This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2022) |
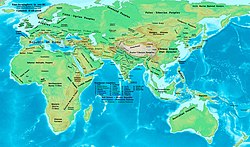
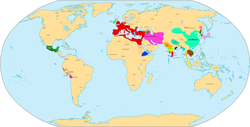
This timeline of ancient history lists historical events of the documented ancient past from the beginning of recorded history until the Early Middle Ages. Prior to this time period, prehistory civilizations were pre-literate and did not have written language.
Contents
- Early history
- Classical antiquity
- End of ancient history in Europe
- Horizontal timeline
- Maps
- See also
- References
- Citations and notes
(Common Era years in astronomical year numbering) |
 |
Millennia: 4th millennium BC – 3rd millennium BC – 2nd millennium BC – 1st millennium BC – 1st millennium
Centuries: 34th BC – 33rd BC – 32nd BC – 31st BC – 30th BC – 29th BC – 28th BC – 27th BC – 26th BC – 25th BC – 24th BC – 23rd BC – 22nd BC – 21st BC – 20th BC – 19th BC – 18th BC – 17th BC – 16th BC – 15th BC – 14th BC – 13th BC – 12th BC – 11th BC – 10th BC – 9th BC – 8th BC – 7th BC – 6th BC – 5th BC – 4th BC – 3rd BC – 2nd BC – 1st BC – 1st AD – 2nd AD – 3rd AD – 4th AD — 5th AD