
In molecular biology, SNORD115 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule known as a small nucleolar RNA which usually functions in guiding the modification of other non-coding RNAs. This type of modifying RNA is usually located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. HBII-52 refers to the human gene, whereas RBII-52 is used for the rat gene and MBII-52 is used for naming the mouse gene.
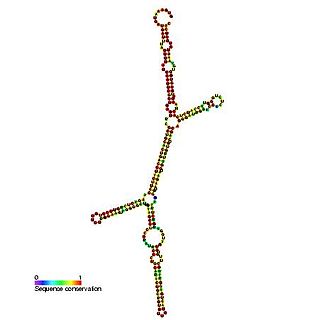
In molecular biology, SNORD17 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, SNORD19 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, snoRNA U42 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the modification of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is usually located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.
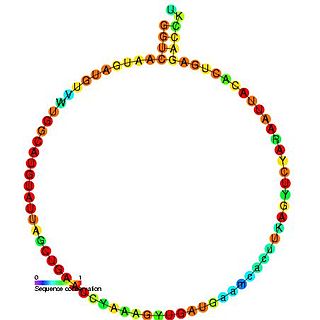
In molecular biology, snoRNA U45 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the modification of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is usually located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, SNORD64 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.
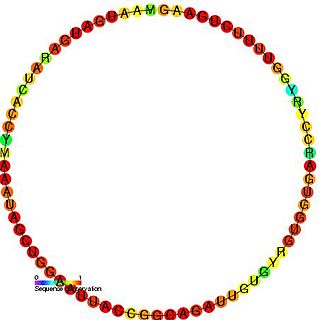
In molecular biology, SNORD65 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA. SNORD19 belongs to the C/D box class of snoRNAs which contain the conserved sequence motifs known as the C box (UGAUGA) and the D box (CUGA). Most of the members of the box C/D family function in directing site-specific 2'-O-methylation of substrate RNAs.

In molecular biology, SNORD66 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the modification of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is usually located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, SNORD67 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.
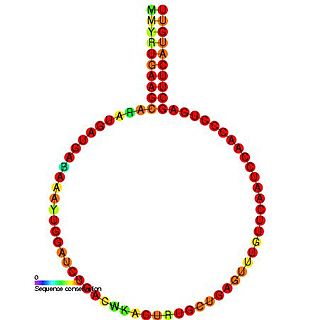
In molecular biology, snoRNA HBII-210 belongs to the C/D family of snoRNAs. It is the human orthologue of the mouse MBII-210 and is predicted to guide the 2'O-ribose methylation of large 28S rRNA on residue G4464.

In molecular biology, snoRNA SNORD70 (HBII-234) is a non-coding RNA that belongs to the C/D family of snoRNAs. It is the human orthologue of the mouse MBII-234 and is predicted to guide 2'O-ribose methylation of the small 18S rRNA on position A512. It is hosted, together with HBII-95, by the core C/D box snoRNA protein encoding gene NOP5/NOP58.
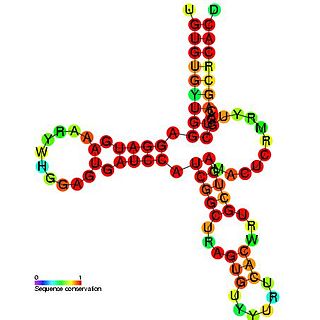
In molecular biology, snoRNA HBII-239 belongs to the family of C/D snoRNAs. It is the human orthologue of the mouse MBII-239 described and is predicted to guide 2'O-ribose methylation of 5.8S rRNA on residue U14.
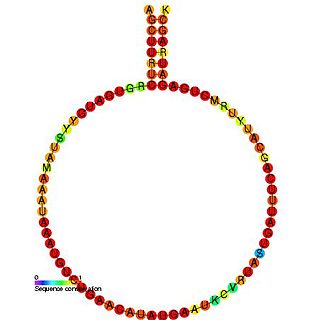
In molecular biology, SNORD72 belongs to the C/D family of snoRNAs. It is the human orthologue of the mouse MBII-240 and is predicted to guide 2'O-ribose methylation of the large 28S rRNA at residue U4590.
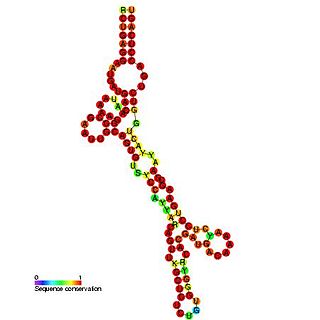
In molecular biology, snoRNA HBII-289 belongs to the family of C/D snoRNAs. It is the human orthologue of the mouse MBII-289 and has no identified RNA target.
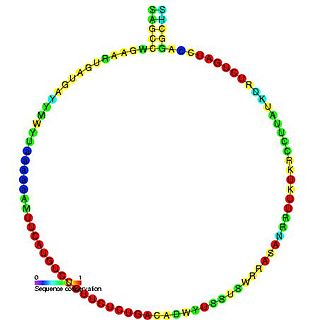
In molecular biology, Small Nucleolar RNA SNORD111 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, Small Nucleolar RNA SNORD93 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule that functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the Eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and is also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, Small Nucleolar RNA SNORD23 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, Small Nucleolar RNA SNORD88 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, Small Nucleolar RNA SNORD92 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.
In molecular biology, Small nucleolar RNA SNORD113 is a small nucleolar RNA molecule which is located in the imprinted human 14q32 locus and may play a role in the evolution and/or mechanism of the epigenetic imprinting process.




















