In the Latter Day Saint movement, priesthood is the power and authority of God given to man, including the authority to perform ordinances and to act as a leader in the church. A group of priesthood holders is referred to as a quorum.

In Mormonism, the endowment is a two-part ordinance (ceremony) designed for participants to become kings, queens, priests, and priestesses in the afterlife. As part of the first ceremony, participants take part in a scripted reenactment of the Biblical creation and fall of Adam and Eve. The ceremony includes a symbolic washing and anointing, and receipt of a "new name" which they are not to reveal to others except at a certain part in the ceremony, and the receipt of the temple garment, which Mormons then are expected to wear under their clothing day and night throughout their life. Participants are taught symbolic gestures and passwords considered necessary to pass by angels guarding the way to heaven, and are instructed not to reveal them to others. As practiced today in the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, the endowment also consists of a series of covenants that participants make, such as a covenant of consecration to the LDS Church. All LDS Church members who choose to serve as missionaries or participate in a celestial marriage in a temple must first complete the first endowment ceremony.

Sealing is an ordinance (ritual) performed in Latter Day Saint temples by a person holding the sealing authority. The purpose of this ordinance is to seal familial relationships, making possible the existence of family relationships throughout eternity. Sealings are typically performed as marriages or as sealing of children to parents. They were performed prior to the death of Joseph Smith, and are currently performed in the largest of the faiths that came from the movement, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. LDS Church teachings place great importance on the specific authority required to perform these sealings. Church doctrine teaches that this authority, called the priesthood, corresponds to that given to Saint Peter in Matthew 16:19.

In the Latter Day Saint movement, the second anointing is the pinnacle ordinance of the temple and an extension of the endowment ceremony. Founder Joseph Smith taught that the function of the ordinance was to ensure salvation, guarantee exaltation, and confer godhood. In the ordinance, a participant is anointed as a "priest and king" or a "priestess and queen", and is sealed to the highest degree of salvation available in Mormon theology.
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints has several unique teachings about Judaism and the House of Israel. The largest denomination in the Latter Day Saint movement, the LDS Church teaches the belief that the Jewish people are God's chosen people and it also teaches the belief that its members share a common and literal Israelite ancestry with the Jewish people.

Washing and anointing is a Latter-day Saint practice of ritual purification. It is a key part of the temple endowment ceremony as well as the controversial Second Anointing ceremony practiced by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and Mormon fundamentalists. It was also part of the female-only healing rituals among Latter-day Saints until at least the 1940s.

In the Latter Day Saint movement, a temple is a building dedicated to being a house of God and is reserved for special forms of worship. A temple differs from a church meetinghouse, which is used for weekly worship services. Temples have been a significant part of the Latter Day Saint movement since early in its inception. Today, temples are operated by several Latter Day Saint denominations. The most prolific builder of temples of the Latter Day Saint movement is the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. The LDS Church has 367 temples in various phases, which includes 202 dedicated temples, 3 scheduled for dedication, 51 under construction, 2 scheduled for groundbreaking, and 112 others announced. Several others within the movement have built or attempted to build temples. The Community of Christ operates one temple in the United States, which is open to the public and used for worship services, performances, and religious education. Other denominations with temples are the Apostolic United Brethren, the Church of Christ, the Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints, and the Righteous Branch of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.

Celestial marriage is a doctrine that marriage can last forever in heaven. This is a unique teaching of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and branches of Mormon fundamentalism.
In temples of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, an ordinance room is a room where the ceremony known as the Endowment is administered, as well as other ordinances such as Sealings. Some temples perform a progressive-style ordinance where patrons move from room to room, each room representing a progression of mankind: the Creation room, representing the Genesis creation story; the Garden room represents the Garden of Eden where Adam and Eve lived prior to the fall of man; the World room, where Adam and Eve lived after the fall; the Terrestrial room; and the Celestial room representing the Celestial Kingdom of God, or more commonly, heaven. There is also an additional ordinance room, the Sealing room, and at least one temple has a Holy of Holies. These two rooms are reserved for the administration of ordinances beyond the Endowment. The Holy of Holies is representative of that talked about when the temple is discussed in the bible.

The Endowment House was an early building used by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints to administer temple ordinances in Salt Lake City, Utah Territory. From the construction of the Council House in 1852, Salt Lake City's first public building, until the construction of the Endowment House, the members of the LDS Church used the top floor of the Council House for administering temple ordinances. When this arrangement proved impractical, Brigham Young directed Truman O. Angell, architect of the Salt Lake Temple, to design a temporary temple. Completed in 1855, the building was dedicated by Heber C. Kimball and came to be called the Endowment House after the endowment ceremonies that were conducted inside it.

