Kuru is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod from the Late Cretaceous Barun Goyot Formation of Mongolia. The genus contains a single species, Kuru kulla, known from a fragmentary skeleton including a partial skull.

Citipati is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. It is mainly known from the Ukhaa Tolgod locality at the Djadokhta Formation, where the first remains were collected during the 1990s. The genus and type species Citipati osmolskae were named and described in 2001. A second species from the adjacent Zamyn Khondt locality may also exist. Citipati is one of the best-known oviraptorids thanks to a number of well-preserved specimens, including individuals found in brooding positions atop nests of eggs, though most of them were initially referred to the related Oviraptor. These nesting specimens have helped to solidify the link between non-avian dinosaurs and birds.

The Djadochta Formation is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. The type locality is the Bayn Dzak locality, famously known as the Flaming Cliffs. Dinosaur, mammal, and other reptile remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.

Estesia is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous anguimorph lizard found in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia. It was discovered in June 1990 by a joint expedition made up of Mongolian and American palaeontologists, and described in 1992 by Mark Norell, Malcolm McKenna and Michael Novacek. This animal is of interest to palaeontologists, not only because it is close to the lineage of modern Gila monsters (Heloderma), but also because its dentition shows evidence that it was venomous.

Minotaurasaurus is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur that lived in Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Djadochta Formation.
Ovoo gurvel is an extinct monitor lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It is one of the smallest and earliest monitor lizards. It was described in 2008. Ovoo possesses a pair of two small bones in its skull that are not seen in any other lizard.
Aiolosaurus is an extinct genus of monitor lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. The type and only species, Aiolosaurus oriens, was named in 2000 from Ukhaa Tolgod, a rich fossil site in the Campanian-age Djadochta Formation.
Hoburogekko is an extinct genus of gecko that includes a single species, Hoburogekko suchanovi, from the Early Cretaceous of Mongolia. It is known from two fossil specimens, one preserving the front part of the skull and the other preserving part of the lower jaw. Hoburogekko is one of four known Mesozoic geckos or gecko-like lizards, the others being Cretaceogekko from the Early Cretaceous of Burma, AMNH FR21444, an undescribed specimen from a slightly older deposit in Mongolia, and Gobekko from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Hoburogekko is the third oldest known gecko behind AMNH FR21444 and Cretaceogekko.

