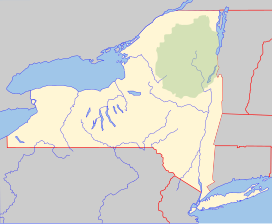
The Adirondack Mountains are a massif of mountains in Northeastern New York which form a circular dome approximately 160 miles (260 km) wide and covering about 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2). The region contains more than 100 peaks, including Mount Marcy, which is the highest point in New York at 5,344 feet (1,629 m). The Adirondack High Peaks, a traditional list of 46 peaks over 4,000 feet (1,200 m), are popular hiking destinations. There are over 200 named lakes with the number of smaller lakes, ponds, and other bodies of water reaching over 3,000. Among the named lakes around the mountains are Lake George, Lake Placid, and Lake Tear of the Clouds. The region has over 1,200 miles (1,900 km) of river.

Indian Lake is a town in Hamilton County, New York, United States. The population was 1,352 at the 2010 census. The name is from a lake of the same name that is largely inside the town. There are no permanent stop lights in the town. Law enforcement is provided by New York State Troopers and Hamilton County Sheriff's Office.
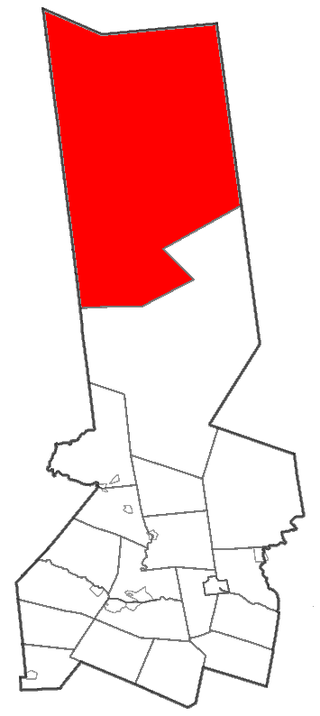
Webb is the northernmost town in Herkimer County, New York, United States. As of the 2020 Census it had a population of 1,797.

Clifton is a town in St. Lawrence County, New York, United States. The population was 675 at the 2020 census. The town takes its name from a mining company.

The Adirondack Park is a park in northeastern New York protecting the Adirondack Mountains. The park was established in 1892 for "the free use of all the people for their health and pleasure", and for watershed protection. At 6.1 million acres, it is the largest park in the contiguous United States.

Mount Marcy is the highest point in the U.S. state of New York, with an elevation of 5,343.1 feet (1,628.6 m). It is located in the town of Keene in Essex County. The mountain is in the heart of the High Peaks Wilderness Area in Adirondack Park. Like the surrounding Adirondack Mountains, Marcy was heavily affected by large glaciers during recent ice ages, which deposited boulders on the mountain slopes and carved valleys and depressions on the mountain. One such depression is today filled by Lake Tear of the Clouds, which is often cited as the highest source of the Hudson River. The majority of the mountain is covered by hardwood and spruce-fir forests, although the highest few hundred feet are above the tree line. The peak is dominated by rocky outcrops, lichens, and alpine plants. The mountain supports a diverse number of woodland mammals and birds.

Whiteface Mountain is the fifth-highest mountain in the U.S. state of New York, and one of the High Peaks of the Adirondack Mountains, located in the town of Wilmington in Essex County. Set apart from most of the other High Peaks, the summit offers a 360-degree view of the Adirondacks and clear-day glimpses of Vermont and Canada, where Montreal can be seen on a very clear day. Because of its relative isolation, the mountain is exposed to prevailing winds from the west and frequently capped with snow and ice, making it an area of interest to meteorologists. Weather data has been collected on the summit since 1937. The mountain's east slope is home to a major ski area which boasts the greatest vertical drop east of the Rockies, and which hosted the alpine skiing competitions of the 1980 Winter Olympics. Unique among the High Peaks, Whiteface features a developed summit and seasonal accessibility by motor vehicle. The Whiteface Veterans Memorial Highway reaches a parking area at an elevation shortly below the summit, with the remaining distance covered by tunnel and elevator. The peak can also be reached on two hiking trails.

Dix Mountain is a mountain in the Dix Range of the Adirondacks in the U.S. state of New York. With an elevation of 4,857 feet (1,480 m), it is the sixth highest peak in New York and one of the 46 Adirondack High Peaks. It is located roughly on the boundary between the towns of North Hudson and Keene in Essex County, and in the High Peaks Wilderness Area of Adirondack Park. The crest of the peak consists of a very narrow ridge, which continues to the southeast and rises to a subsidiary peak named Beckhorn, then continues south to other peaks of the Dix Range. The summit is also in an alpine zone above the treeline. The ridge offers unobstructed views of Elk Lake to the southwest, the Great Range to the northwest, and Lake Champlain and the Green Mountains to the east.

