This article needs additional citations for verification .(April 2022) |
| Misls of the Sikh Confederacy |
|---|
 |
The Singh Krora Misl, also known as the Karorsinghia Misl or Panjgarhia Misl, was one of the twelve misls of the Sikh Confederacy. [1]
This article needs additional citations for verification .(April 2022) |
| Misls of the Sikh Confederacy |
|---|
 |
The Singh Krora Misl, also known as the Karorsinghia Misl or Panjgarhia Misl, was one of the twelve misls of the Sikh Confederacy. [1]
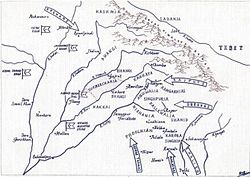
The misl was founded by Jats. [2] Sardar Karora Singh, resident of Barki (district Lahore) was the first chief of this Misl; earlier, Karora Singh was the deputy of the jatha led by Sardar Sham Singh of village Narli (district Lahore); after the death of Sham Singh in 1739, Sardar Karam Singh (of village Pechgarh) became the chief of this Jatha; he too died in the early days of 1748 and Karora Singh became the chief of the Jatha. [3]
In March 1748, when the Misls were formed, his jatha became a Misl; then this jatha came to be known as Karorsinghia Misl. Karora Singh had the command of 7-8 thousand horsemen; his first possessions were Hariana and Sham Churasi (in Hoshiarpur district); Karora Singh died in the Battle of Taravari in 1761.
Karora Singh was succeeded by Baghel Singh of Jhabal (district Amritsar); Baghel Singh was fond of adventures; he left the Majha area and launched his actions in Karnal, Saharanpur and other areas of Gang-Doab; he was one of those five generals who unfurled blue Khalsa flag on Red Fort at Delhi on 11 March 1783.
Baghel Singh died in 1802 without an heir. Jodh Singh and Sukhu Singh each claimed to be the chief of this Misl. During this interregnum, Baghel Singh's two widows, Ram Kaur and Rattan Kaur, ruled this Misl. [4]
The misl originated form Narli and Barki near Lahore and also Jhabal near Amritsar. [2] The Karorsinghias held territory in southeastern Malwa and the Upper Gangetic Doab. [2] The Karorsinghia Misl controlled areas held eastward from the Sutlej river and also Chhachhrauli (which later formed into Kalsia State). [5]
| No. | Name (Birth–Death) | Portrait | Reign | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sham Singh (died 1739) |  | ? – 1739 | [4] [2] | |
| 2 | Karam Singh | ? | ? | [4] [2] | |
| 3 | Karora Singh (died 1761) | ? | ? – 1761 | [4] [2] | |
| 4 | Baghel Singh (died 1802) |  | 1761 – 1802 | [4] [2] | |
| 5 (disputed) | Jodh Singh (born 1751) | Sukhu Singh | ? | 1802 – ? | [4] |