
The darters, anhingas, or snakebirds are mainly tropical waterbirds in the family Anhingidae, which contains a single genus, Anhinga. There are four living species, three of which are very common and widespread while the fourth is rarer and classified as near-threatened by the IUCN. The term snakebird is usually used without any additions to signify whichever of the completely allopatric species occurs in any one region. It refers to their long thin neck, which has a snake-like appearance when they swim with their bodies submerged, or when mated pairs twist it during their bonding displays. "Darter" is used with a geographical term when referring to particular species. It alludes to their manner of procuring food, as they impale fishes with their thin, pointed beak. The American darter is more commonly known as the anhinga. It is sometimes called "water turkey" in the southern United States; though the anhinga is quite unrelated to the wild turkey, they are both large, blackish birds with long tails that are sometimes hunted for food.

The Anatidae are the biological family of water birds that includes ducks, geese, and swans. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring on all the world's continents except Antarctica. These birds are adapted for swimming, floating on the water surface, and, in some cases, diving in at least shallow water. The family contains around 174 species in 43 genera.

Anguidae refers to a large and diverse family of lizards native to the Northern Hemisphere. Common characteristics of this group include a reduced supratemporal arch, striations on the medial faces of tooth crowns, osteoderms, and a lateral fold in the skin of most taxa. The group is divided into two living subfamilies, the legless Anguinae, which contains slow worms and glass lizards, among others, found across the Northern Hemisphere, and Gerrhonotinae, which contains the alligator lizards, native to North and Central America. The family Diploglossidae was also formerly included. The family contains about 87 species in 8 genera.

Nimravidae is an extinct family of carnivorans, sometimes known as false saber-toothed cats, whose fossils are found in North America and Eurasia. Not considered to belong to the true cats, the nimravids are generally considered closely related and classified as a distinct family in the suborder Feliformia. Fossils have been dated from the Middle Eocene through the Late Miocene epochs, spanning about 33.2 million years.

Sauropelta is a genus of nodosaurid dinosaur that existed in the Early Cretaceous Period of North America. One species has been named. Anatomically, Sauropelta is one of the most well-understood nodosaurids, with fossilized remains recovered in the U.S. states of Wyoming, Montana, and possibly Utah. It is also the earliest known genus of nodosaurinae; most of its remains are found in a section of the Cloverly Formation dated to 108.5 million years ago.
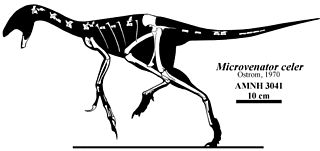
Microvenator is a genus of dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Cloverly Formation in what is now south central Montana. Microvenator was an oviraptorosaurian theropod. The holotype fossil is an incomplete skeleton, most likely a juvenile with a length of 1.3 m (4.3 ft), and consequently, the adult size remains uncertain. Microvenator celer is primitive and may be the "sister taxon to all other oviraptorosaurs."

Rhineura is a genus of worm lizard endemic to North America. The genus has only one extant species but more are known from fossil record. They are also known as the North American worm lizards.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1997.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1970.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1969.

Archaeohippus is an extinct three toed member of the family Equidae known from fossils of early Oligocene to middle Miocene age. The genus is noted for several distinct skeletal features. The skull possesses deeply pocketed fossa in a notably long preorbital region. The genus is considered an example of phyletic dwarfism with adults estimated at being on average 20 kilograms in weight. This is in contrast to the most common equid of the period, Miohippus. Characters of the teeth show a mix of both primitive and advanced traits. The advanced traits are very similar to those shown in the genus Parahippus. The noted similarities of Archaeohippus and Parahippus show them to be descended from a common ancestor. They are considered sister species.
Nordenosaurus is an extinct genus of crocodilian. When first named in 1973 the genus was thought to be a squamate and was assigned to the family Xenosauridae. A single frontal bone was found from the Norden Bridge locality of the lower Valentine Formation in Brown County, Nebraska, thought to date back to the late Miocene. The size of the bone was initially taken as evidence that it was a giant xenosaurid. The specific name of the type species, N. magnus, alludes to its extremely large size in comparison to other xenosaurids known at the time. In 1982, paleontologist Jacques Gauthier reinterpreted Nordenosaurus as a small crocodilian rather than a giant xenosaurid. The frontal bone is hour-glass shaped and covered in deep pits, unlike those of any lizard but similar to the frontals of most crocodilians.

