Related Research Articles

Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer.

Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares. Complications may include abnormal dilation of the colon (megacolon), inflammation of the eye, joints, or liver, and colon cancer.

Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and the rectum.

Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine (colon). Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. It broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases.
Proctitis is an inflammation of the anus and the lining of the rectum, affecting only the last 6 inches of the rectum.
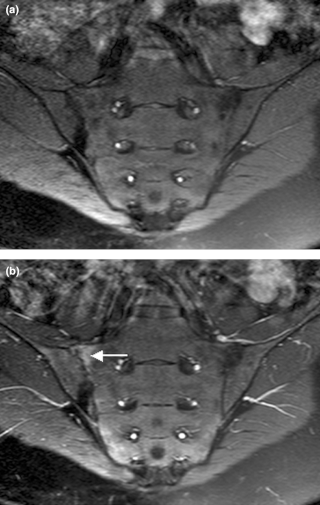
Sacroiliitis is inflammation within the sacroiliac joint. It is a feature of spondyloarthropathies, such as axial spondyloarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis or arthritis related to inflammatory bowel diseases, including ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. It is also the most common presentation of arthritis from brucellosis.

Blood in stool or rectal bleeding looks different depending on how early it enters the digestive tract—and thus how much digestive action it has been exposed to—and how much there is. The term can refer either to melena, with a black appearance, typically originating from upper gastrointestinal bleeding; or to hematochezia, with a red color, typically originating from lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Evaluation of the blood found in stool depends on its characteristics, in terms of color, quantity and other features, which can point to its source, however, more serious conditions can present with a mixed picture, or with the form of bleeding that is found in another section of the tract. The term "blood in stool" is usually only used to describe visible blood, and not fecal occult blood, which is found only after physical examination and chemical laboratory testing.
Pouchitis is an umbrella term for inflammation of the ileal pouch, an artificial rectum surgically created out of ileum in patients who have undergone a proctocolectomy or total colectomy. The ileal pouch-anal anastomosis is created in the management of patients with ulcerative colitis, indeterminate colitis, familial adenomatous polyposis, cancer, or rarely, other colitides.

Microscopic colitis refers to two related medical conditions which cause diarrhea: collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis. Both conditions are characterized by the presence of chronic non-bloody watery diarrhea, normal appearances on colonoscopy and characteristic histopathology findings of inflammatory cells.
Lower gastrointestinal bleeding, commonly abbreviated LGIB, is any form of gastrointestinal bleeding in the lower gastrointestinal tract. LGIB is a common reason for seeking medical attention at a hospital's emergency department. LGIB accounts for 30–40% of all gastrointestinal bleeding and is less common than upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB). It is estimated that UGIB accounts for 100–200 per 100,000 cases versus 20–27 per 100,000 cases for LGIB. Approximately 85% of lower gastrointestinal bleeding involves the colon, 10% are from bleeds that are actually upper gastrointestinal bleeds, and 3–5% involve the small intestine.

Abdominal distension occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate in the abdomen causing its expansion. It is typically a symptom of an underlying disease or dysfunction in the body, rather than an illness in its own right. People with this condition often describe it as "feeling bloated". Affected people often experience a sensation of fullness, abdominal pressure, and sometimes nausea, pain, or cramping. In the most extreme cases, upward pressure on the diaphragm and lungs can also cause shortness of breath. Through a variety of causes, bloating is most commonly due to buildup of gas in the stomach, small intestine, or colon. The pressure sensation is often relieved, or at least lessened, by belching or flatulence. Medications that settle gas in the stomach and intestines are also commonly used to treat the discomfort and lessen the abdominal distension.

Ischemic colitis is a medical condition in which inflammation and injury of the large intestine result from inadequate blood supply. Although uncommon in the general population, ischemic colitis occurs with greater frequency in the elderly, and is the most common form of bowel ischemia. Causes of the reduced blood flow can include changes in the systemic circulation or local factors such as constriction of blood vessels or a blood clot. In most cases, no specific cause can be identified.

In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the descending colon is the part of the colon extending from the left colic flexure to the level of the iliac crest. The function of the descending colon in the digestive system is to store the remains of digested food that will be emptied into the rectum.
Management of ulcerative colitis involves first treating the acute symptoms of the disease, then maintaining remission. Ulcerative colitis is a form of colitis, a disease of the intestine, specifically the large intestine or colon, that includes characteristic ulcers, or open sores, in the colon. The main symptom of active disease is usually diarrhea mixed with blood, of gradual onset which often leads to anaemia. Ulcerative colitis is, however, a systemic disease that affects many parts of the body outside the intestine.

Biological therapy, the use of medications called biopharmaceuticals or biologics that are tailored to specifically target an immune or genetic mediator of disease, plays a major role in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Even for diseases of unknown cause, molecules that are involved in the disease process have been identified, and can be targeted for biological therapy. Many of these molecules, which are mainly cytokines, are directly involved in the immune system. Biological therapy has found a niche in the management of cancer, autoimmune diseases, and diseases of unknown cause that result in symptoms due to immune related mechanisms.
The Crohn's Disease Activity Index or CDAI is a research tool used to quantify the symptoms of patients with Crohn's disease. This is of useful importance in research studies done on medications used to treat Crohn's disease; most major studies on newer medications use the CDAI in order to define response or remission of disease. As Crohn's disease is a disease with a variety of symptoms that affect quality of life, the quantification of symptoms may be of secondary importance to a quantitative assessment of the effect on quality of life. This has been addressed by the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (IBDQ) and other indices of quality of life for patients with Crohn's disease.
Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies (ASCAs) are antibodies against antigens presented by the cell wall of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. These antibodies are directed against oligomannose sequences α-1,3 Man n. ASCAs and perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (pANCAs) are the two most useful and often discriminating biomarkers for colitis. ASCA tends to recognize Crohn's disease more frequently, whereas pANCA tend to recognize ulcerative colitis.
Vedolizumab, sold under the brand name Entyvio, is a monoclonal antibody medication developed by Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It binds to integrin α4β7. Blocking the α4β7 integrin results in gut-selective anti-inflammatory activity.

Alicaforsen is an antisense oligonucleotide therapeutic that targets the messenger RNA for the production of human ICAM-1 receptor and is being developed for the treatment of acute disease flares in moderate to severe Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
References
- ↑ Walmsley, R S; Ayres, R C S; Pounder, R E; Allan, R N (1998). "A simple clinical colitis activity index". Gut. 43 (1): 29–32. doi:10.1136/gut.43.1.29. ISSN 0017-5749. PMC 1727189 . PMID 9771402.
- ↑ Mardini, Houssam E.; Grigorian, Alla Y. (2014). "Probiotic Mix VSL#3 Is Effective Adjunctive Therapy for Mild to Moderately Active Ulcerative Colitis". Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 20 (9): 1562–1567. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000084 . ISSN 1078-0998. PMID 24918321. S2CID 36218602; Access provided by the University of Pittsburgh
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)