| Small nucleolar RNA SNORA41 | |
|---|---|
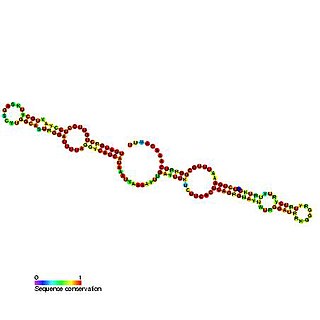
 Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of SNORA41 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SNORA41 |
| Alt. Symbols | snoACA41 |
| Rfam | RF00403 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; snRNA; snoRNA; H/ACA-box |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota |
| GO | 0006396 0005730 |
| SO | 0000594 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
In molecular biology, SNORA41 (also known as ACA41) is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines. [1]

Molecular biology is a branch of biology that concerns the molecular basis of biological activity between biomolecules in the various systems of a cell, including the interactions between DNA, RNA, proteins and their biosynthesis, as well as the regulation of these interactions. Writing in Nature in 1961, William Astbury described molecular biology as:
...not so much a technique as an approach, an approach from the viewpoint of the so-called basic sciences with the leading idea of searching below the large-scale manifestations of classical biology for the corresponding molecular plan. It is concerned particularly with the forms of biological molecules and [...] is predominantly three-dimensional and structural – which does not mean, however, that it is merely a refinement of morphology. It must at the same time inquire into genesis and function.
Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs. There are two main classes of snoRNA, the C/D box snoRNAs, which are associated with methylation, and the H/ACA box snoRNAs, which are associated with pseudouridylation. SnoRNAs are commonly referred to as guide RNAs but should not be confused with the guide RNAs that direct RNA editing in trypanosomes.
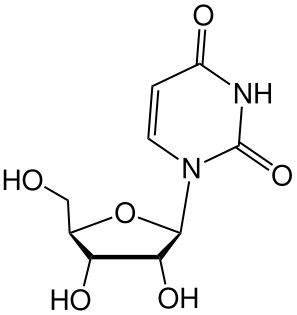
Uridine is a glycosylated pyrimidine-analog containing uracil attached to a ribose ring (or more specifically, a ribofuranose) via a β-N1-glycosidic bond.
The family also includes the mouse sequence MBI-83. [2]

A mouse, plural mice, is a small rodent characteristically having a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse. It is also a popular pet. In some places, certain kinds of field mice are locally common. They are known to invade homes for food and shelter.