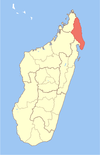
Antsiranana is a former province of Madagascar with an area of 43,406 km2. It had a population of 1,188,425. Its capital was Antsiranana. A diversity of ethnic groups are found in the province, including Anjoaty, Sakalava, Antakarana, Tsimihety, Antemoro, Betsimisaraka, Antandroy, etc.

Andapa is a town and commune in northern Madagascar. It belongs to the district of Andapa, which is a part of Sava Region. According to 2018 commune census the population of Andapa was 34,616.

Sambava is a city and commune at the east coast of northern Madagascar. It is the capital of Sambava District and Sava Region. The population of the commune was 84,039 in as of the 2018 commune census.

Diana is a region in Madagascar at the northern part of the island. It borders the regions of Sava to the southeast and Sofia to the southwest. It covers an area of 19,266 km2, and had a population of 889,736 in 2018. The regional capital is Antsiranana.

Marofinaritra is a rural municipality and village in northeast Madagascar. It belongs to the district of Antalaha, which is a part of Sava Region.

Ambohimalaza is a municipality in northern Madagascar. It belongs to the district of Sambava, which is a part of Sava Region. The population of the commune was estimated to be approximately 8,000 in 2001 commune census.

Analanjirofo is a region in northeastern Madagascar. Until 2009 it was a part of Toamasina Province. It borders Sava Region to the north, Sofia Region to the west, Alaotra-Mangoro Region to the southwest and Atsinanana Region to the south.

Daraina is a town and commune in northern Madagascar. It belongs to the district of Vohemar, which is a part of Sava Region. The city is located at the unpaved part of the Route Nationale 5a between Vohemar and Ambilobe.

Andapa District is a district in northern Madagascar. It is a part of Sava Region and borders the districts of Ambilobe and Sambava to the north, Antalaha to the east, Maroantsetra to the south, and Befandriana Nord and Bealanana to the west. The area is 4,051.48 km2 (1,564 sq mi) and the population was estimated to be 227,941 in 2020.

Antalaha District is a district in northeastern Madagascar. The district contains the Masoala Peninsula, and is limited by Antongil Bay in south-west and the Indian Ocean on east. It is a part of Sava Region and borders the districts of Sambava into the north, Andapa to the north-west and Maroantsetra to the west. The area is 6,795 km2 (2,624 sq mi) and the population was estimated to be 222,203 in 2009 and 282,921 in 2018. At the time of the last Madagascar census in 1993 149,684 inhabitants lived in this district.
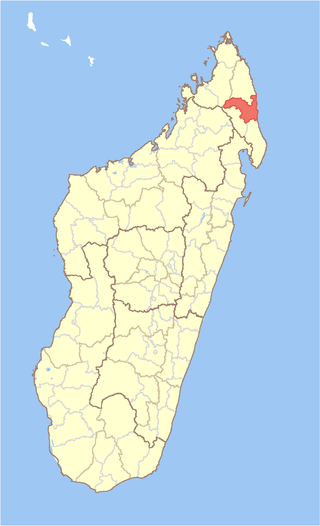
Sambava District is a district in northern Madagascar. It is a part of Sava Region and borders the districts of Antalaha to the south, Andapa to the south-west, Ambilobe to the north-west and Iharana to the north. The area is 4,681.76 km2 (1,808 sq mi) and the population was estimated to be 429,947 in 2020.

Vohemar District is a district in northern Madagascar. It is a part of Sava Region and borders the districts of Sambava to the south, Ambilobe to the west and Antsiranana II to the north. The area is 8,268.55 km2 (3,193 sq mi) and the population was estimated to be 264,236 in 2020. Its capitol is Vohemar.

Boeny is a region in northwestern Madagascar. It borders Sofia Region to the northeast, Betsiboka to the south and Melaky to the southwest. The capital of the region is Mahajanga, and the population was 931,171 in 2018. The area of Boeny is 31,046 km2 (11,987 sq mi).

Melaky is a region in northwestern Madagascar. It borders Boeny Region in northeast, Betsiboka in east, Bongolava in southeast and Menabe in south. The capital of the region is Maintirano. The population was estimated to be 309,805 in 2018 within the area of 38,852 km2 (15,001 sq mi). Melaky has the smallest population and the lowest population density of all Malagasy regions.

Atsinanana is a coastal region in eastern Madagascar. It borders Analanjirofo region in the north, Alaotra-Mangoro in the west, Vakinankaratra and Amoron'i Mania in the southwest, and Vatovavy in the south. The region contains over 285km of coastline, which includes many beaches and cultural heritage sites.

Haute Matsiatra is a region in Madagascar. It borders Amoron'i Mania region in north, Vatovavy-Fitovinany in east, Ihorombe in south and Atsimo-Andrefana in west. The capital of the region is Fianarantsoa, and the population was 1,447,296 in 2018. The area is 21,080 km2 (8,139 sq mi).

Marojejy National Park is a national park in the Sava region of northeastern Madagascar. It covers 55,500 ha (214 sq mi) and is centered on the Marojejy Massif, a mountain chain that rises to an elevation of 2,132 m (6,995 ft). Access to the area around the massif was restricted to research scientists when the site was set aside as a strict nature reserve in 1952. In 1998, it was opened to the public when it was converted into a national park. It became part of the World Heritage Site known as the Rainforests of the Atsinanana in 2007. "Unique in the world, a place of dense, jungly rainforests, sheer high cliffs, and plants and animals found nowhere else on earth", Marojejy National Park has received plaudits in the New York Times and Smithsonian Magazine for its natural beauty and rich biodiversity that encompasses critically endangered members of the silky sifaka. To that end, a global consortium of conservation organizations, including the Lemur Conservation Foundation, Duke Lemur Center and Madagascar National Parks, have sought to promote research and conservation programs in Marojejy National Park, neighboring Anjanaharibe-Sud Reserve and Antanetiambo Private Reserve, to protect the endemic flora and fauna that reside in northeastern Madagascar. In addition, these organizations have implemented a variety of community-based initiatives to mitigate human encroachment on the park, such as poaching and selective logging, by encouraging local communities to engage in afforestation and silvicultural initiatives to promote a sustainable alternative to mining, slash-and-burn agriculture, and wood collection.

Illegal logging has been a problem in Madagascar for decades and is perpetuated by extreme poverty and government corruption. Often taking the form of selective logging, the trade has been driven by high international demand for expensive, fine-grained lumber such as rosewood and ebony. Historically, logging and exporting in Madagascar have been regulated by the Malagasy government, although the logging of rare hardwoods was explicitly banned from protected areas in 2000. Since then, government orders and memos have intermittently alternated between permitting and banning exports of precious woods. The most commonly cited reason for permitting exports is to salvage valuable wood from cyclone damage, although this reasoning has come under heavy scrutiny. This oscillating availability of Malagasy rosewood and other precious woods has created a market of rising and falling prices, allowing traders or "timber barons" to stockpile illegally sourced logs during periodic bans and then flood the market when the trade windows open and prices are high. Over 350,000 trees were illegally felled in Madagascar between 2010 and 2015, according to TRAFFIC.

Route nationale 5a is a secondary highway in Madagascar of 406 km, running from Ambilobe to Antalaha. It crosses the regions of Diana and Sava.

Loky-Manambato is a protected area near Daraina in northern Madagascar, in the northern part of the Vohemar District. It is located in northern Sava Region, bounded on the north by the Loky River, on the south by the Manambato River, and on the east by the Indian Ocean. In its center flows the Manankolana river.