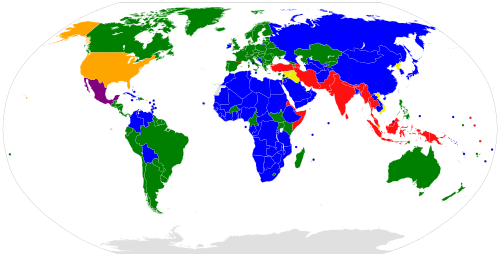
| State [2] [3] [4] | Year of ratification/accession/succession [Note 1] | Notes |
|---|
| GC I–IV [5] [6] [7] [8] | Protocol I [9] | Protocol II [10] | Protocol III [11] | Prot. I
Art. 90
Declaration
[12] |
|---|
 Afghanistan Afghanistan | 1956 | 2009 | 2009 | — | — | |
 Albania Albania | 1957 | 1993 | 1993 | 2008 | — | |
 Algeria Algeria | 1960 | 1989 | 1989 | — | 1989 | |
 Andorra Andorra | 1993 | 2025 | 2025 | 2025 | 2025 | |
 Angola Angola | 1984 | 1984 | 2019 | S | — | |
 Antigua and Barbuda Antigua and Barbuda | 1986 | 1986 | 1986 | — | — | |
 Argentina Argentina | 1956 | 1986 | 1986 | 2011 | 1996 | |
 Armenia Armenia | 1993 | 1993 | 1993 | 2011 | — | |
 Australia Australia | 1958 | 1991 | 1991 | 2009 | 1992 | |
 Austria Austria | 1953 | 1982 | 1982 | 2009 | 1982 | |
 Azerbaijan Azerbaijan | 1993 | — | — | — | — | |
 Bahamas Bahamas | 1975 | 1980 | 1980 | — | — | |
 Bahrain Bahrain | 1971 | 1986 | 1986 | — | — | |
 Bangladesh Bangladesh | 1972 | 1980 | 1980 | — | — | |
 Barbados Barbados | 1968 | 1990 | 1990 | — | — | |
 Belarus Belarus | 1954 | 1989 | 1989 | 2011 | 1989 | Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–II ratified as the  Byelorussian SSR. Byelorussian SSR. |
 Belgium Belgium | 1952 | 1986 | 1986 | 2015 | 1987 | |
 Belize Belize | 1984 | 1984 | 1984 | 2007 | — | |
 Benin Benin | 1961 | 1986 | 1986 | — | — | |
 Bhutan Bhutan | 1991 | — | — | — | — | |
 Bolivia Bolivia | 1976 | 1992 | 1983 | S | 1992 | |
 Bosnia and Herzegovina Bosnia and Herzegovina | 1992 | 1992 | 1992 | S | 1992 | |
 Botswana Botswana | 1968 | 1979 | 1979 | — | — | |
 Brazil Brazil | 1957 | 1992 | 1992 | 2009 | 1993 | |
 Brunei Brunei | 1991 | 1991 | 1991 | — | — | |
 Bulgaria Bulgaria | 1954 | 1989 | 1989 | 2006 | 1994 | |
 Burkina Faso Burkina Faso | 1961 | 1987 | 1987 | 2016 | 2004 | |
 Burundi Burundi | 1971 | 1993 | 1993 | S | — | |
 Cambodia Cambodia | 1958 | 1998 | 1998 | — | — | |
 Cameroon Cameroon | 1963 | 1984 | 1984 | 2021 | — | |
 Canada Canada | 1965 | 1990 | 1990 | 2007 | 1990 | |
 Cape Verde Cape Verde | 1984 | 1995 | 1995 | S | 1995 | |
 Central African Republic Central African Republic | 1966 | 1984 | 1984 | — | — | |
 Chad Chad | 1970 | 1997 | 1997 | — | — | |
 Chile Chile | 1950 | 1991 | 1991 | 2008 | 1991 | |
 China China | 1956 | 1983 | 1983 | — | — | Conventions I–IV ratified as the  Republic of China which was a signatory in 1956. Republic of China which was a signatory in 1956.
 Macau was declared by China to be covered by its ratification of Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–II from 20 December 1999, [13] [14] the same date Portugal renounced their obligations for the territory [13] following the transfer of sovereignty over Macau to China. Macau was declared by China to be covered by its ratification of Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–II from 20 December 1999, [13] [14] the same date Portugal renounced their obligations for the territory [13] following the transfer of sovereignty over Macau to China.