Mount Colden is a mountain in the Adirondacks in the U.S. state of New York. It is the eleventh-highest peak in New York, with an elevation of 4,714 feet (1,437 m), and one of the 46 High Peaks in Adirondack Park. It is located in the town of Keene in Essex County. The peak is named after David C. Colden, an investor in the McIntyre Iron Works at Tahawus. The mountain is known for the Trap Dike, a large crevice that runs from a point near the summit on its west face to nearby Avalanche Lake. The summit of Mount Colden can be reached by two hiking trails, which are frequently combined to form a circuit through Avalanche Pass, or by climbing the Trap Dike. The summit is in an alpine tundra zone above the treeline, and offers views of surrounding mountains and lakes.

Mount Jo is a 2,832-foot-tall (863 m) mountain in the heart of the Adirondack Mountains of New York. It is in North Elba, New York on land owned by the Adirondack Mountain Club. The Adirondack Loj and Heart Lake are at the foot of Mount Jo. There are two trails that lead to its summit.

Macomb Mountain is a mountain in the Dix Range of the Adirondacks in the U.S. state of New York. It is the 21st-highest of the Adirondack High Peaks, with an elevation of 4,405 feet (1,343 m), and the most southeasterly of the High Peaks. It is located in the town of North Hudson in Essex County. The mountain is named for Alexander Macomb, an American general who became famous for his victory at the Battle of Plattsburgh in 1814. The name first appeared in print in 1842. The earliest recorded ascent of the mountain was made in 1872 by guide Mel Trumbull and artist Arthur H. Wyant. Major slides on the western face of the mountain were caused by hurricanes in 1947 and 1950 and expanded by Hurricane Irene in 2011.

MacNaughton Mountain is a mountain located in Essex County, New York, named after James MacNaughton (1851–1905), the grandson of Archibald McIntyre. The mountain is part of the Street Range of the Adirondack Mountains.
Nye Mountain is a mountain located in Essex County, New York, named after William B. Nye (c.1815–1893), an Adirondack mountain guide. Nye Mountain is part of the Street Range of the Adirondack Mountains; it is flanked to the southwest by Street Mountain.

Street Mountain is a mountain located in Essex County, New York, named after Alfred Billings Street (1811–1881), a poet and New York State Librarian. The mountain is the high point of the Street Range of the Adirondack Mountains. Street's northeast ridge is Nye Mountain.

Snowy Mountain is a mountain located in Hamilton County, New York. Initially known as 'Squaw Bonnet', its summit is the highest point in the county. While most maps show the elevation as 3899 feet, some suggest that more recent surveys have it as 3904 feet or even 3908 feet.
Gore Mountain is a mountain located near the village of North Creek in Warren County, New York, of which its peak is the highest point. Gore is flanked to the north by South Mountain, and to the southwest by Height of Land Mountain. The mountain is the site of the popular Gore Mountain ski resort. The mountain is the site of the Gore Mountain Fire Observation Station which was built in 1918.

Ampersand Mountain is a 3,352 ft (1,021.7 m) mountain in Franklin County in the High Peaks Wilderness Area of the northeastern Adirondacks, west of the High Peaks proper in New York State. The trail up the mountain begins on New York State Route 3 8.1 miles (13.0 km) southwest of the village of Saranac Lake, near Middle Saranac Lake; it is a popular day hike. The mountain takes its name from nearby Ampersand Creek, so named because it twists and turns like the ampersand symbol. The summit is bare rock, with extensive views of the High Peaks to the east and the Saranac Lakes to the west. Stony Creek Mountain is located west-southwest of Ampersand Mountain. The mountain is notable as the land surrounding its hiking trail's initial ascent is generally acknowledged as unlogged old growth forest.

Wallface Mountain is a mountain located in Essex County, New York, United States. The mountain is named after the cliff on its southeastern side. Wallface is flanked to the west by MacNaughton Mountain, and faces Mount Marshall to the southeast across Indian Pass.

Cranberry Lake is a hamlet in the eastern part of the Town of Clifton, in St. Lawrence County, New York, United States. It lies along New York State Route 3 on the north shore of Cranberry Lake. The population was 200 at the 2010 census, which lists the community as a census-designated place.
Loon Lake Mountains are a pair of mountains, the tallest being 3,311-foot-tall (1,009 m), near Loon Lake in Franklin County, New York. On the summit is the Loon Lake Mountain Fire Observation Station, which was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2015.