
Infrared is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light and shorter than radio waves. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). IR is commonly divided between longer wavelength thermal infrared that is emitted from terrestrial sources and shorter wavelength near-infrared that is part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon.

Forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras, typically used on military and civilian aircraft, use a thermographic camera that senses infrared radiation.

Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night vision compared to many animals such as cats, foxes and rabbits, in part because the human eye lacks a tapetum lucidum, tissue behind the retina that reflects light back through the retina thus increasing the light available to the photoreceptors.

A thermographic camera is a device that creates an image using infrared (IR) radiation, similar to a normal camera that forms an image using visible light. Instead of the 400–700 nanometre (nm) range of the visible light camera, infrared cameras are sensitive to wavelengths from about 1,000 nm to about 14,000 nm (14 μm). The practice of capturing and analyzing the data they provide is called thermography.
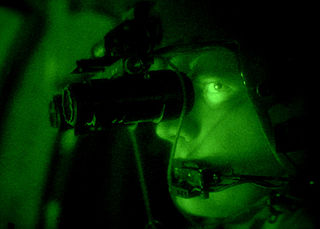
A night-vision device (NVD), also known as a night optical/observation device (NOD), night-vision goggle (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows visualization of images in low levels of light, improving the user's night vision. The device enhances ambient visible light and converts near-infrared light into visible light which can be seen by the user; this is known as I2 (image intensification). By comparison, viewing of infrared thermal radiation is referred to as thermal imaging and operates in a different section of the infrared spectrum. A night vision device usually consists of an image intensifier tube, a protective housing, and may have some type of mounting system. Many NVDs also include a protective sacrificial lens, mounted over the front lens (ie. objective lens) on NVDs to protect the latter from damage by environmental hazards and some can incorporate telescopic lenses. The image produced by an NVD is typically monochrome green, as green was considered to be the easiest color to look at for prolonged periods in the dark. Night vision devices may be passive, relying solely on ambient light, or may be active, using an IR (infrared) illuminator to better visualize the environment.

Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgrounds; humans and other warm-blooded animals become easily visible against the environment, day or night. As a result, thermography is particularly useful to the military and other users of surveillance cameras.

A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in a narrow beam towards the object and measuring the time taken by the pulse to be reflected off the target and returned to the sender. Due to the high speed of light, this technique is not appropriate for high precision sub-millimeter measurements, where triangulation and other techniques are often used. It is a type of scannerless lidar.
A thermal imaging camera is a type of the thermographic camera used in firefighting. By rendering infrared radiation as visible light, such cameras allow firefighters to see areas of heat through smoke, darkness, or heat-permeable barriers. Thermal imaging cameras are typically handheld, but may be helmet-mounted. They are constructed using heat- and water-resistant housings, and ruggedized to withstand the hazards of fireground operations.

Teledyne FLIR LLC, formerly FLIR Systems Inc,, a subsidiary of Teledyne Technologies, specializes in the design and production of thermal imaging cameras and sensors. Its main customers are governments and in 2020, approximately 31% of its revenues were from the federal government of the United States and its agencies.

The AN/PVS-14 Monocular Night Vision Device (MNVD) is in widespread use by the United States Armed Forces as well as NATO allies around the world. It uses a third generation image intensifier tube, and is primarily manufactured by Litton Industries and Elbit Systems of America. It is often used 'hands free' using a head harness or attached to a combat helmet such as the PASGT, MICH TC-2000 Combat Helmet, Advanced Combat Helmet, Marine Lightweight Helmet or IHPS. It can also be used as a weapons night sight. In addition, it was part of the equipment fielded in the U.S. Army's Land Warrior program. Morovision Night Vision was the law enforcement distributor of the NEPVS-14 for ITT.
Thermographic inspection refers to the nondestructive testing (NDT) of parts, materials or systems through the imaging of the temperature fields, gradients and/or patterns ("thermograms") at the object's surface. It is distinguished from medical thermography by the subjects being examined: thermographic inspection generally examines inanimate objects, while medical thermography generally examines living organisms. Generally, thermographic inspection is performed using an infrared sensor.
Infrared vision is the capability of biological or artificial systems to detect infrared radiation. The terms thermal vision and thermal imaging, are also commonly used in this context since infrared emissions from a body are directly related to their temperature: hotter objects emit more energy in the infrared spectrum than colder ones.
F-INSAS is India's programme to equip its infantry with state-of-the-art equipment, F-INSAS standing for Future Infantry Soldier As a System. However the Indian Army has decided to drop the F-INSAS program in favour of two separate projects. The new program will have two components: one to arm the future infantry soldier with the best available assault rifle, carbines and personal equipment, such as helmets and bulletproof vests. The second component is the Battlefield Management Systems (BMS).