 Hong Kong was declared by China to be covered by its ratification of Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–II from 1 July 1997, [15] the same date the UK renounced their obligations for the territory [16] [17] following the transfer of sovereignty over Hong Kong to China. Hong Kong was declared by China to be covered by its ratification of Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–II from 1 July 1997, [15] the same date the UK renounced their obligations for the territory [16] [17] following the transfer of sovereignty over Hong Kong to China.
|
 Colombia Colombia | 1961 | 1993 | 1995 | S | 1996 | |
 Comoros Comoros | 1985 | 1985 | 1985 | — | — | |
 Democratic Republic of the Congo Democratic Republic of the Congo | 1961 | 1982 | 2002 | — | 2002 | |
 Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo | 1967 | 1983 | 1983 | S | — | |
 Cook Islands Cook Islands | 2002 | 2002 | 2002 | 2011 | 2002 | |
 Costa Rica Costa Rica | 1969 | 1983 | 1983 | 2008 | 1999 | |
 Côte d'Ivoire Côte d'Ivoire | 1961 | 1989 | 1989 | — | — | |
 Croatia Croatia | 1992 | 1992 | 1992 | 2007 | 1992 | |
 Cuba Cuba | 1954 | 1982 | 1999 | — | — | |
 Cyprus Cyprus | 1962 | 1979 | 1996 | 2007 | 2002 | |
 Czech Republic Czech Republic | 1993 | 1993 | 1993 | 2007 | 1995 | |
 Denmark Denmark | 1951 | 1982 | 1982 | 2007 | 1982 | All the treaties extended to the Faroe Islands and to Greenland. [Note 2] |
 Djibouti Djibouti | 1978 | 1991 | 1991 | — | — | |
 Dominica Dominica | 1981 | 1996 | 1996 | — | — | |
 Dominican Republic Dominican Republic | 1958 | 1994 | 1994 | 2009 | — | |
 Ecuador Ecuador | 1954 | 1979 | 1979 | 2020 | — | |
 Egypt Egypt | 1952 | 1992 | 1992 | — | — | |
 El Salvador El Salvador | 1953 | 1978 | 1978 | 2007 | — | |
 Equatorial Guinea Equatorial Guinea | 1986 | 1986 | 1986 | — | — | |
 Eritrea Eritrea | 2000 | — | — | — | — | |
 Estonia Estonia | 1993 | 1993 | 1993 | 2008 | 2009 | |
 Ethiopia Ethiopia | 1969 | 1994 | 1994 | S | — | |
 Fiji Fiji | 1971 | 2008 | 2008 | 2008 | — | |
 Finland Finland | 1955 | 1980 | 1980 | 2009 | 1980 | |
 France France | 1951 | 2001 | 1984 | 2009 | — | |
 Gabon Gabon | 1965 | 1980 | 1980 | — | — | |
 The Gambia The Gambia | 1966 | 1989 | 1989 | — | — | |
 Georgia Georgia | 1993 | 1993 | 1993 | 2007 | — | |
 Germany Germany | 1954 | 1991 | 1991 | 2009 | 1991 | |
 Ghana Ghana | 1958 | 1978 | 1978 | S | — | |
 Greece Greece | 1956 | 1989 | 1993 | 2009 | 1998 | |
 Grenada Grenada | 1981 | 1998 | 1998 | — | — | |
 Guatemala Guatemala | 1952 | 1987 | 1987 | 2008 | — | |
 Guinea Guinea | 1984 | 1984 | 1984 | — | 1993 | |
 Guinea-Bissau Guinea-Bissau | 1974 | 1986 | 1986 | — | — | |
 Guyana Guyana | 1968 | 1998 | 1998 | 2009 | — | |
 Haiti Haiti | 1957 | 2006 | 2006 | S | — | |
 Holy See Holy See | 1951 | 1985 | 1985 | — | — | |
 Honduras Honduras | 1965 | 1995 | 1995 | 2006 | — | |
 Hungary Hungary | 1954 | 1989 | 1989 | 2006 | 1991 | |
 Iceland Iceland | 1965 | 1987 | 1987 | 2006 | 1987 | |
 India India | 1950 | — | — | — | — | |
 Indonesia Indonesia | 1958 | — | — | — | — | |
