The Helmert transformation is also called a seven-parameter transformation and is a similarity transformation.

An Earth ellipsoid is a mathematical figure approximating the Earth's form, used as a reference frame for computations in geodesy, astronomy, and the geosciences. Various different ellipsoids have been used as approximations.

The Hellenic Geodetic Reference System 1987 or HGRS87 is a geodetic system commonly used in Greece (SRID=2100). The system specifies a local geodetic datum and a projection system. In some documents it is called Greek Geodetic Reference System 1987 or GGRS87.

Web Mercator, Google Web Mercator, Spherical Mercator, WGS 84 Web Mercator or WGS 84/Pseudo-Mercator is a variant of the Mercator projection and is the de facto standard for Web mapping applications. It rose to prominence when Google Maps adopted it in 2005. It is used by virtually all major online map providers, including Google Maps, Mapbox, Bing Maps, OpenStreetMap, Mapquest, Esri, and many others. Its official EPSG identifier is EPSG:3857, although others have been used historically.
Well-known text representation of coordinate reference systems (WKT) is a text markup language for representing spatial reference systems and transformations between spatial reference systems. The formats were originally defined by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) and described in their Simple Feature Access and Well-known text representation of coordinate reference systems specifications. The current standard definition is in the ISO 19162:2015.