A helmet-mounted display (HMD) is a headworn device that uses displays and optics to project imagery and/or symbology to the eyes. It provides visual information to the user where head protection is required—-most notably in military aircraft. The display-optics assembly can be attached to a helmet or integrated into the design of the helmet. An HMD provides the pilot with situation awareness, an enhanced image of the scene, and in military applications cue weapons systems, to the direction their head is pointing. Applications which allow cuing of weapon systems are referred to as helmet-mounted sight and display (HMSD) or helmet-mounted sights (HMS).

An automotive night vision system uses a thermographic camera to increase a driver's perception and seeing distance in darkness or poor weather beyond the reach of the vehicle's headlights. Such systems are offered as optional equipment on certain premium vehicles. The technology was first introduced in the year 2000 on the Cadillac Deville. This technology is based on the night vision devices (NVD), which generally denotes any electronically enhanced optical devices operate in three modes: image enhancement, thermal imaging, and active illumination. The automotive night vision system is a combination of NVDs such as infrared cameras, GPS, Lidar, and Radar, among others to sense and detect objects.

The AN/PSQ-20 Enhanced Night Vision Goggle (ENVG) is a third-generation passive monocular night vision device developed for the United States Armed Forces by ITT Exelis. It fuses image-intensifying and thermal-imaging technologies, enabling vision in conditions with very little light. The two methods can be used simultaneously or individually. The ENVG was selected by the US Army's Program Executive Office Soldier as a supporting device for the Future Force Warrior program in 2004, and is intended to replace the older AN/PVS-7 and AN/PVS-14 systems. Although more expensive and heavier than previous models, US Special Forces began using the goggles in 2008 and the US Army's 10th Mountain Division began fielding the AN/PSQ-20 in 2009. Improvements to the goggles have been attempted to make them lighter, as well as enabling the transmission of digital images to and from the battlefield.
This is a list of infrared topics.

Adaptiv is an active camouflage technology developed by BAE Systems AB to protect military vehicles from detection by far infrared night vision devices, providing infrared stealth. It consists of an array of hexagonal Peltier plates which can be rapidly heated and cooled to form any desired image, such as of the natural background or of a non-target object. Its goal is to develop stealth ground vehicles.

Ratnik is a Russian future infantry combat system. Some components, including the communication systems and night vision technologies, have extremely limited military distribution. It is designed to improve the connectivity and combat effectiveness of combat personnel in the Russian Armed Forces. Improvements include modernised body armour, a helmet with a special eye monitor, communication systems, and special headphones. It includes 10 subsystems and 59 individual items.

The AN/PSQ-42 Enhanced Night Vision Goggle-Binocular (ENVG-B) is a third-generation passive binocular night vision device developed for the United States Army by L3Harris. It combines dual tube image-intensifying (I²) and thermal-imaging technologies into a single goggle, enabling vision in low-light conditions. The two methods can be used individually or simultaneously in a fused mode. The ENVG-B is intended to be issued to the dismounted combat arms soldiers within the Army's Brigade combat teams (BCT), and so far over 10,000 have been issued to several BCT's within the 1st Infantry Division, 2nd Infantry Division, 25th Infantry Division, 82nd Airborne Division and 101st Airborne Division. The US Marine Corps has also purchased 3,100 ENVG-B units.