 Iran Iran | 1957 | S | S | — | — | |
 Iraq Iraq | 1956 | 2010 | — | — | — | |
 Ireland Ireland | 1962 | 1999 | 1999 | S | 1999 | |
 Israel Israel | 1951 | — | — | 2007 | — | |
 Italy Italy | 1951 | 1986 | 1986 | 2009 | 1986 | |
 Jamaica Jamaica | 1964 | 1986 | 1986 | S | — | |
 Japan Japan | 1953 | 2004 | 2004 | — | 2004 | |
 Jordan Jordan | 1951 | 1979 | 1979 | — | — | |
 Kazakhstan Kazakhstan | 1992 | 1992 | 1992 | 2009 | — | |
 Kenya Kenya | 1966 | 1999 | 1999 | 2013 | — | |
 Kiribati Kiribati | 1989 | — | — | — | — | |
 North Korea North Korea | 1957 | 1988 | — | — | — | |
 South Korea South Korea | 1966 | 1982 | 1982 | S | 2004 | |
 Kuwait Kuwait | 1967 | 1985 | 1985 | — | 2013 | |
 Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyzstan | 1992 | 1992 | 1992 | 2019 | — | |
 Laos Laos | 1956 | 1980 | 1980 | — | 1998 | |
 Latvia Latvia | 1991 | 1991 | 1991 | 2007 | — | |
 Lebanon Lebanon | 1951 | 1997 | 1997 | — | — | |
 Lesotho Lesotho | 1968 | 1994 | 1994 | 2020 | 2010 | |
 Liberia Liberia | 1954 | 1988 | 1988 | — | — | |
 Libya Libya | 1956 | 1978 | 1978 | — | — | |
 Liechtenstein Liechtenstein | 1950 | 1989 | 1989 | 2006 | 1989 | |
 Lithuania Lithuania | 1996 | 2000 | 2000 | 2007 | 2000 | |
 Luxembourg Luxembourg | 1953 | 1989 | 1989 | 2015 | 1993 | |
 North Macedonia North Macedonia | 1993 | 1993 | 1993 | 2008 | 1993 | |
 Madagascar Madagascar | 1963 | 1992 | 1992 | 2018 | 1993 | |
 Malawi Malawi | 1968 | 1991 | 1991 | — | 2014 | |
 Malaysia Malaysia | 1962 | — | — | — | — | |
 Maldives Maldives | 1991 | 1991 | 1991 | — | — | |
 Mali Mali | 1965 | 1989 | 1989 | — | 2003 | |
 Malta Malta | 1968 | 1989 | 1989 | S | 1989 | |
 Marshall Islands Marshall Islands | 2004 | — | — | — | — | |
 Mauritania Mauritania | 1962 | 1980 | 1980 | — | — | |
 Mauritius Mauritius | 1970 | 1982 | 1982 | — | — | |
 Mexico Mexico | 1952 | 1983 | — | 2008 | — | |
 Federated States of Micronesia Federated States of Micronesia | 1995 | 1995 | 1995 | — | — | |
 Moldova Moldova | 1993 | 1993 | 1993 | 2008 | — | |
 Monaco Monaco | 1950 | 2000 | 2000 | 2007 | 2007 | |
 Mongolia Mongolia | 1958 | 1995 | 1995 | — | 1995 | |
 Montenegro Montenegro | 2006 | 2006 | 2006 | — | 2007 | |
 Morocco Morocco | 1956 | 2011 | 2011 | — | — | |
 Mozambique Mozambique | 1983 | 1983 | 2002 | — | — | |
 Myanmar Myanmar | 1992 | — | — | — | — | |
 Namibia Namibia | 1991 | 1994 | 1994 | — | 1994 | The United Nations Council for Namibia acceded to Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–II in 1983. [19] Namibia succeeded to Conventions I-IV in 1991, [20] and Protocols I-II in 1994. [21] |
 Nauru Nauru | 2006 | 2006 | 2006 | 2012 | — | |
 Nepal Nepal | 1964 | — | — | S | — | |
 Netherlands Netherlands | 1954 | 1987 | 1987 | 2006 | 1987 | Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–III have been extended to Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, and the Caribbean Netherlands. [22] [23] [24] [Note 3] |
