
A wargame is a strategy game in which two or more players command opposing armed forces in a simulation of an armed conflict. Wargaming may be played for recreation, to train military officers in the art of strategic thinking, or to study the nature of potential conflicts. Many wargames re-create specific historic battles, and can cover either whole wars, or any campaigns, battles, or lower-level engagements within them. Many simulate land combat, but there are wargames for naval, air combat, and cyber as well as many that combine various domains.

A strategy game or strategic game is a game in which the players' uncoerced, and often autonomous, decision-making skills have a high significance in determining the outcome. Almost all strategy games require internal decision tree-style thinking, and typically very high situational awareness.
Real-time strategy (RTS) is a subgenre of strategy video games that does not progress incrementally in turns, but allow all players to play simultaneously, in "real time". By contrast, in turn-based strategy (TBS) games, players take turns to play. The term "real-time strategy" was coined by Brett Sperry to market Dune II in the early 1990s.

A role-playing video game, a role-playing game (RPG) or computer role-playing game (CRPG), is a video game genre where the player controls the actions of a character immersed in some well-defined world, usually involving some form of character development by way of recording statistics. Many role-playing video games have origins in tabletop role-playing games and use much of the same terminology, settings, and game mechanics. Other major similarities with pen-and-paper games include developed story-telling and narrative elements, player character development, complexity, as well as replay value and immersion. The electronic medium removes the necessity for a gamemaster and increases combat resolution speed. RPGs have evolved from simple text-based console-window games into visually rich 3D experiences.

4X is a subgenre of strategy-based computer and board games, and includes both turn-based and real-time strategy titles. The gameplay generally involves building an empire. Emphasis is placed upon economic and technological development, as well as a range of military and non-military routes to supremacy.
Micromanagement in gaming is the handling of detailed gameplay elements by the player. It appears in a wide range of games and genres, including strategy video games, construction and management simulations, and pet-raising simulations. Micromanagement has been perceived in different ways by game designers and players for many years: some perceive it as a useful addition to games that adds options and technique to the gameplay, something that is necessary if the game is to support top-level competitions; some enjoy opportunities to use tactical skill in strategic games; others regard it as an unwelcome distraction from higher levels of strategic thinking and dislike having to do a lot of detailed work. Some developers attempt to minimize micromanagement in a game's interface for this reason.
Tactical role-playing games, also known as strategy role-playing games and in Japan as simulation RPGs, are a video game genre that combines core elements of role-playing video games with those of tactical strategy video games. The formats of tactical RPGs are much like traditional tabletop role-playing games and strategy games in appearance, pacing, and rule structure. Likewise, early tabletop role-playing games are descended from skirmish wargames such as Chainmail, which were primarily concerned with combat.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to video games:
A war game is a type of strategy game that simulates warfare realistically.
Turn-based tactics (TBT) is a video game genre of strategy video games. They are turn-based simulations of operational warfare and military tactics in generally small-scale confrontations as opposed to more strategic considerations of turn-based strategy (TBS) games. Turn-based tactical gameplay is characterized by the expectation of players to complete their tasks using only the combat forces provided to them in a generally realistic manner.
Real-time tactics (RTT) is a subgenre of tactical wargames played in real-time, simulating the considerations and circumstances of operational warfare and military tactics. It is differentiated from real-time strategy gameplay by the lack of classic resource micromanagement and base or unit building, as well as the greater importance of individual units and a focus on complex battlefield tactics.

A tile-based video game, or grid-based video game, is a type of video game where the playing area consists of small square graphic images referred to as tiles laid out in a grid. That the screen is made of such tiles is a technical distinction, and may not be obvious to people playing the game. The complete set of tiles available for use in a playing area is called a tileset. Tile-based games usually simulate a top-down, side view, or 2.5D view of the playing area, and are almost always two-dimensional.

A grand strategy wargame or simply grand strategy game (GSG) is a wargame that places focus on grand strategy: military strategy at the level of movement and use of a nation state or empire's resources. The genre has considerable overlap with 4X games, but differs in being "asymmetrical", meaning that players are more bound to a specific setup and not among equally free factions in exploring and progressing the game and an open world.
In video games and other games, the passage of time must be handled in a way that players find fair and easy to understand. This is usually done in one of the two ways: real-time and turn-based.
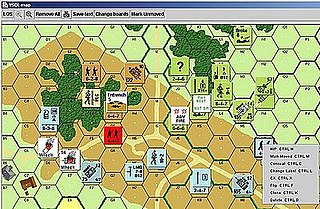
A computer wargame is a wargame played on a digital device. Descended from board wargaming, it simulates military conflict at the tactical, operational or strategic level. Computer wargames are both sold commercially for recreational use and, in some cases, used for military purposes.
Strategy is a major video game genre that emphasizes thinking and planning over direct instant action in order to achieve victory. Although many types of video games can contain strategic elements, as a genre, strategy games are most commonly defined as those with a primary focus on high-level strategy, logistics and resource management. They are also usually divided into two main sub-categories: turn-based and real-time, but there are also many strategy cross/sub-genres that feature additional elements such as tactics, diplomacy, economics and exploration.

A board wargame is a wargame with a set playing surface or board, as opposed to being played on a computer or in a more free-form playing area as in miniatures games. The modern, commercial wargaming hobby developed in 1954 following the publication and commercial success of Tactics. The board wargaming hobby continues to enjoy a sizeable following, with a number of game publishers and gaming conventions dedicated to the hobby both in the English-speaking world and further afield.

A game is a structured type of play, usually undertaken for entertainment or fun, and sometimes used as an educational tool. Many games are also considered to be work or art.

The Great Battles of Alexander is a 1997 turn-based computer wargame developed by Erudite Software and published by Interactive Magic. Adapted from the GMT Games physical wargame of the same name, it depicts 10 of Alexander the Great's key conflicts, and simulates the interplay between Ancient Macedonian battle tactics and its rival military doctrines. Gameplay occurs at the tactical level: players direct predetermined armies on discrete battlefields, in a manner that one commentator compared to chess.









