
Pattadakal, also called Raktapura, is a complex of 7th and 8th century CE Hindu and Jain temples in northern Karnataka, India. Located on the west bank of the Malaprabha River in Bagalkot district, this UNESCO World Heritage Site is 23 kilometres (14 mi) from Badami and about 9.7 kilometres (6 mi) from Aihole, both of which are historically significant centres of Chalukya monuments. The monument is a protected site under Indian law and is managed by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).

Badami, formerly known as Vātāpi, is a town and headquarters of a taluk by the same name, in the Bagalkot district of Karnataka, India. It was the regal capital of the Badami Chalukyas from 540 to 757. It is famous for its rock cut monuments such as the Badami cave temples, as well as the structural temples such as the Bhutanatha temples, Badami Shivalaya and Jambulingesvara Temple. It is located in a ravine at the foot of a rugged, red sandstone outcrop that surrounds Agastya lake.

Koppala district, officially known as Koppala district is an administrative district in the state of Karnataka in India. In the past Koppal was referred to as 'Kopana Nagara'. Hampi, a World heritage center, covers some areas of Koppala District. It is situated approximately 38 km away. Anegundi, is also a famous travel destination.

Aihole (ಐಹೊಳೆ), also referred to as Aivalli, Ahivolal or Aryapura, is a historic site of ancient and medieval era Buddhist, Hindu and Jain monuments in Karnataka, India that dates from the sixth century through the twelfth century CE. Most of the surviving monuments at the site date from the 7th to 10th centuries. Located around an eponymous small village surrounded by farmlands and sandstone hills, Aihole is a major archaeological site, featuring over 120 stone and cave temples spread along the Malaprabha river valley, in Bagalakote district.

Vesara is a hybrid form of Indian temple architecture that combines Dravidian Southern Indian site layouts with shape details characteristic of the Nagara style of North India. This fusion style likely originated in the historic architecture schools of the Dharwad region. It is common in the surviving temples of later Chalukyas and Hoysalas in the Deccan region, particularly Karnataka. According to Indian texts, Vesara Style was popular in central India, particularly in between the Vindhya Range and the Krishna River. It is one of six major types of Indian temple architecture found in historic texts, the others being Nagara, Dravida, Bhumija, Kalinga, and Varata.

Trikuteshwara temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Shiva. The carved temple is in the town of Gadag, 50 km southeast of Hubli-Dharwad, in Karnataka, India. It is dedicated to Shiva and has three lingas mounted on the same stone. There is a shrine dedicated to Saraswathi in this temple and it has carved columns.

The Badami cave temples are a complex of Budhist,Hindu and Jain cave temples located in Badami, a town in the Bagalkot district in northern part of Karnataka, India. The caves are important examples of Indian rock-cut architecture, especially Badami Chalukya architecture, and the earliest date from the 6th century. Badami is a modern name and was previously known as "Vataapi", the capital of the early Chalukya dynasty, which ruled much of Karnataka from the 6th to the 8th century. Badami is situated on the west bank of a man-made lake ringed by an earthen wall with stone steps; it is surrounded on the north and south by forts built during Early Chalukya and in later times.

Badami Chalukya architecture is a style in Hindu temple architecture that evolved in the 5th – 8th centuries CE in the Malaprabha river basin, in the present-day Bagalkot district of Karnataka state of India, under the Chalukya dynasty; later it spread more widely. This style is sometimes called the Vesara style and Chalukya style, a term that also includes the much later Western Chalukya architecture of the 11th and 12th centuries. Early Chalukya architecture, used by George Michell and others, equates to Badami Chalukya.

Dravidian architecture, or the Southern Indian temple style, is an architectural idiom in Hindu temple architecture that emerged from Southern India, reaching its final form by the sixteenth century.
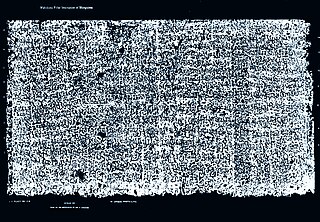
Mahakuta Pillar, also known as Makuta pillar, Magada stambha or Mangalesa Dharma Jayastambha, is a deep red sandstone pillar with an early 7th-century inscription of Early Western Chalukya era. It was found near Mahakuta group of Hindu temples near Badami, Karnataka, India. Inscribed with 16 lines of Sanskrit in Old Kannada script by king Mangalesha, it is an important and partly disputed source of historic information about the times of Badami Chalukya, the dynasty, and his influential father Pulakeshin I.

Western Chalukya architecture, also known as Kalyani Chalukya or Later Chalukya architecture and broadly classified under the Vesara Style, is the distinctive style of ornamented architecture that evolved during the rule of the Western Chalukya Empire in the Tungabhadra region of modern central Karnataka, India, during the 11th and 12th centuries. Western Chalukyan political influence was at its peak in the Deccan Plateau during this period. The centre of cultural and temple-building activity lay in the Tungabhadra region, where large medieval workshops built numerous monuments. These monuments, regional variants of pre-existing dravida temples, form a climax to the wider regional temple architecture tradition called Vesara or Karnata dravida. Temples of all sizes built by the Chalukyan architects during this era remain today as examples of the architectural style.

