History
The first airports in Greenland were built by and for the United States defense. The first and largest was Kangerlussuaq Airport in 1941, followed by Narsarsuaq Airport in 1942 (and now-abandoned USAAF airfields Bluie East Two and Marrak Point, both in 1942) and Pituffik Space Base in 1953 (although Pituffik is not operated as a civilian airport) and Kulusuk Airport in 1956. Due to their distance from major settlements, these were not initially used for civilian travel. In the early 1960s, Greenlandair was founded, commencing civilian flights between the air bases, and helicopter and sea plane flights to large settlements. SAS operated the connection from Copenhagen to Kangerlussuaq, beginning in 1954 as a fuel stop en route to United States, which was later taken over in 2000 by Air Greenland.
Beginning with Nuuk Airport in 1979 and Ilulissat Airport in 1983, several airports with short runways were built.
Airports
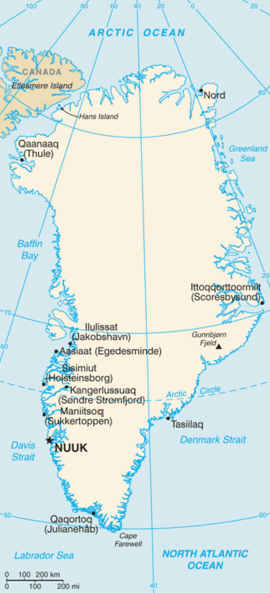
Location of airports. Airports in red have international flights (may be seasonal).
Many locations in Greenland have Danish names in addition to their Greenlandic names. The Danish name, where applicable, is shown in italics. Airport or heliport names shown in bold indicate the facility has scheduled passenger service on a commercial airline.
Several of the airports do not have road connection with the local major settlement, so a helicopter transfer is often needed by most passengers to some airports. Airports with a very small population reachable by road include Kangerlussuaq Airport, Kulusuk Airport, Narsarsuaq Airport, Nerlerit Inaat Airport and Qaarsut Airport. 13 civil airports (not Pituffik Space Base) and 47 helipads in Greenland are operated by the state-owned enterprise Greenland Airport Authority (Mittarfeqarfiit).
Heliports
The following 47 heliports are listed under AD 4 HELIPORTS at Naviair. [16]
The following four heliports are not listed by Naviair.
Statistics
Mittarfeqarfiit only publishes statistics summarized for Atlantic airports (Kangerlussuaq and Narsarsuaq) and for other airports (11 airports). 13 airports are included, not Pituffik Space Base. [66]
| 2013 | 2015 | 2017 | 2019 |
|---|
| Atlantic airports, passengers | 159,432 | 166,688 | 173,523 | 197,038 |
| Other airports, passengers | 193,812 | 198,921 | 200,075 | 217,173 |
| Heliports, passengers | 44,612 | 41,675 | 39,789 | 28,790 |
| Atlantic airports, takeoffs | 7,988 | 8,286 | 7,653 | 8,209 |
| Other airports, takeoffs | 15,069 | 16,007 | 16,958 | 15,691 |
| Heliports, takeoffs | 10,646 | 11,289 | 9,533 | 7,623 |
Future
At a late 2011 Air Greenland meeting, plans to move the main Greenland intercontinental air hub away from Kangerlussuaq were agreed upon. From 2011 it has not been possible to buy new aircraft, except for very small ones, which can use the 800–900 m (2,600–3,000 ft) airstrips which are common in Greenland including Nuuk Airport. So something needs to be done before the fleet of Bombardier Dash 8 Q200 is retired in future (before 2030).
A decision was made in 2016 to extend the runways of both Nuuk airport and Ilulissat airport to 2,200 m (7,200 ft), allowing them to receive medium size jetliners from Denmark. [67] [68] Also to replace Narsarsuaq with a new airport at Qaqortoq. [69] Construction start of Nuuk was late 2019, the opening was in November 2024. [70] [71]
Alongside Kangerlussuaq, if airports at Qaqortoq, Tasiilaq and Ittoqqortoormiit are built, the airports at Narsarsuaq, Kulusuk and Nerlerit Inaat will also be closed. [72] The remaining airports in Greenland will keep their short size and smaller aircraft be used for them.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.