 New Zealand New Zealand | 1959 | 1988 | 1988 | 2013 | 1988 |  Niue is considered bound by New Zealand's ratification of Conventions I–IV in 1959 by the International Committee of the Red Cross [25] [26] on the basis of Niue's enactment of its own Geneva Conventions Act 1958. [27] Niue is considered bound by New Zealand's ratification of Conventions I–IV in 1959 by the International Committee of the Red Cross [25] [26] on the basis of Niue's enactment of its own Geneva Conventions Act 1958. [27]
New Zealand declared that its ratification of Protocols I–II does not extend to the  Cook Islands (which subsequently independently ratified the Protocols), Cook Islands (which subsequently independently ratified the Protocols),  Niue and Niue and  Tokelau. [28] Tokelau. [28] |
 Nicaragua Nicaragua | 1953 | 1999 | 1999 | 2009 | — | |
 Niger Niger | 1964 | 1979 | 1979 | — | — | |
 Nigeria Nigeria | 1961 | 1988 | 1988 | — | — | |
 Norway Norway | 1951 | 1981 | 1981 | 2006 | 1981 | |
 Oman Oman | 1974 | 1984 | 1984 | — | — | |
 Pakistan Pakistan | 1951 | S | S | — | — | |
 Palau Palau | 1996 | 1996 | 1996 | — | — | |
 Palestine Palestine | 2014 | 2014 | 2015 | 2015 | 2018 | The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) unilaterally declared itself bound by Conventions I–IV and Protocol I in 1982. [29]
In 1989, the PLO submitted a letter to the Swiss Federal Department of Foreign Affairs which stated in part that the State of Palestine had decided to "adhere to the Four Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949 and the two Protocols additional thereto." [30] However, the Swiss Government, which acts as the depositary for the Conventions, responded by stating that it was "not in a position to decide whether this communication can be considered as an instrument of accession" due to "the incertainty [sic] within the international community as to the existence or non-existence of a State of Palestine." [29] [30] In 1990, the PLO submitted a "Memorandum on the accession of the State of Palestine to the four Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949" to the depository and requested that the issue be reconsidered. However, the Swiss Government reiterated its prior conclusions. [31]
Following the United Nations General Assembly passing a resolution granting non-member observer state status to Palestine in November 2012, Palestine acceded to Conventions I-IV and Protocol I in April 2014. [32] In January 2015 Palestine acceded to Protocols II and III. [33] |
 Panama Panama | 1956 | 1995 | 1995 | 2012 | 1999 | |
 Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea | 1976 | — | — | — | — | |
 Paraguay Paraguay | 1961 | 1990 | 1990 | 2008 | 1998 | |
 Peru Peru | 1956 | 1989 | 1989 | 2018 | — | |
 Philippines Philippines | 1951 (I)
1952 (II–IV) | 2012 | 1986 | 2006 | — | |
 Poland Poland | 1954 | 1991 | 1991 | 2009 | 1992 | |
 Portugal Portugal | 1961 | 1992 | 1992 | 2014 | 1994 | |
 Qatar Qatar | 1975 | 1988 | 2005 | — | 1991 | |
 Romania Romania | 1954 | 1990 | 1990 | 2015 | 1995 | |
 Russia Russia | 1954 | 1989 | 1989 | S | 1989 | Conventions I–IV and Protocols I and II ratified as the  Soviet Union. Soviet Union.
