
Flaviviridae is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors. The family gets its name from the yellow fever virus; flavus is Latin for "yellow", and yellow fever in turn was named because of its propensity to cause jaundice in victims. There are 89 species in the family divided among four genera. Diseases associated with the group include: hepatitis (hepaciviruses), hemorrhagic syndromes, fatal mucosal disease (pestiviruses), hemorrhagic fever, encephalitis, and the birth defect microcephaly (flaviviruses).

The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small, enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer and lymphomas in humans.
GB virus C (GBV-C), formerly known as hepatitis G virus (HGV) and also known as human pegivirus – HPgV is a virus in the family Flaviviridae and a member of the Pegivirus, is known to infect humans, but is not known to cause human disease. Reportedly, HIV patients coinfected with GBV-C can survive longer than those without GBV-C, but the patients may be different in other ways. Research is active into the virus' effects on the immune system in patients coinfected with GBV-C and HIV.

Murine coronavirus (M-CoV) is a virus in the genus Betacoronavirus that infects mice. Belonging to the subgenus Embecovirus, murine coronavirus strains are enterotropic or polytropic. Enterotropic strains include mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) strains D, Y, RI, and DVIM, whereas polytropic strains, such as JHM and A59, primarily cause hepatitis, enteritis, and encephalitis. Murine coronavirus is an important pathogen in the laboratory mouse and the laboratory rat. It is the most studied coronavirus in animals other than humans, and has been used as an animal disease model for many virological and clinical studies.

Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) is a protein that is essential for antiviral innate immunity. MAVS is located in the outer membrane of the mitochondria, peroxisomes, and mitochondrial-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM). Upon viral infection, a group of cytosolic proteins will detect the presence of the virus and bind to MAVS, thereby activating MAVS. The activation of MAVS leads the virally infected cell to secrete cytokines. This induces an immune response which kills the host's virally infected cells, resulting in clearance of the virus.

VAMP-Associated Protein A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAPA gene. Together with VAPB and VAPC it forms the VAP protein family. They are integral endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins of the type II and are ubiquitous among eukaryotes.
NS2-3 protease is an enzyme responsible for proteolytic cleavage between NS2 and NS3, which are non-structural proteins that form part of the HCV virus particle. NS3 protease of hepatitis C virus, on the other hand, is responsible for the cleavage of non-structural protein downstream. Both of these proteases are directly involved in HCV genome replication, that is, during the viral life-cycle that leads to virus multiplication in the host that has been infected by the virus.

Nonstructural protein 3 (NS3), also known as p-70, is a viral nonstructural protein that is 70 kDa cleavage product of the hepatitis C virus polyprotein. It acts as a serine protease. C-terminal two-thirds of the protein also acts as helicase and nucleoside triphosphatase. First (N-terminal) 180 aminoacids of NS3 has additional role as cofactor domains for NS2 protein.

Nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) is a zinc-binding and proline-rich hydrophilic phosphoprotein that plays a key role in Hepatitis C virus RNA replication. It appears to be a dimeric form without trans-membrane helices.

Nonstructural protein 4A (NS4A) is a viral protein found in the hepatitis C virus. It acts as a cofactor for the enzyme NS3.

Nonstructural protein 2 (NS2) is a viral protein found in the hepatitis C virus. It is also produced by influenza viruses, and is alternatively known as the nuclear export protein (NEP).
A hepatitis C vaccine, a vaccine capable of protecting against the hepatitis C virus (HCV), is not yet available. Although vaccines exist for hepatitis A and hepatitis B, development of an HCV vaccine has presented challenges. No vaccine is currently available, but several vaccines are currently under development.

Daclatasvir, sold under the brand name Daklinza, is an antiviral medication used in combination with other medications to treat hepatitis C (HCV). The other medications used in combination include sofosbuvir, ribavirin, and interferon, vary depending on the virus type and whether the person has cirrhosis. It is taken by mouth.

Nonstructural protein 5B (NS5B) is a viral protein found in the hepatitis C virus (HCV). It is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, having the key function of replicating HCV's viral RNA by using the viral positive RNA strand as a template to catalyze the polymerization of ribonucleoside triphosphates (rNTP) during RNA replication. Several crystal structures of NS5B polymerase in several crystalline forms have been determined based on the same consensus sequence BK. The structure can be represented by a right hand shape with fingers, palm, and thumb. The encircled active site, unique to NS5B, is contained within the palm structure of the protein. Recent studies on NS5B protein genotype 1b strain J4's (HC-J4) structure indicate a presence of an active site where possible control of nucleotide binding occurs and initiation of de-novo RNA synthesis. De-novo adds necessary primers for initiation of RNA replication.

Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir, sold under the trade name Harvoni among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is a fixed-dose combination of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir. Cure rates are 94% to 99% in people infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1. Some evidence also supports use in HCV genotype 3 and 4. It is taken daily by mouth for 8–24 weeks.
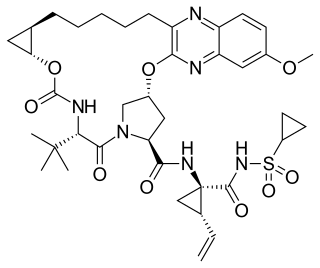
Grazoprevir is a drug approved for the treatment of hepatitis C. It was developed by Merck and completed Phase III trials, used in combination with the NS5A replication complex inhibitor elbasvir under the trade name Zepatier, either with or without ribavirin.

Elbasvir is a drug approved by the FDA in January 2016 for the treatment of hepatitis C. It was developed by Merck and completed Phase III trials, used in combination with the NS3/4A protease inhibitor grazoprevir under the trade name Zepatier, either with or without ribavirin.

Nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) inhibitors are direct acting antiviral agents (DAAs) that target viral proteins, and their development was a culmination of increased understanding of the viral life cycle combined with advances in drug discovery technology. However, their mechanism of action is complex and not fully understood. NS5A inhibitors were the focus of much attention when they emerged as a part of the first curative treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections in 2014. Favorable characteristics have been introduced through varied structural changes, and structural similarities between NS5A inhibitors that are clinically approved are readily apparent. Despite the recent introduction of numerous new antiviral drugs, resistance is still a concern and these inhibitors are therefore always used in combination with other drugs.
Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (G/P), sold under the brand names Mavyret and Maviret, is a fixed-dose combination medication used to treat hepatitis C. It contains glecaprevir and pibrentasvir. It works against all six types of hepatitis C. At twelve weeks following treatment between 81% and 100% of people have no evidence of hepatitis C. It is taken once a day by mouth with food.
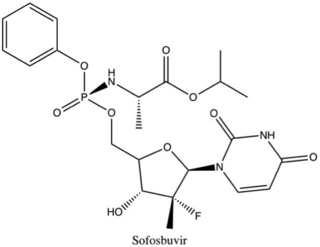
Non-structural protein 5B (NS5B) inhibitors are a class of direct-acting antivirals widely used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Depending on site of action and chemical composition, NS5B inhibitors may be categorized into three classes—nucleoside active site inhibitors (NIs), non-nucleoside allosteric inhibitors, and pyrophosphate analogues. Subsequently, all three classes are then subclassified. All inhibit RNA synthesis by NS5B but at different stages/sites resulting in inability of viral RNA replication. Expression of direct-acting NS5B inhibitors does not take place in cells that are not infected by hepatitis C virus, which seems to be beneficial for this class of drugs.











