
Edmontonia is a genus of panoplosaurin nodosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period. It is part of the Nodosauridae, a family within Ankylosauria. It is named after the Edmonton Formation, the unit of rock where it was found.

Pinacosaurus is a genus of ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, mainly in Mongolia and China.

Gastonia is a genus of herbivorous ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of North America, around 139 to 134.6 million years ago. It is often considered a nodosaurid closely related to Polacanthus. Gastonia has a sacral shield and large shoulder spikes.

Ankylosauridae is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. These animals were mainly herbivorous and were obligate quadrupeds, with leaf-shaped teeth and robust, scute-covered bodies. Ankylosaurids possess a distinctly domed and short snout, wedge-shaped osteoderms on their skull, scutes along their torso, and a tail club.

Aletopelta is a monospecific genus of basal ankylosaurid dinosaur from Southern California that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Point Loma Formation. The type and only species, Aletopelta coombsi, is known from a partial skeleton preserving osteoderms. It was originally described in 1996 by W. P. Coombs, Jr. and T.A. Deméré before being named in 2001 by Tracy Ford and James Kirkland. Aletopelta has an estimated size of 5 metres and weight of 2 tonnes. The holotype formed a miniature reef and was scavenged upon by invertebrates and sharks.

Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous periods in what is now Asia, Europe, North America, and possibly South America. While traditionally regarded as a monophyletic clade as the sister taxon to the Ankylosauridae, some analyses recover it as a paraphyletic grade leading to the ankylosaurids.

Dyoplosaurus is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur from Alberta that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Dinosaur Park Formation. Dyoplosaurus represents a close relative of Scolosaurus and Anodontosaurus, two ankylosaurids known from the Horseshoe Canyon and Dinosaur Park Formation.
Shamosaurus is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from Early Cretaceous deposits of Höövör, Mongolia.
Stegosaurides is a genus of herbivorous thyreophoran dinosaur. It lived during the Cretaceous. Its fossils were found in the Xinminbao Group near Heishan in Gansu Province in China. These fossils consist of fragmentary material, including dermal spine elements. The genus is occasionally misspelled as "Stegosauroides".

Texasetes is a genus of ankylosaurian dinosaurs from the late Lower Cretaceous of North America. This poorly known genus has been recovered from the Paw Paw Formation near Haslet, Tarrant County, Texas, which has also produced the nodosaurid ankylosaur Pawpawsaurus.

Cedarpelta is an extinct genus of basal ankylosaurid dinosaur from Utah that lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now the Mussentuchit Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation. The type and only species, Cedarpelta bilbeyhallorum, is known from multiple specimens including partial skulls and postcranial material. It was named in 2001 by Kenneth Carpenter, James Kirkland, Don Burge, and John Bird. Cedarpelta has an estimated length of 7 metres and weight of 5 tonnes (11,023 lbs). The skull of Cedarpelta lacks extensive cranial ornamentation and is one of the only known ankylosaurs with individual skull bones that are not completely fused together.

Mymoorapelta is a nodosaurid ankylosaur from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation of western Colorado and central Utah, USA. The animal is known from a single species, Mymoorapelta maysi, and few specimens are known. The most complete specimen is the holotype individual from the Mygatt-Moore Quarry, which includes osteoderms, a partial skull, vertebrae, and other bones. It was initially described by James Kirkland and Kenneth Carpenter in 1994. Along with Gargoyleosaurus, it is one of the earliest known nodosaurids.

Talarurus is a genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about 96 million to 89 million years ago. The first remains of Talarurus were discovered in 1948 and later described by the Russian paleontologist Evgeny Maleev with the type species T. plicatospineus. It is known from multiple yet sparse specimens, making it one of the most well known ankylosaurines, along with Pinacosaurus. Elements from the specimens consists of various bones from the body; five skulls have been discovered and assigned to the genus, although the first two were very fragmented.
Heishansaurus, meaning "Heishan lizard" after the area in China where it was discovered, is the name given to a dubious genus of herbivorous ornithischian dinosaur, probably belonging to the Ankylosauridae.
Peishansaurus was a genus of ornithischian dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, roughly 85-72 million years ago.
Polacanthinae is a subfamily of ankylosaurs, most often nodosaurids, from the Late Jurassic through Early Cretaceous of Europe and potentially North America and Asia. The group is defined as the largest clade closer to Polacanthus foxii than Nodosaurus textilis or Ankylosaurus magniventris, as long as that group nests within either Nodosauridae or Ankylosauridae. If Polacanthus, and by extent Polacanthinae, falls outside either family-level clade, then the -inae suffix would be inappropriate, and the proper name for the group would be the informally defined Polacanthidae.

Ahshislepelta is a monospecific genus of ankylosaur dinosaur from New Mexico that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Hunter Wash Member of the Kirtland Formation. The type and only species, Ahshislepelta minor, is known only from an incomplete postcranial skeleton of a small subadult or adult individual. It was named in 2011 by Michael Burns and Robert M. Sullivan. Based on the size of the humerus, Ahshislepelta is larger than Pinacosaurus mephistocephalus but smaller than Talarurus and Pinacosaurus grangeri.
Dongyangopelta is an monospecific genus of nodosaurid dinosaur that lived in China during the Early to Late Cretaceous period in what is now the Chaochuan Formation. The type and only known species, Dongyangopelta yangyanensis, is known from a partial postcranial skeleton preserving osteoderms and ossified tendons. It was named in 2013 by Rongjun Chen, Wenjie Zheng, Yoichi Azuma, Masateru Shibata, Tianling Lou, Qiang Jin and Xinsheng Jin. Dongyangopelta represents one of the only nodosaurids known from Asia, along with Taohelong and Sauroplites.
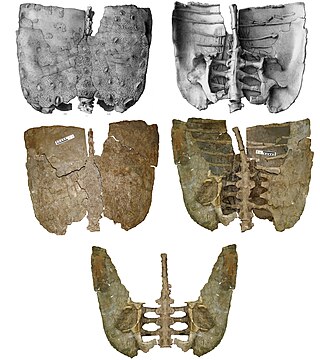
Europelta is a monospecific genus of nodosaurid dinosaur from Spain that lived during the Early Cretaceous in what is now the lower Escucha Formation of the Teruel Province. The type and only species, Europelta carbonensis, is known from two associated partial skeletons, and represents the most complete ankylosaur known from Europe. Europelta was named in 2013 by James I. Kirkland and colleagues. Europelta has an estimated length of 5 metres and weight of 1.3 tonnes, making it the largest member of the clade Struthiosaurini.
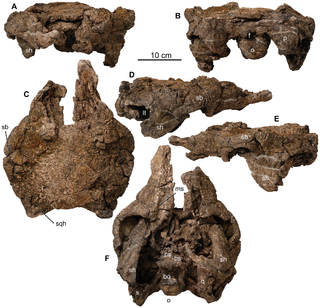
Zaraapelta is an extinct genus of herbivorous ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. The type species is Zaraapelta nomadis, named and described by Arbour et al in 2014. Zaraapelta is known from a single skull from the Barun Goyot Formation. It was found to be closest to Tarchia in the phylogenetic analysis within its description.