Gekkonomorpha is a clade of lizards that includes geckos and their closest relatives. Although it was first named in 1900, Gekkonomorpha was not widely used as a formal taxon until it was given a phylogenetic definition in the 1990s. Under this definition, Gekkonomorpha is a stem-based taxon containing the node-based taxon Gekkota, the group that includes the last common ancestor of all living geckos and its descendants. The extent of Gekkonomorpha beyond gekkotans differs between studies. For example, Lee (1998) defined Gekkonomorpha in such a way that it included not only Gekkota but the legless amphisbaenian and dibamid lizards as well. The phylogenetic analysis of Conrad (2008), which did not support a close relationship between geckos and legless lizards, used Gekkonomorpha in a much more restrictive sense so that it included only Gekkota and a few extinct lizards more closely related to Gekkota than to any other living group of lizards. Some of the most recent phylogenetic analyses suggest that the extinct lizards Gobekko and Parviraptor may be stem gekkotans, although other analyses find that Gobekko may instead be within Gekkota and Parviraptor outside Gekkonomorpha.
Carusia is an extinct genus of lizards from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It is a close relative of the family Xenosauridae, which includes living knob-scaled lizards. Fossils of the type and only species Carusia intermedia come from the late-Campanian age Barun Goyot Formation and have been found in the Flaming Cliffs, Ukhaa Tolgod, and Kheerman Tsav fossil localities. Carusia was first described in 1985 under the name Carolina intermedia, but since the name Carolina was preoccupied by a genus of scarab beetles that had been named in 1880, it was renamed Carusia intermedia. Carusia had initially been known from fragmentary skull material, complicating efforts to determine its evolutionary relationships with other lizards; it had variously been described as an indeterminate scincomorph, a xenosaurid, or some other type of autarchoglossan lizard convergent with xenosaurids. However, the discovery of 35 complete skulls in the 1990s, three of which were described in a detailed 1998 monograph, revealed that Carusia was the sister taxon of Xenosauridae, compelling the authors of the monograph to create a new clade called Carusioidea to include both taxa.
Carusioidea is a clade of lizards that includes the family Xenosauridae from Central America and the extinct genus Carusia from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It was named in 1998 after a sister-group relationship was found between Carusia and Xenosauridae. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that Carusioidea is the most basal clade within Anguimorpha. Features that help define Carusioidea include closely spaced orbits or eye sockets separated by fused frontal bones, a connection between the jugal and squamosal bones below the supratemporal arch, and a covering of bony osteoderms over the skull roof. Below is a cladogram showing the phylogenetic relationships of carusioids from Gao and Norell (1998):
Priscagamidae is an extinct family of iguanian lizards known from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia and China and the Eocene of India, spanning a range from 75 to 54 million years ago. It includes the genera Heterodontagama, Mimeosaurus, Phrynosomimus, Priscagama, and possibly Pleurodontagama. The first fossils of priscagamids were found in the Djadochta and Khermeen Tsav formations of Mongolia. More recently they have been found in the Cambay Formation in India, leading to the naming of Heterodontagama in 2013. Priscagamidae was originally described as a subfamily of Agamidae called Priscagaminae in 1984, but it was reclassified as a distinct family in 1989. Most phylogenetic analyses still find a close relationship between Priscagamidae and Agamidae, although a 2015 study found it to be basal to all other iguanian clades, warranting its removal from Iguania and placement in a larger clade called Iguanomorpha.
Saichangurvel is an extinct genus of iguanian lizards from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It is a member of a clade called Gobiguania, an exclusively Late Cretaceous group of iguanian lizards that was likely endemic to the Gobi Desert. The type species, Saichangurvel davidsoni, was named by paleontologists Jack Conrad and Mark Norell of the American Museum of Natural History in 2007. It is known from a single nearly complete and fully articulated skeleton called IGM 3/858, which was found eroding from a block of sandstone during a thunderstorm at a fossil locality called Ukhaa Tolgod. IGM 3/858 comes from the Djadochta Formation, which is between 75 and 71 million years in age. Just as it is today, the Gobi was a desert during the Cretaceous. IGM 3/858 may have died in a collapsing sand dune, the rapid burial preserving its skeleton in pristine condition.
Priscagama is an extinct genus of iguanian lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia and China. It belongs to an extinct family of iguanians called Priscagamidae. Several incomplete skulls have been found in the Barun Goyot and Djadochta formations, and were originally referred to the genus Mimeosaurus; the type species Priscagama gobiensis was named in 1984 when it was recognized that these skulls belonged to a distinct species. Priscagama differs from most other priscagamids in having a more elongate, lightly built skull. It is very similar in appearance to another priscagamid called Pleurodontagama, as the two can only be distinguished by the shape of their teeth.
Phrynosomimus is an extinct genus of iguanian lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia belonging to the extinct family Priscagamidae. The type species Phrynosomimus asper was named in 1996. Fossils have been found in the Barun Goyot and Djadochta formations and include several complete skulls. Phrynosomimus has a short, triangular skull with bony spikes projecting from the back, stemming from the squamosal and parietal bones. These spikes give it a similar appearance to the modern horned lizard Phrynosoma and inspire its name, which means "Phrynosoma mimic". Like other priscagamids it has an acrodont dentition, meaning that its teeth grow from the margins of the jaws rather than their inner surfaces, as is the case for the pleurodont dentitions of most lizards.
Anchaurosaurus is an extinct genus of iguanian lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Inner Mongolia, China. It belongs to an extinct clade of iguanians called Gobiguania that was endemic to the Gobi Desert during the Late Cretaceous. The type species, Anchaurosaurus gilmorei, was named in 1995 on the basis of a well-preserved skull and incomplete skeleton from the Djadochta Formation. Compared to other iguanians, Anchaurosaurus has a relatively elongated skull, large eye sockets, and higher tooth crowns. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that among gobiguanians, Anchaurosaurus is most closely related to Zapsosaurus from Mongolia. Below is a cladogram from Daza et al. (2012) showing the phylogenetic relationships of Anchaurosaurus:
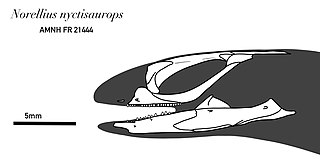
Norellius is an extinct genus of scleroglossan lizard from the Early Cretaceous Öösh Formation of Mongolia. It is known from a well-preserved skull that was collected by an American Museum of Natural History expedition to Mongolia in 1923 and cataloged as AMNH FR 21444. After its initial cataloging, the specimen was not mentioned again in the scientific literature until 2004, when it was recognized as belonging to a potential early relative of modern groups of squamates such as gekkotans, amphisbaenians, dibamids, and snakes. AMNH FR 21444 was more fully described in a 2006 study that used high-resolution computed tomography to examine the skull and its braincase, and was described as a new genus and species, Norellius nyctisaurops, in 2015. The genus name honors paleontologist Mark Norell. The 2006 study incorporated the specimen into a phylogenetic analysis and found it to be a basal member of an evolutionary grouping called Gekkonomorpha, a stem-based taxon that includes living geckos and legless lizards (pygopodids) and all taxa more closely related to them than to any other living lizard. Norellius lies outside the node-based taxon Gekkota, a more strictly-defined subgroup of Gekkonomorpha that includes geckos, pygopodids, and all descendants of their most recent common ancestor. Therefore, while Norellius is more closely related to geckos and pygopodids than it is to any other living group of lizards, it branched off before the most recent common ancestor of these two groups. Below is a cladogram showing the position of Norellius according to this phylogeny:
Magnuviator is a genus of extinct iguanomorph lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Montana, US. It contains one species, M. ovimonsensis, described in 2017 by DeMar et al. from two specimens that were discovered in the Egg Mountain nesting site. Magnuviator is closest related to the Asian Saichangurvel and Temujinia, which form the group Temujiniidae. Unlike other members of the Iguanomorpha, however, Magnuviator bears a distinct articulating notch on its tibia for the ankle bones, which has traditionally been considered a characteristic of non-iguanomorph lizards. The morphology of its teeth suggests that its diet would have mainly consisted of wasps, like the modern phyrnosomatid iguanians Callisaurus and Urosaurus, although it also shows some adaptations to herbivory.

Eichstaettisaurus is a genus of lizards from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Germany, Spain, and Italy. With a flattened head, forward-oriented and partially symmetrical feet, and tall claws, Eichstaettisaurus bore many adaptations to a climbing lifestyle approaching those of geckoes. The type species, E. schroederi, is among the oldest and most complete members of the Squamata, being known by one specimen originating from the Tithonian-aged Solnhofen Limestone of Germany. A second species, E. gouldi, was described from another skeleton found in the Matese Mountains of Italy. Despite being very similar to E. schroederi, it lived much later, during the Albian stage. Fossils of both species show exceptional preservation due to deposition in low-oxygen marine environments.

Almas is a genus of troodontid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It contains a single species, Almas ukhaa, named in 2017 by Pei Rui and colleagues, based on a partial articulated skeleton. The only known specimen was found in the Djadochta Formation, which is late Campanian in age.








