
The economy of Ecuador is the eighth largest in Latin America and the 69th largest in the world by total GDP. Ecuador's economy is based on the export of oil, bananas, shrimp, gold, other primary agricultural products and money transfers from Ecuadorian emigrants employed abroad. In 2017, remittances constituted 2.7% of country's GDP. The total trade amounted to 98% of the Ecuador's GDP in 2017.

Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often revised before being considered a reliable indicator. GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) may be more useful when comparing living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. The ratio of GDP to the total population of the region is the per capita GDP.

The economy of Sierra Leone is $4.082 billion by gross domestic product as of 2018. Since the end of the Sierra Leone Civil War in 2002, the economy is gradually recovering with a gross domestic product growth rate between 4 and 7%. In 2008 it in PPP ranked between 147th by World Bank, and 153rd by CIA, largest in the world.

The economy of the Gambia is heavily reliant on agriculture. The Gambia has no significant mineral or other natural resources, and has a limited agricultural base. About 75% of the population depends on crops and livestock for its livelihood. Small-scale manufacturing activity features the processing of peanuts, fish, and animal hides.
The world economy or global economy is the economy of all humans of the world, referring to the global economic system which includes all economic activities which are conducted both within and between nations, including production, consumption, economic management, work in general, exchange of financial values and trade of goods and services. In some contexts, the two terms are distinct "international" or "global economy" being measured separately and distinguished from national economies while the "world economy" is simply an aggregate of the separate countries' measurements. Beyond the minimum standard concerning value in production, use and exchange, the definitions, representations, models and valuations of the world economy vary widely. It is inseparable from the geography and ecology of planet Earth.

Research and development, known in Europe as research and technological development (RTD), is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products, and improving existing ones. Research and development constitutes the first stage of development of a potential new service or the production process.

Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual or collective needs of the community, is classed as government final consumption expenditure. Government acquisition of goods and services intended to create future benefits, such as infrastructure investment or research spending, is classed as government investment. These two types of government spending, on final consumption and on gross capital formation, together constitute one of the major components of gross domestic product.
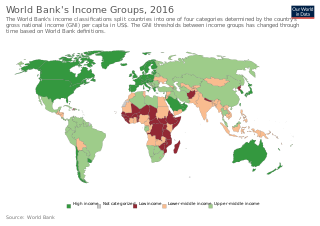
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents, minus income earned in the domestic economy by nonresidents. Comparing GNI to GDP shows the degree to which a nation's GDP represents domestic or international activity. GNI has gradually replaced GNP in international statistics. While being conceptually identical, it is calculated differently. GNI is the basis of calculation of the largest part of contributions to the budget of the European Union. In February 2017, Ireland's GDP became so distorted from the base erosion and profit shifting ("BEPS") tax planning tools of U.S. multinationals, that the Central Bank of Ireland replaced Irish GDP with a new metric, Irish Modified GNI. In 2017, Irish GDP was 162% of Irish Modified GNI.

Research funding is a term generally covering any funding for scientific research, in the areas of natural science, technology, and social science. Different methods can be used to disburse funding, but the term often connotes funding obtained through a competitive process, in which potential research projects are evaluated and only the most promising receive funding. It is often measured via Gross domestic expenditure on R&D (GERD).

Income in India discusses the financial state in India. With rising economic growth and prosperity, India’s income is also rising rapidly. As an overview, India's per capita net national income or NNI was around 135 thousand rupees in 2020. The per-capita income is a crude indicator of the prosperity of a country. In contrast, the gross national income at constant prices stood at over 128 trillion rupees. The same year, GNI growth rate at constant prices was around 6.6 percent. While GNI and NNI are both indicators for a country's economic performance and welfare, the GNI is related to the GDP or the gross domestic product plus the net receipts from abroad, including wages and salaries, property income, net taxes and subsidies receivable from abroad. On the other hand, the NNI of a country is equal to its GNI net of depreciation.
Research and development intensity is generally defined as expenditures by a firm on its research and development (R&D) divided by the firm's sales. There are two types of R&D intensity: direct and indirect. R&D intensity varies, in general, according to a firm's industry sector, product knowledge, manufacturing, and technology, and is a metric that can be used to gauge the level of a company's investment to spur innovation in and through basic and applied research. A further aim of R&D spending, ultimately, is to increase productivity as well as an organization's salable output.

This article includes a list of China's historical gross domestic product (GDP) values, the market value of all final goods and services produced by a nation in a given year. The GDP dollar estimates presented here are either calculated at market or government official exchange rates (nominal), or derived from purchasing power parity (PPP) calculations. This article also includes historical GDP growth.
Expenditure for scientific research and Development in Albania does not exceed 0.18% of GDP, which marks the lowest level in Europe. Economic competitiveness and exports are low, with the economy still heavily skewed towards low technology.
The International Comparison Program is a partnership of various statistical administrations of up to 199 countries guided by the World Bank. The main partners of this program are the World Bank, IMF, UN, ADB, OECD, CISSTAT, Eurostat, AfDB ESCWA, ECLAC, DFID, ABS, IDB, NMoFA who are also all part of the executive board.
This is a list of countries by gross national savings. Gross national saving is derived by deducting final consumption expenditure from Gross national disposable income, and consists of personal saving, plus business saving, plus government saving, but excludes foreign saving. The figures are presented as a percent of GDP. A negative number indicates that the economy as a whole is spending more income than it produces, thus drawing down national wealth.









