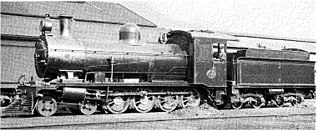
Type ZC tender (5½ LT) on CGR 7th Class of 1902 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The South African type ZC tender was a steam locomotive tender from the pre-Union era in the Cape of Good Hope.

The Union of South Africa is the historical predecessor to the present-day Republic of South Africa. It came into being on 31 May 1910 with the unification of the Cape Colony, the Natal Colony, the Transvaal, and the Orange River Colony. It included the territories that were formerly a part of the South African Republic and the Orange Free State.

The Cape of Good Hope, also known as the Cape Colony, was a British colony in present-day South Africa, named after the Cape of Good Hope. The British colony was preceded by an earlier Dutch colony of the same name, the Kaap de Goede Hoop, established in 1652 by the Dutch East India Company. The Cape was under Dutch rule from 1652 to 1795 and again from 1803 to 1806. The Dutch lost the colony to Great Britain following the 1795 Battle of Muizenberg, but had it returned following the 1802 Peace of Amiens. It was re-occupied by the UK following the Battle of Blaauwberg in 1806, and British possession affirmed with the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814.
Contents
- Manufacturers
- Characteristics
- Locomotives
- Classification letters
- Modifications and rebuilding
- Modifications
- Rebuilding to Type ZE
- Illustration
- References
The Type ZC tender first entered service in 1896, as tenders to the second version of the 7th Class4-8-0 Mastodon type steam locomotive to be acquired by the Cape Government Railways. These locomotives were designated Class 7A on the South African Railways in 1912. [1] [2] [3]

The Cape Government Railways (CGR) was the government-owned railway operator in the Cape Colony from 1874 until the creation of the South African Railways (SAR) in 1910.

The South African Railways Class 7A 4-8-0 of 1896 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Cape of Good Hope.