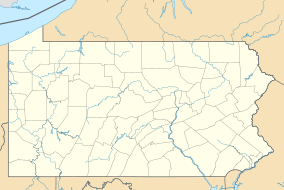
Tuscarora State Park is a Pennsylvania state park on 1,618 acres (655 ha) in Rush, Ryan, Schuylkill Townships, Schuylkill County, Pennsylvania in the United States. The most prominent features of the park are Locust Mountain and Tuscarora Lake. The park is named for the Tuscarora Indians, who lived in the area, following the Tuscarora War in North Carolina, until they were forced out by the colonial settlers of Pennsylvania. Tuscarora State Park is 2 miles (3.2 km) west of Tamaqua just off of Pennsylvania Route 54.

Rothrock State Forest is a Pennsylvania state forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #5. The main offices are located in Huntingdon in Huntingdon County, Pennsylvania in the United States.

Bald Eagle State Forest is a Pennsylvania state forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #7. The main office is located in Laurelton in Union County, Pennsylvania. The forest is found in Centre, Clinton, Mifflin, Snyder, and Union Counties. Bald Eagle shares a common border on its western extent with Rothrock State Forest and on its northern extent with Tiadaghton State Forest.

Moshannon State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #9. The main offices are located in the unincorporated village of Penfield in Huston Township, Clearfield County, Pennsylvania in the United States.

Susquehannock State Forest is a Pennsylvania state forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #15. The main office is located in Coudersport in Potter County, Pennsylvania in the United States.
Cornplanter State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #14. The main office is located in North Warren in Warren County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is named for Chief Cornplanter of the Seneca Nation, one of the tribes of the Iroquois Confederacy.

Forbes State Forest is a Pennsylvania state forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #4. The main offices are located in Laughlintown in Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania in the United States. Mount Davis, the highest peak in Pennsylvania, is located in the forest.

Gallitzin State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #6. The main offices are located in Ebensburg in Cambria County, Pennsylvania in the United States.

Clear Creek State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #8. The main offices are located in Clarion in Clarion County, Pennsylvania in the United States. Until August 2007, it was named Kittanning State Forest.

William Penn State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #17. The main offices are located in Elverson in Chester County, Pennsylvania in the United States.

Tiadaghton State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources, Bureau of Forestry. The forest is primarily in western and southern Lycoming County, with small portions in Clinton, Potter, Tioga, and Union Counties. The district's topography consists of narrow, flat to sloping plateaus cut by deep, steep-sloped valleys carved by fast moving mountain streams, including Pine Creek, Slate Run, and their tributaries. The Tiadaghton district extends south across the lowland along the west branch of the Susquehanna River to the narrow crests of Bald Eagle Mountain and North and South White Deer Ridge. The majority of forest cover is dominated by mixed oak forests, with some areas of northern hardwoods. The Tiadaghton State Forest is one of eight forest districts in the Pennsylvania Wilds region.

Sproul State Forest is a Pennsylvania state forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #10. The main offices are located in Renovo, Pennsylvania in Clinton County in the United States.

Tioga State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in District #16, in the Allegheny Plateau region within Tioga County, Pennsylvania.

Pinchot State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #11. The main offices are located in Lackawanna State Park in North Abington Township in Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, in the United States.

Weiser State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #18. The main offices are located in Cressona in Schuylkill County, Pennsylvania in the United States.

Delaware State Forest is a 85,114-acre (344.44 km2) Pennsylvania state forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #19. The main offices are located in Swiftwater in Monroe County, Pennsylvania in the United States.

Michaux State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #1. The main offices are located in Fayetteville in Franklin County, Pennsylvania, USA.

Loyalsock State Forest is a Pennsylvania state forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #20. The forest spans across the northern tier's "Endless Mountains" and is a total of 114,552 acres (46,358 ha). The Loyalsock is a “working forest” and is managed for pure water, recreation, plant and animal habitats, sustainable timber, and natural gas.

Buchanan State Forest is a Pennsylvania State Forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #2. The main office is located in McConnellsburg in Fulton County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. The forest also includes tracts in Franklin and Bedford Counties. It is named for James Buchanan of Pennsylvania, the fifteenth President of the United States.

Simon B. Elliott State Park is a 318-acre (129 ha) Pennsylvania state park located in Pine Township, Clearfield County, Pennsylvania in the United States. The park is surrounded by Moshannon State Forest. The park is entirely wooded with second growth forests of mixed oak species, including northern red oak, chestnut oak, shagbark hickory, red maple, and tulip poplar, and northern hard woods, including sugar maple, black cherry, aspen, birch, hemlock, and ash. S. B. Elliott State park is 9 miles (14 km) north of Clearfield on Pennsylvania Route 153 just off exit 111 of Interstate 80.