Declaration under Article 90 of Protocol 1 withdrawn in 2019. [34] [35] |
 Rwanda Rwanda | 1964 | 1984 | 1984 | — | 1993 | |
 Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Kitts and Nevis | 1986 | 1986 | 1986 | — | 2014 | |
 Saint Lucia Saint Lucia | 1981 | 1982 | 1982 | — | — | |
 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 1981 | 1983 | 1983 | — | 2013 | |
 Samoa Samoa | 1984 | 1984 | 1984 | — | — | |
 San Marino San Marino | 1953 | 1994 | 1994 | 2007 | — | |
 Sao Tome and Principe Sao Tome and Principe | 1976 | 1996 | 1996 | — | — | |
 Saudi Arabia Saudi Arabia | 1963 | 1987 | 2001 | — | — | |
 Senegal Senegal | 1963 | 1985 | 1985 | — | — | |
 Serbia Serbia | 2001 | 2001 | 2001 | 2010 | 2001 | Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–II ratified as the  Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. |
 Seychelles Seychelles | 1984 | 1984 | 1984 | — | 1992 | |
 Sierra Leone Sierra Leone | 1965 | 1986 | 1986 | S | — | |
 Singapore Singapore | 1973 | — | — | 2008 | — | |
 Slovakia Slovakia | 1993 | 1993 | 1993 | 2007 | 1995 | |
 Slovenia Slovenia | 1992 | 1992 | 1992 | 2008 | 1992 | |
 Solomon Islands Solomon Islands | 1981 | 1988 | 1988 | — | — | |
 Somalia Somalia | 1962 | — | — | — | — | |
 South Africa South Africa | 1952 | 1995 | 1995 | — | — | |
 South Sudan South Sudan | 2013 | 2013 | 2013 | 2013 | — | |
 Spain Spain | 1952 | 1989 | 1989 | 2010 | 1989 | |
 Sri Lanka Sri Lanka | 1959 | — | — | — | — | |
 Sudan Sudan | 1957 | 2006 | 2006 | — | — | |
 Suriname Suriname | 1976 | 1985 | 1985 | 2013 | — | |
 Eswatini Eswatini | 1973 | 1995 | 1995 | — | — | |
 Sweden Sweden | 1953 | 1979 | 1979 | 2014 | 1979 | |
 Switzerland Switzerland | 1950 | 1982 | 1982 | 2006 | 1982 | |
 Syria Syria | 1953 | 1983 | — | — | — | |
 Tajikistan Tajikistan | 1993 | 1993 | 1993 | — | 1997 | |
 Tanzania Tanzania | 1962 | 1983 | 1983 | S | — | Conventions I–IV ratified as  Tanganyika . Tanganyika . |
 Thailand Thailand | 1954 | — | — | — | — | |
 Timor-Leste Timor-Leste | 2003 | 2005 | 2005 | 2011 | — | |
 Togo Togo | 1962 | 1984 | 1984 | S | 1991 | |
 Tonga Tonga | 1978 | 2003 | 2003 | — | 2003 | |
 Trinidad and Tobago Trinidad and Tobago | 1963 | 2001 | 2001 | — | 2001 | |
 Tunisia Tunisia | 1957 | 1979 | 1979 | — | — | |
 Turkey Turkey | 1954 | — | — | S | — | |
 Turkmenistan Turkmenistan | 1992 | 1992 | 1992 | — | — | |
 Tuvalu Tuvalu | 1981 | — | — | — | — | |
 Uganda Uganda | 1964 | 1991 | 1991 | 2008 | — | |
 Ukraine Ukraine | 1954 | 1990 | 1990 | 2010 | 1990 | Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–II ratified as the  Ukrainian SSR. Ukrainian SSR. |
 United Arab Emirates United Arab Emirates | 1972 | 1983 | 1983 | — | 1992 | |
 United Kingdom United Kingdom | 1957 | 1998 | 1998 | 2009 | 1999 | Protocols I–III have been extended to all three Crown dependencies and to 13 of the 14 British Overseas Territories (excluding Gibraltar). [36] [37] [38] |
 United States United States | 1955 | S | S | 2007 | — | Signed in 1949. [39] Ratified June 9, 1955. [40] Protocols I–II not ratified |
 Uruguay Uruguay | 1969 | 1985 | 1985 | 2012 | 1990 | |
 Uzbekistan Uzbekistan | 1993 | 1993 | 1993 | — | — | |
 Vanuatu Vanuatu | 1982 | 1985 | 1985 | — | — | |
 Venezuela Venezuela | 1956 | 1998 | 1998 | — | — | |
 Vietnam Vietnam | 1957 | 1981 | — | — | — | Conventions I–IV ratified as the  North Vietnam. [4] North Vietnam. [4]
Also ratified by the State of Vietnam in 1953 and the Provisional Revolutionary Government of the Republic of South Vietnam in 1973 prior to Vietnamese reunification. [4] |
 Yemen Yemen | 1970 | 1990 | 1990 | — | — | Conventions I–IV and Protocols I–II ratified as  North Yemen. [4] [41] North Yemen. [4] [41]
Conventions I–IV also ratified by  South Yemen in 1977 prior to Yemeni unification. [42] South Yemen in 1977 prior to Yemeni unification. [42] |
 Zambia Zambia | 1966 | 1995 | 1995 | — | — | |
 Zimbabwe Zimbabwe | 1983 | 1992 | 1992 | — | — | |
| Totals | | | | | | |
|---|
| Ratified | 196 | 175 | 170 | 80 | 77 | |
|---|
| Signed only | 0 | 3 | 3 | 20 | N/A | |
|---|