
Meade County is a county in the U.S. state of South Dakota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 29,852, making it the 6th most populous county in South Dakota. Its county seat is Sturgis. The county was created in 1889 and named for Fort Meade, which was garrisoned as a United States military post in the area in 1878 and itself named for General George Meade.

Fort Meade is a city in Polk County, Florida, United States. As of 2020, the population recorded by the U.S. Census Bureau is 5,100. It is part of the Lakeland–Winter Haven Metropolitan Statistical Area.
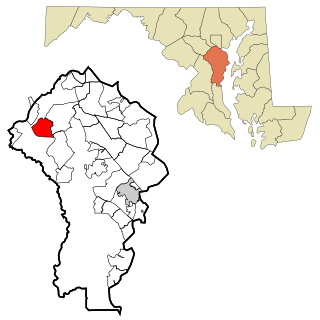
Fort Meade is a census-designated place (CDP) in Anne Arundel County, Maryland, United States. The population was 9,327 at the 2010 census. It is the home to the National Security Agency, Central Security Service, United States Cyber Command and the Defense Information Systems Agency, which are located on the U.S. Army post Fort George G. Meade.

Fort George G. Meade is a United States Army installation located in Maryland, that includes the Defense Information School, the Defense Media Activity, the United States Army Field Band, and the headquarters of United States Cyber Command, the National Security Agency, the Defense Courier Service, Defense Information Systems Agency headquarters, and the U.S. Navy's Cryptologic Warfare Group Six. It is named for George G. Meade, a Union general from the U.S. Civil War, who served as commander of the Army of the Potomac. The fort's smaller census-designated place includes support facilities such as schools, housing, and the offices of the Military Intelligence Civilian Excepted Career Program (MICECP).

Sturgis is a city in Meade County, South Dakota, United States. The population was 7,020 as of the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Meade County and is named after Samuel D. Sturgis, a Union general during the Civil War.

George Gordon Meade was a United States Army Major General who commanded the Army of the Potomac during the American Civil War from 1863 to 1865. He fought in many of the key battles of the Eastern theater and defeated the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia led by General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Gettysburg.
Piedmont is a city in Meade County, South Dakota, United States. According to the 2020 census, its population was 971. Piedmont lies along Interstate 90 between Rapid City and Sturgis. Piedmont has been assigned the ZIP Code of 57769.
Green Hills is an affluent neighborhood in Nashville, Tennessee, United States. Green Hills is located south of downtown Nashville on Hillsboro Pike.

Shinnecock Hills Golf Club is a links-style golf club located in an unincorporated area of the Town of Southampton on Long Island, New York, situated between the Peconic Bay and the Atlantic Ocean.

Black Hills National Forest is located in southwestern South Dakota and northeastern Wyoming, United States. The forest has an area of over 1.25 million acres (5,066 km2) and is managed by the Forest Service. Forest headquarters are located in Custer, South Dakota. There are local ranger district offices in Custer, Rapid City, and Spearfish in South Dakota, and in Sundance, Wyoming.

The Nashville metropolitan area is a metropolitan statistical area in north-central Tennessee. Its principal city is Nashville, the capital of and largest city in Tennessee. With a population of over 2 million, it is the most populous metropolitan area in Tennessee. It is also the largest metropolitan area in Tennessee in terms of land area.

Berlin Mountain is a 2,818-foot-tall (859 m) prominent peak in the Taconic Mountains of western New England and is located adjacent to Massachusetts's border with New York State. It is the highest point in Rensselaer County. The summit and west side of the mountain are located in New York; the east side lies within Williamstown, Massachusetts. The mountain is a bald, notable for its grassy summit and expansive views of the Hudson River Valley to the west. The 37-mile (60 km) Taconic Crest Trail traverses the mountain. Several other hiking trails approach the summit from the east. Much of the upper slopes and summit are within protected conservation land. Historically the lower slopes of the mountain were farmed heavily throughout the 19th Century. In addition to agriculture, there are several remnants of charcoal kilns located on the mountain that produced fuel for iron smelting.

The Black Hills is an isolated mountain range rising from the Great Plains of North America in western South Dakota and extending into Wyoming, United States. Black Elk Peak, which rises to 7,242 feet (2,207 m), is the range's highest summit. The name of the range in Lakota is Pahá Sápa. It encompasses the Black Hills National Forest. It formed as a result of an upwarping of ancient rock, after which the removal of the higher portions of the mountain mass by stream erosion produced the present-day topography. The hills are so called because of their dark appearance from a distance, as they are covered in evergreen trees.

The Phosphoria Formation of the western United States is a geological formation of Early Permian age. It represents some 15 million years of sedimentation, reaches a thickness of 420 metres (1,380 ft) and covers an area of 350,000 square kilometres (140,000 sq mi).

Fort Meade, originally known as Camp Sturgis and later Camp Ruhlen, is a former United States Army post located just east of Sturgis, South Dakota, United States. The fort was active from 1878 to 1944; the cantonment is currently home to a Veterans Health Administration hospital and South Dakota Army National Guard training facilities. Much of the former reservation is now managed by the Bureau of Land Management as the Fort Meade Recreation Area. It is also home of Fort Meade National Cemetery. Fort Meade was established in 1878 to protect illegal white settlements on the Great Sioux Reservation in the northern Black Hills, especially the nearby gold mining area around Deadwood. Several stage and freighting routes passed through Fort Meade en route to Deadwood.
Pakatakan Mountain is a mountain located in the Catskill Mountains of New York southeast of Margaretville. Pakataghkan Mountain is the variant name. Kettle Hill is located north, Meade Hill is located east-northeast and Dry Brook Ridge is located southeast of Pakatakan Mountain.
Fleischmann Mountain is a mountain located in the Catskill Mountains of New York east of Arkville. Hog Mountain is located north of Fleischmann Mountain and Meade Hill is located west.
Red Hill is a mountain located in the Catskill Mountains of New York east-south of Frost Valley. Woodhull Mountain is located northeast of Red Hill.
The Cobble is a mountain in Schoharie County, New York. It is located northeast of Summit. Meade Hill is located southwest and Fulton Hill is located east-southeast of The Cobble.
Leonard Hill is a 2,592-foot-tall (790 m) mountain in Schoharie County, New York. It is located east-southeast of North Blenheim. Safford Hill is located northwest and Hubbard Hill is located southeast of Leonard Hill. In 1948, the Conservation Commission built an 80-foot-tall (24 m) steel fire lookout tower on the mountain. The tower ceased fire watching operations at the end of the 1988 season and was officially closed in early 1989. The tower remains on the summit, but is closed to the public. A local group is planning to restore the tower and reopen it to the public.














