
In military operations, military reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, the terrain, and civil activities in the area of operations. In military jargon, reconnaissance is abbreviated to recce and to recon, both derived from the root word reconnoitre.

In military terminology, a squad is among the smallest of military organizations and is led by a non-commissioned officer. NATO and U.S. doctrine define a squad as an organization "larger than a team, but smaller than a section." while U.S. Army doctrine further defines a squad as a "small military unit typically containing two or more fire teams." In American usage, a squad consists of eight to fourteen soldiers, and may be further subdivided into fireteams.

A fireteam or fire team is a small modern military subordinated element of infantry designed to optimize "NCO initiative", "combined arms", "bounding overwatch" and "fire and movement" tactical doctrine in combat. Depending on mission requirements, a typical "standard" fireteam consists of four or fewer members: an automatic rifleman, a grenadier, a rifleman, and a designated fireteam leader. The role of each fireteam leader is to ensure that the fireteam operates as a cohesive unit. Two or three fireteams are organized into a section or squad in co-ordinated operations, which is led by a squad leader.

In military terminology, friendly fire or fratricide is an attack by belligerent or neutral forces on friendly troops while attempting to attack enemy/hostile targets. Examples include misidentifying the target as hostile, cross-fire while engaging an enemy, long range ranging errors or inaccuracy. Accidental fire not intended to attack enemy/hostile targets, and deliberate firing on one's own troops for disciplinary reasons, is not called friendly fire, and neither is unintentional harm to civilian or neutral targets, which is sometimes referred to as collateral damage. Training accidents and bloodless incidents also do not qualify as friendly fire in terms of casualty reporting.

Close-quarters combat (CQC) or close-quarters battle (CQB) is a close combat situation between multiple combatants involving ranged or melee combat. It can occur between military units, law enforcement and criminal elements, and in other similar situations. CQB is typically defined as a short duration, high intensity conflict characterized by sudden violence at close range.

Enfilade and defilade are concepts in military tactics used to describe a military formation's exposure to enemy fire. A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be directed along its longest axis. A unit or position is "in defilade" if it uses natural or artificial obstacles to shield or conceal itself from enfilade and hostile fire. The strategies, named by the English during the Hundred Years' War, use the French enfiler and défiler spoken by English nobility of the time.

Patrick Daniel Tillman Jr. was an American professional football player for the Arizona Cardinals of the National Football League (NFL) who left his sports career and enlisted in the United States Army in May 2002 in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks. His service in Iraq and Afghanistan, as well as his subsequent death, were the subject of national attention. This increased after it was revealed that he was killed by friendly fire.

In military science, suppressive fire is "fire that degrades the performance of an enemy force below the level needed to fulfill its mission". When used to protect exposed friendly troops advancing on the battlefield, it is commonly called covering fire. Suppression is usually only effective for the duration of the fire. It is one of three types of fire support, which is defined by NATO as "the application of fire, coordinated with the maneuver of forces, to destroy, neutralise or suppress the enemy".

Fire support is a military term used to describe weapons fire used to support friendly forces by engaging, suppressing, or destroying enemy forces, facilities, or materiel in combat. It is often provided through indirect fire, though the term may also be used for some forms of supporting direct fire.

A peel is a type of retreat conducted by infantry which allows them to maintain effective defensive suppressive fire while retreating. Though generally considered a modern-day infantry technique, the concept dates back to Greek and Roman times. This particular tactic is more specifically designed for situations where smaller groups of infantry withdraw from an engagement of a much larger force.

Fire and movement, or fire and maneuver, is the basic modern military low-level unit tactic used to maneuver on the battlefield in the presence of the enemy, especially when under fire. It involves heavy use of all available cover, and highly-coordinated exchanges of rapid movement by some elements of the squad or platoon while other elements cover this movement with suppression fire. It is used both to advance on enemy positions as part of an attack, or withdrawal from current positions under attack by the enemy. The moving and supporting (suppressing) elements may be teams or individuals, and may quickly and continuously exchange roles until the entire unit completes the maneuver objective. Some members will specialize more in different roles within fire and movement as fits their range, equipment, terrain, and ability to maneuver. This is usually applied to standard infantry tactics, but forms of this are also used with armored fighting vehicles or when supported by artillery or airpower.
Hasty attack is a specific form of attack identified within United States and Canadian military doctrine, in which upon contact with the enemy that is unprepared a unit decides to conduct an attack with limited planning and coordination and with rapid preparation and execution to exploit the enemy's weakness. Though applicable to infantry operations historically and in modern times, hasty attacks are a hallmark of mechanized force operations. During the Civil War, the command for a hasty attack was "sally forth".

Bounding overwatch is a military tactic of alternating movement of coordinated units to allow, if necessary, suppressive fire in support of offensive forward "fire and movement" or defensive "center peel" disengagement.

In military tactics, a flanking maneuver is a movement of an armed force around an enemy force's side, or flank, to achieve an advantageous position over it. Flanking is useful because a force's fighting strength is typically concentrated in its front, therefore, to circumvent an opposing force's front and attack its flank is to concentrate one's own offense in the area where the enemy is least able to concentrate defense.
In military terminology, a base of fire is a supporting force that provides overwatch and covering fire to other advancing units while they are executing fire and movement tactics. A base of fire can be a platoon during company fire and movement, by individual armoured fighting vehicles or infantry sections, in platoon fire and movement, or even by fireteams or individual soldiers, in the final stages of an assault.
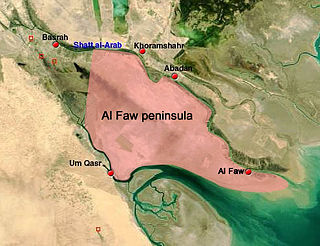
The Battle of Al Faw was one of the first battles of the Iraq War; it took place March 20-24, 2003.
The Battle of Prek Klok I occurred on February 28, 1967 during Operation Junction City, a search and destroy mission by American military forces in Tay Ninh Province of South Vietnam, to the west of the capital Saigon. A few days before the battle, the 1st Battalion, 16th Infantry Regiment was brought into the area near Suoi Da and Prek Klok to defend a highway, airfield, and artillery base in the area, and to carry out search and destroy operations around it. On the morning of 28 February, elements of the battalion headed east, and were attacked from the front by Viet Cong (VC) infantry with gunfire, rockets and mortars. Soon after, they were attacked from all fronts as the VC tried to surround them with a battalion-sized force. However, with superior firepower available, the Americans called in air strikes and artillery, and by mid afternoon, had repelled the VC attacks. The Americans lost 25 killed while the VC lost 167.
The Overwatch franchise, a series of first-person shooter games developed by Blizzard Entertainment, consists of 40 playable characters across both games. The original 2016 game, Overwatch, featured 32 playable characters known as heroes and a number of supporting characters as part of the game's narrative, which is told through animated media and digital comics outside of the game. Its sequel, Overwatch 2, was released in October 2022 and replaced Overwatch. The sequel builds upon the same hero roster and added more characters, currently consisting of 40 heroes. However, as Overwatch 2 had been developed to be a faster game with five-versus-five teams rather than six-versus-six, several of the characters had tweaks or major rebuilds within Overwatch 2, as well as different character designs.















