In molecular biology, SNORA1 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, SNORA13 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, SNORA14 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, SNORA18 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, SNORA20 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, SNORA22 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, SNORA24 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.
In molecular biology, SNORA25 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.
In molecular biology, SNORA26 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, SNORA33 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, SNORA38 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.
In molecular biology, SNORA42 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.
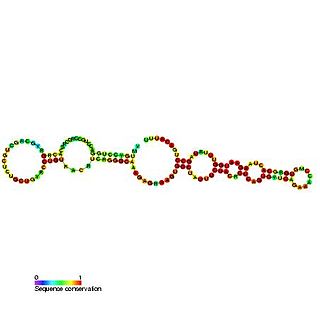
In molecular biology, Small nucleolar RNA SNORA43 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a 'guide RNA'.
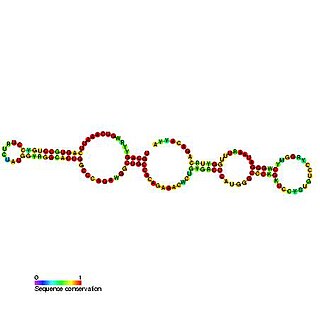
In molecular biology, SNORA5 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, Small nucleolar RNA SNORA50 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a 'guide RNA'. ACA50 was originally cloned from HeLa cells and belongs to the H/ACA box class of snoRNAs as it has the predicted hairpin-hinge-hairpin-tail structure, has the conserved H/ACA-box motifs and is found associated with GAR1 protein. snoRNA ACA50 is predicted to guide the pseudouridylation of U34 and U105 of 18S ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Pseudouridylation is the to the different isomeric form pseudouridine.
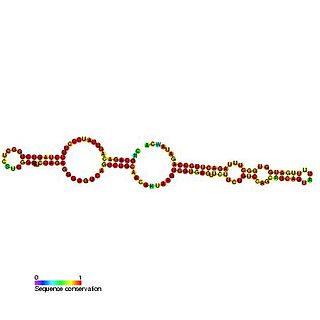
In molecular biology, Small nucleolar RNA SNORA56 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a 'guide RNA'. ACA56 was originally cloned from HeLa cells and belongs to the H/ACA box class of snoRNAs as it has the predicted hairpin-hinge-hairpin-tail structure, has the conserved H/ACA-box motifs and is found associated with GAR1 protein. snoRNA ACA56 is predicted to guide the pseudouridylation of U1664 of 28S ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Pseudouridylation is the to the different isomeric form pseudouridine.
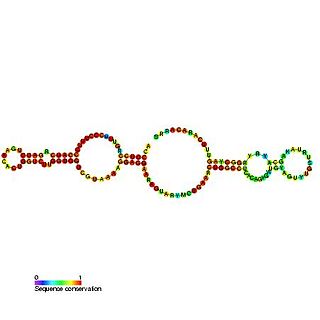
In molecular biology, Small nucleolar RNA SNORA61 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a 'guide RNA'. ACA61 was originally cloned from HeLa cells and belongs to the H/ACA box class of snoRNAs as it has the predicted hairpin-hinge-hairpin-tail structure, has the conserved H/ACA-box motifs and is found associated with GAR1 protein. snoRNA ACA61 is predicted to guide the pseudouridylation of U2495 of 28S ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Pseudouridylation is the to the different isomeric form pseudouridine.

In molecular biology, SNORA8 is a member of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA that guide the sites of modification of uridines to pseudouridines.

In molecular biology, small nucleolar RNA SNORA10 and small nuclear RNA SNORA64 are homologous members of the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA). This family of ncRNAs involved in the maturation of ribosomal RNA. snoRNA in this family act as guides in the modification of uridines to pseudouridines. This family includes the human snoRNAs U64 and ACA10 and mouse MBI-29.

In molecular biology, Small nucleolar RNA SNORA77 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA).




















