
Tartaric acid is a white, crystalline organic acid that occurs naturally in many fruits, most notably in grapes, but also in bananas, tamarinds, and citrus. Its salt, potassium bitartrate, commonly known as cream of tartar, develops naturally in the process of fermentation. It is commonly mixed with sodium bicarbonate and is sold as baking powder used as a leavening agent in food preparation. The acid itself is added to foods as an antioxidant E334 and to impart its distinctive sour taste. Naturally occurring tartaric acid is a useful raw material in organic chemical synthesis. Tartaric acid, an alpha-hydroxy-carboxylic acid, is diprotic and aldaric in acid characteristics, and is a dihydroxyl derivative of succinic acid.

Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), also known as dibutylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound, chemically a derivative of phenol, that is useful for its antioxidant properties. BHT is widely used to prevent free radical-mediated oxidation in fluids and other materials, and the regulations overseen by the U.S. F.D.A.—which considers BHT to be "generally recognized as safe"—allow small amounts to be added to foods. Despite this, and the earlier determination by the National Cancer Institute that BHT was noncarcinogenic in an animal model, societal concerns over its broad use have been expressed. BHT has also been postulated as an antiviral drug, but as of December 2022, use of BHT as a drug is not supported by the scientific literature and it has not been approved by any drug regulatory agency for use as an antiviral.

Potassium bitartrate, also known as potassium hydrogen tartrate, with formula KC4H5O6, is a chemical compound with a number of uses, including:

Disodium guanylate, also known as sodium 5'-guanylate and disodium 5'-guanylate, is a natural sodium salt of the flavor enhancing nucleotide guanosine monophosphate (GMP). Disodium guanylate is a food additive with the E number E627. It is commonly used in conjunction with glutamic acid.

A tartrate is a salt or ester of the organic compound tartaric acid, a dicarboxylic acid. The formula of the tartrate dianion is O−OC-CH(OH)-CH(OH)-COO− or C4H4O62−.

Allura Red AC is a red azo dye that goes by several names, including FD&C Red 40. It is used as a food dye and has the E number E129.

Dihydrogen phosphate is an inorganic ion with the formula [H2PO4]−. Phosphates occur widely in natural systems.

Potassium fumarate is a compound with formula K2C4H2O4. It is the potassium salt of fumaric acid.

Sodium fumarate, also called disodium fumarate, is a compound with the molecular formula Na2C4H2O4. It is the sodium salt of fumaric acid, used as an acidity regulator in processed foods. Sodium fumarate and fumaric acid are sometimes used as terminal electron acceptors in the cultivation of certain anaerobic microorganisms. It appears as an odourless, white, crystalline powder and is soluble in water.

Ammonium ferric citrate (also known as ferric ammonium citrate or ammoniacal ferrous citrate) has the formula (NH4)5[Fe(C6H4O7)2]. A distinguishing feature of this compound is that it is very soluble in water, in contrast to ferric citrate which is not very soluble.

Disodium citrate, also known as disodium hydrogen citrate, Alkacitron, and sesquihydrate, is an acid salt of citric acid with the chemical formula Na2C6H6O7.

Dicalcium citrate is a compound with formula C6H6Ca2O7. It is a calcium acid salt of citric acid.
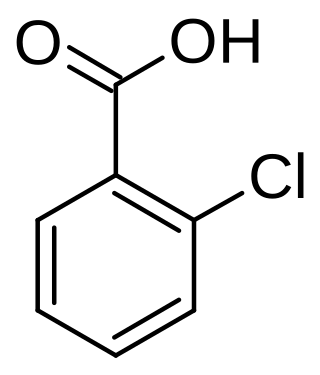
2-Chlorobenzoic acid is an organic compound with the formula ClC6H4CO2H. It is one of three isomeric chlorobenzoic acids, the one that is the strongest acid. This white solid is used as a precursor to a variety of drugs, food additives, and dyes.

Monosodium tartrate or sodium bitartrate is a sodium acid salt of tartaric acid. As a food additive it is used as an acidity regulator and is known by the E number E335. As an analytical reagent, it can be used in a test for ammonium cation which gives a white precipitate.

Ferrous citrate, also known as iron(II) citrate or iron(2+) citrate, describes coordination complexes containing citrate anions with Fe2+ formed in aqueous solution. Although a number of complexes are possible (or even likely), only one complex has been crystallized. That complex is the coordination polymer with the formula [Fe(H2O)6]2+{[Fe(C6H5O7)(H2O)]−}2.2H2O, where C6H5O73- is HOC(CH2CO2−)2(CO2−, i.e., the triple conjugate base of citric acid wherein the three carboxylic acid groups are ionized. Ferrous citrates are all paramagnetic, reflecting the weak crystal field of the carboxylate ligands.

Potassium erythorbate (C6H7KO6) is a food additive. Chemically, it is the potassium salt of erythorbic acid. As an antioxidant structurally related to vitamin C, it helps improve flavor stability and prevents the formation of carcinogenic nitrosamines.

Bitartrate is an anion which is the conjugate base of tartaric acid. It may also refer to any salt or monoester of tartaric acid.
Alkali citrate is an inhibitor of kidney stones. It is used to increase urine citrate levels - this prevents calcium oxalate stones by binding to calcium and inhibiting its binding to oxalate. It is also used to increase urine pH - this prevents uric acid stones and cystine stones.

Choline bitartrate is an organic compound with the chemical formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+HOOC−CH(OH)−CH(OH)−COO−. It is a white crystalline powder with an acid taste. It is hygroscopic when exposed to air. Modern texts refer to the choline salt of the natural form of tartaric acid, that is, the salt called choline dextrobitartrate, choline (2R,3R)-bitartrate or choline L-(+)-bitartrate.


