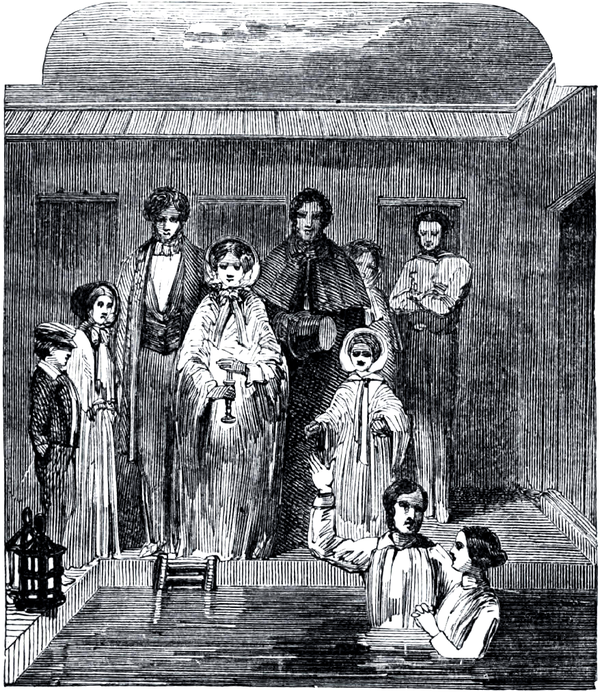
In the Latter Day Saint movement, baptism is recognized as the first of several ordinances (rituals) of the gospel.

An ordinance is a term used by certain Christian denominations for a religious ritual that was instituted by Jesus for Christians to observe.

The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints focuses its doctrine and teaching on Jesus Christ; that he was the Son of God, born of Mary, lived a perfect life, performed miracles, bled from every pore in the Garden of Gethsemane, died on the cross, rose on the third day, appeared again to his disciples, and now resides, authoritatively, on the right hand side of God. In brief, some beliefs are in common with Catholics, Orthodox and Protestant traditions. However, teachings of the LDS Church differ significantly in other ways and encompass a broad set of doctrines, so that the above-mentioned denominations usually place the LDS Church outside the bounds of orthodox Christian teaching as summarized in the Nicene Creed.

Baptism for the dead, vicarious baptism or proxy baptism today commonly refers to the religious practice of baptizing a person on behalf of one who is dead—a living person receiving the rite on behalf of a deceased person.

In the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, a temple is a building dedicated to be a House of the Lord. Temples are considered by church members to be the most sacred structures on earth.
In the theology of the Latter Day Saint movement, an endowment refers to a gift of "power from on high", typically associated with the ordinances performed in Latter Day Saint temples. The purpose and meaning of the endowment varied during the life of movement founder Joseph Smith. The term has referred to many such gifts of heavenly power, including the confirmation ritual, the institution of the High Priesthood in 1831, events and rituals occurring in the Kirtland Temple in the mid-1830s, and an elaborate ritual performed in the Nauvoo Temple in the 1840s.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and a topical guide to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Exaltation is a belief in Mormonism that after death some people will reach the highest level of salvation in the celestial kingdom and eternally live in God's presence, continue as families, become gods, create worlds, and make spirit children over whom they will govern. In the largest Mormon denomination, the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, top leaders have taught that God wants exaltation for all humankind and that humans are "gods in embryo". A verse in the LDS Church's canonized scripture states that those who are exalted will become gods, and a 1925 statement from the church's highest governing body said that "All men and women are in the similitude of the universal Father and Mother ... [and are] capable, by experience through ages and aeons, of evolving into a God."

In the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints —there have been numerous changes to temple ceremonies over time in the church's over-200-year history. Temples are not churches or meetinghouses designated for public weekly worship services, but rather sacred places that only admit members in good standing with a recommendation from their leaders. LDS Church members perform rituals within temples. They are taught that God has deemed these ordinances as essential to achieving the faith's ultimate goal after death of exaltation. They are also taught that a vast number of dead spirits exist in a condition termed spirit prison for whom when the temple ordinances are completed will have the option to accept the ordinances and be freed of their imprisonment. These temple ordinances are performed by a living church member for themself and "on behalf of the dead" or "by proxy".