
Plasmodium is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of Plasmodium species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect, continuing the life cycle.

Mabuya is a genus of long-tailed skinks restricted to species from various Caribbean islands. They are primarily carnivorous, though many are omnivorous. The genus is viviparous, having a highly evolved placenta that resembles that of eutherian mammals. Formerly, many Old World species were placed here, as Mabuya was a kind of "wastebasket taxon". These Old World species are now placed in the genera Chioninia, Eutropis, and Trachylepis. Under the older classification, the New World species were referred to as "American mabuyas", and now include the genera Alinea, Aspronema, Brasiliscincus, Capitellum, Maracaiba, Marisora, Varzea, and Copeoglossum.
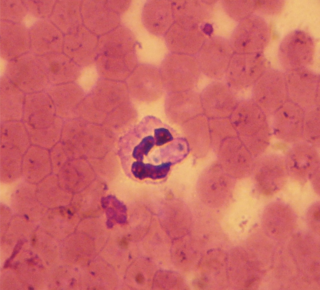
Hepatozoon is a genus of Apicomplexa alveolates which incorporates over 300 species obligate intraerythrocytic parasites. Species have been described from all groups of tetrapod vertebrates, as well as a wide range of haematophagous arthropods, which serve as both the vectors and definitive hosts of the parasite. By far the most biodiverse and prevalent of all haemogregarines, the genus is distinguished by its unique reciprocal trophic lifecycle which lacks the salivary transmission between hosts commonly associated with other apicomplexans. While particularly prevalent in amphibians and reptiles, the genus is more well known in veterinary circles for causing a tick-borne disease called hepatozoonosis in some mammals.
Plasmodium minasense is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Carinamoeba.
Plasmodium brumpti is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Sauramoeba. As in all Plasmodium species, P. brumpti has both vertebrate and insect hosts. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are reptiles.
Plasmodium diploglossi is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Sauramoeba. As in all Plasmodium species, P. diploglossi has both vertebrate and insect hosts. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are reptiles.

Leucocytozoon is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa.
Plasmodium basilisci is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Carinamoeba.
Plasmodium clelandi is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Carinamoeba.
Plasmodium uluguruense is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Lacertamoeba.
Plasmodium loveridgei is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Lacertamoeba.

Haemoproteus is a genus of alveolates that are parasitic in birds, reptiles and amphibians. Its name is derived from Greek: Haima, "blood", and Proteus, a sea god who had the power of assuming different shapes. The name Haemoproteus was first used in the description of Haemoproteus columbae in the blood of the pigeon Columba livia by Kruse in 1890. This was also the first description of this genus. Two other genera — Halteridium and Simondia — are now considered to be synonyms of Haemoproteus.
Plasmodium neusticuri is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium.
Plasmodium morulum is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium.

Eutropis is a genus of skinks belonging to the subfamily Mabuyinae. For long, this genus was included in the "wastebin taxon" Mabuya; it contains the Asian mabuyas. They often share their habitat with the related common skinks (Sphenomorphus), but they do not compete significantly as their ecological niches differ. This genus also contains the only member of the subfamily to occur in Australasia, the many-lined sun skink, whose wide range includes New Guinea.

The Noronha skink is a species of skink from the island of Fernando de Noronha off northeastern Brazil. It is covered with dark and light spots on the upperparts and is usually about 7 to 10 cm in length. The tail is long and muscular, but breaks off easily. Very common throughout Fernando de Noronha, it is an opportunistic feeder, eating both insects and plant material, including nectar from the Erythrina velutina tree, as well as other material ranging from cookie crumbs to eggs of its own species. Introduced predators such as feral cats prey on it and several parasitic worms infect it.
The Greater Martinique skink is a species of skink found on Martinique. It has shiny, bronze-colored skin, with a pair of light stripes that run along its upper flanks.
Nycteria is a genus of protozoan parasites that belong to the phylum Apicomplexa. It is composed of vector-borne haemosporidian parasites that infect a wide range of mammals such as primates, rodents and bats. Its vertebrate hosts are bats. First described by Garnham and Heisch in 1953, Nycteria is mostly found in bat species where it feeds off the blood of their hosts and causes disease. Within the host, Nycteria develops into peculiar lobulated schizonts in parenchyma cells of the liver, similarly to the stages of Plasmodium falciparum in the liver. The vector of Nycteria has been hard to acquire and identify. Because of this, the life cycle of Nycteria still remains unknown and understudied. It has been suggested that this vector could be an arthropod rather than a mosquito or the vector of most haemosporidian parasites.
Garnia is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexia.
Plasmodium mabuiae is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Carinamoeba.