Saniwa is an extinct genus of varanid lizard that lived during the Eocene epoch. It is known from well-preserved fossils found in the Bridger and Green River Formations of Wyoming, United States. The type species S. ensidens was described in 1870 as the first fossil lizard known from North America. A second species, S.orsmaelensis, is recognised from remains found in Europe. It is a close relative of Varanus, the genus that includes monitor lizards.

Glyptosaurinae is an extinct subfamily of anguid lizards that lived in the Northern Hemisphere during the Late Cretaceous and the Paleogene.

Helodermoides is an extinct genus of anguid lizards from the Oligocene of North America. The genus is monotypic, including only the species Helodermoides tuberculatus. Helodermoides belongs to an extinct subfamily of anguids called Glyptosaurinae. In addition to many fragmentary bones, several complete skeletons of Helodermoides are known. Like other glyptosaurines, Helodermoides was covered in small scale-like bones called osteoderms. The osteoderms covering its skull are hexagonal, tightly interlocking, raised, and rounded.

The Valentine Formation is a geologic unit formation or member within the Ogallala unit in northcentral Nebraska near the South Dakota border. It preserves fossils dating to the Miocene epoch of the Neogene period and is particularly noted for Canid fossils. This unit consists of loosely-consolidated sandstone that crumbles easily. These sands carry the water of the Ogallala Aquifer and is the source of much of the water in the Niobrara River. A particular feature of the Valentine is lenticular beds of green-gray opaline sandstone that can be identified in other states, including South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, and Colorado. Although three mammalian fauna stages can be mapped throughout the range of the Ogallala, no beddings of the Ogallala are mappable and all attempts of formally applying the Valentine name to any mappable lithology beyond the type location have been abandoned. Even so, opaline sandstone has been used to refer to this green-gray opalized conglomerate sandstone that is widely found in the lower Ogallala Formation.
Odaxosaurus is an extinct genus of anguid lizards that existed in western North America from the Late Cretaceous to the Paleocene. Fossils of the type species Odaxosaurus piger and the species O. priscus are widespread throughout Late Cretaceous formations in the western United States and Canada. First described in 1928 from the Lance Formation in Wyoming, O. piger has since been found in the Hell Creek Formation in Wyoming and Montana, the Frenchman and Scollard formations in Alberta, and the Aguja Formation in Texas. It was one of the few species of lizards to survive the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, which is estimated to have killed off 83% of all lizard species. The second species, O. priscus, was named in 1996 from the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta and has since been found in the Kaiparowits Formation in southern Utah. Remains of an anguid from the Kirtland Formation in New Mexico may also belong to Odaxosaurus.
Magnuviator is a genus of extinct iguanomorph lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Montana, US. It contains one species, M. ovimonsensis, described in 2017 by DeMar et al. from two specimens that were discovered in the Egg Mountain nesting site. Magnuviator is closest related to the Asian Saichangurvel and Temujinia, which form the group Temujiniidae. Unlike other members of the Iguanomorpha, however, Magnuviator bears a distinct articulating notch on its tibia for the ankle bones, which has traditionally been considered a characteristic of non-iguanomorph lizards. The morphology of its teeth suggests that its diet would have mainly consisted of wasps, like the modern phyrnosomatid iguanians Callisaurus and Urosaurus, although it also shows some adaptations to herbivory.
Stenoplacosaurus is an extinct genus of glyptosaurine anguid lizards from the Eocene of Inner Mongolia, China. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species Stenoplacosaurus mongoliensis.

Robert Michael "Bob" Sullivan is a vertebrate paleontologist, noted for his work on fossil lizards and dinosaurs.

