Doddabasappa Temple is a 12th-century Western Chalukyan architectural innovation in Dambal, Karnataka state, India. Dambal is about 20 km (12 mi) southeast of Gadag city and 24 km (15 mi) southwest of Ittagi in Koppal district. The sanctum contains a Shiva linga, the symbol of the presiding deity, God Shiva. The temple interior is a standard construction and consists of a sanctum (cella), a vestibule (antarala) and a main mantapa. The vestibule connects the sanctum to the mantapa. The Western Chalukya monuments, regional variants of existing dravida temples, defined the Karnata dravida architectural tradition.

The Mahadeva Temple is located in the town of Itagi in Yelburga Taluk, in the Koppal District of Karnataka state, India. It is about 7 km (4 mi) from Kuknur and 20 km (12 mi) from Lakkundi.

The Navalinga temple is a cluster of Hindu temples built in the 9th century, during the reign of King Amoghavarsha I or his son Krishna II of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty. The temple is located in the town of Kukkanur, 4 miles (6 km) north of Itagi in Koppal district and 25 miles (40 km) east of Gadag in Karnataka state, India. Built in the South Indian dravida style, each of the nine temples in the cluster has a linga, the universal symbol of Hindu God Shiva, and hence the name Navalinga.

The Kasivisvesvara temple, also referred to as the Kavatalesvara, Kashivishveshvara or Kashi Vishvanatha temple of Lakkundi is located in the Gadag district of Karnataka state, India. It is about 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) from Gadag city, between Hampi and Goa. The Kasivisvesvara temple is one of the best illustrations of fully developed Kalyana Chalukya style of Hindu architecture.

The Bhutanatha group of temples are 7th to 12th century Hindu temples to the east of Agastya lake in Badami, Karnataka state, India. It consists of two subgroups – one called the East Bhutanatha group or Bhutanatha main group from 7th to 8th century mostly in the Dravida architecture style; the other called the North Bhutanatha group or Mallikarjuna group from 11th to 12th century mostly in the Nagara architecture. The former illustrates the Badami Chalukya architects, the latter along with the nearby Yellamma temple the Kalyani Chalukya architects.

The antiquity of architecture of Karnataka can be traced to its southern Neolithic and early Iron Age, Having witnessed the architectural ideological and utilitarian transformation from shelter- ritual- religion. Here the nomenclature 'Architecture' is as old as c.2000 B.C.E. The upper or late Neolithic people in order to make their shelters by their own they constructed huts made of wattle and doab, that were buttressed by stone boulders, presumably having conical roof resting on the bamboo or wooden posts into red murram or paved granite chips as revealed in archaeological excavations in sites like Brhamagiri, Sanganakallu, Tekkalakota, Piklihal. Megaliths are the dominant archaeological evidence of the early Iron Age. There are more than 2000 early Iron Age burial sites on record, who laid the foundation for a high non-perishable architecture in the form of various distinct architectural styles of stone-built burials, which are ritualistic in its character. The active religious architecture is evident 345 with that of the Kadamba Dynasty. Karnataka is a state in the southern part of India originally known as the State of Mysore. Over the centuries, architectural monuments within the region displayed a diversity of influences, often relaying much about the artistic trends of the rulers of twelve different dynasties. Its architecture ranges dramatically from majestic monolith, such as the Gomateshwara, to Hindu and Jain places of worship, ruins of ancient cities, mausoleums and palaces of different architectural hue. Mysore Kingdom (Wodeyar) rule has also given an architectural master structure in the St. Philomena's Church at Mysore which was completed in 1956, in addition to many Dravidian style architectural temples. Two of the monuments are listed under the UNESCO World Heritage List of 22 cultural monuments in India. Styles of Indo-Saracenic, Renaissance, Corinthian, Hindu, Indo-Greek and Indo-British style palaces were built in Mysore, the city of palaces. Sikh architecture at Bidar (1512) and also in Bangalore in 1956 can also be cited as having an impact on the architectural composition of the state.

The Chalukya dynasty was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakeshin II. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century. These Western Chalukyas ruled from Kalyani until the end of the 12th century.

The Durga temple is an early 8th-century Hindu temple located in Aihole, Karnataka, India. Originally dedicated to Surya, it has the most embellished and largest relief panels in Aihole depicting artwork of Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism and Vedic deities. Apart from its fine carvings, it is notable for its apsidal plan – a rare example among early Chalukyan Hindu temple architecture.

Alampuram Navabrahma Temples are a group of nine early Badami Chalukyan Hindu temples dated between the 7th and 9th centuries that are located at Alampuram (Hemalapuram) in Telangana, India, near the meeting point of Tungabhadra River and Krishna River at the border of Andhra Pradesh. They are called Nava-Brahma temples though they are dedicated to Shiva. They exemplify early North Indian Nagara style architecture with cut rock as the building block. The temples of Alampur resemble the style of Pattadakal, Aihole style as they were Karnata Dravida, Vesara style native to Karnataka.


























