
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law, binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It states that peoples, based on respect for the principle of equal rights and fair equality of opportunity, have the right to freely choose their sovereignty and international political status with no interference.
Territorial integrity is the principle under international law that gives the right to sovereign states to defend their borders and all territory in them of another state. It is enshrined in Article 2(4) of the UN Charter and has been recognized as customary international law. Conversely it states that imposition by force of a border change is an act of aggression.

The Charter of the United Nations (UN) is the foundational treaty of the UN, an intergovernmental organization. It establishes the purposes, governing structure, and overall framework of the UN system, including its six principal organs: the Secretariat, the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Trusteeship Council.

The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty that commits states parties to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial. It was adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966 and entered into force 23 March 1976 after its thirty-fifth ratification or accession. As of June 2022, the Covenant has 173 parties and six more signatories without ratification, most notably the People's Republic of China and Cuba; North Korea is the only state that has tried to withdraw.
A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3379, adopted on 10 November 1975 by a vote of 72 to 35, "determine[d] that Zionism is a form of racism and racial discrimination". It was revoked in 1991 with UN General Assembly Resolution 46/86. The vote on Resolution 3379 took place approximately one year after UNGA 3237 granted the PLO Permanent Observer status, following PLO president Yasser Arafat's "olive branch" speech to the General Assembly in November 1974. The resolution was passed with the support of the Soviet bloc, in addition to the Arab- and Muslim-majority countries, many African countries, and a few others.

Reference Re Secession of Quebec, [1998] 2 SCR 217 is a landmark judgment of the Supreme Court of Canada regarding the legality, under both Canadian and international law, of a unilateral secession of Quebec from Canada.
A war of aggression, sometimes also war of conquest, is a military conflict waged without the justification of self-defense, usually for territorial gain and subjugation.

Gibraltar, a British Overseas Territory, located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, is the subject of an irredentist territorial claim by Spain. It was captured in 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–1714). The Spanish Crown formally ceded the territory in perpetuity to the British Crown in 1713, under Article X of the Treaty of Utrecht. Spain later attempted to recapture the territory during the thirteenth siege (1727) and the Great Siege (1779–1783). British sovereignty over Gibraltar was confirmed in later treaties signed in Seville (1729) and the Treaty of Paris (1783).
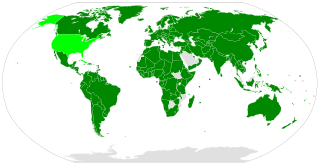
The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly (GA) on 16 December 1966 through GA. Resolution 2200A (XXI), and came in force from 3 January 1976. It commits its parties to work toward the granting of economic, social, and cultural rights (ESCR) to the Non-Self-Governing and Trust Territories and individuals, including labour rights and the right to health, the right to education, and the right to an adequate standard of living. As of July 2020, the Covenant has 171 parties. A further four countries, including the United States, have signed but not ratified the Covenant.
The International law bearing on issues of Arab–Israeli conflict, which became a major arena of regional and international tension since the birth of Israel in 1948, resulting in several disputes between a number of Arab countries and Israel.

Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter defines a non-self-governing territory (NSGT) as a territory "whose people have not yet attained a full measure of self-government". In practice, an NSGT is a territory deemed by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) to be "non-self-governing". Chapter XI of the UN Charter also includes a "Declaration on Non-Self-Governing Territories" that the interests of the occupants of dependent territories are paramount and requires member states of the United Nations in control of such territories to submit annual information reports concerning the development of those territories. Since 1946, the UNGA has maintained a list of non-self governing territories under member states' control. Since its inception, dozens of territories have been removed from the list, typically when they attained independence or internal self-government, while other territories have been added as new administering countries joined the United Nations or the General Assembly reassessed the status of certain territories.
The political status of Kosovo, also known as the Kosovo question, is the subject of a long-running political and territorial dispute between the Serbian government and the Government of Kosovo, stemming from the breakup of Yugoslavia (1991–92) and the ensuing Kosovo War (1998–99). In 1999 the administration of the province was handed on an interim basis to the United Nations under the terms of UNSCR 1244 which ended the Kosovo conflict of that year. That resolution reaffirmed the territorial integrity of Serbia over Kosovo but required the UN administration to promote the establishment of 'substantial autonomy and self-government' for Kosovo pending a 'final settlement' for negotiation between the parties.

Chapter I of the United Nations Charter lays out the purposes and principles of the United Nations organization. These principles include the equality and self-determination of nations, respect of human rights and fundamental freedoms and the obligation of member countries to obey the Charter, to cooperate with the UN Security Council and to use peaceful means to resolve conflicts. These "purposes and principles" reflect a premise that the effectiveness of the United Nations would be enhanced with broad guidelines to guide the actions of its Organisations and member states. However, some members were concerned that these proposals granted what they considered overly broad discretionary powers for the organs of the United Nations in the Dumbarton Oaks Conference proposals. And the adopted purposes and principles have been seen as reflecting the compromise achieved.
The Blue Water Thesis or "Salt Water Thesis", was a limited decolonization approach arising from United Nations General Assembly Resolution 637, which linked self-determination with non-self-governing territories.
The United Nations General Assembly Resolution 58/292 of 6 May 2004 was a resolution in which the United Nations General Assembly affirmed that the status of the Palestinian territory occupied since 1967, including East Jerusalem, remains one of military occupation, and that Israel has only the duties and obligations of an occupying Power under the Geneva Convention relative to the Protection of Civilian Persons and the Hague Convention.

The political status of Nagorno-Karabakh has remained unresolved since Azerbaijan's recognition as an independent state in 1991. During the Soviet Union, it had been an ethnic Armenian autonomous oblast of the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic; however, the disintegration of the USSR was accompanied by the conflict between local Armenians who sought to join Nagorno-Karabakh to Armenia, and local Azerbaijanis who opposed this. The conflict soon boiled over into open warfare in the First Nagorno-Karabakh War and ethnic cleansing, as a result of which Nagorno-Karabakh - as well as 7 surrounding regions of Azerbaijan - came to be occupied by an Armenia-allied de facto state, the Republic of Artsakh. Negotiations took place sporadically over the following decades, during which a ceasefire generally prevailed between Armenia / Artsakh and Azerbaijan. Turkey and Azerbaijan closed their borders to Armenia and Artsakh, and took other diplomatic steps to isolate them. Meanwhile, the United Nations Security Council, OSCE Minsk Group, and other bodies made various statements and proposed dialogue initiatives; none of them successful. In the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war, Azerbaijani forces, backed by Turkey, entered the Artsakh-held territories and retook the southern half of the region, including Shusha. Armenia was forced to concede additional territories in order to preserve Stepanakert and the northern half of the Republic of Artsakh under local Armenian control. The political status of this reduced region was not specified in the agreement, and remains unresolved.

The United Nations Special Committee on the Situation with Regard to the Implementation of the Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples, or the Special Committee on Decolonization (C-24), is a committee of the United Nations General Assembly that was established in 1961 and is exclusively devoted to the issue of decolonization.

Development is a human right that belongs to everyone, individually and collectively. Everyone is “entitled to participate in, contribute to, and enjoy economic, social, cultural and political development, in which all human rights and fundamental freedoms can be fully realized,” states the groundbreaking UN Declaration on the Right to Development, proclaimed in 1986.
There are a wide variety of views regarding the legal status of the State of Palestine, both among the states of the international community and among legal scholars. The existence of a state of Palestine, although controversial, is a reality in the opinions of the states that have established bilateral diplomatic relations. It is a non-member observer state at the United Nations since November, 2012. As of 31 July 2019, a total of 138 countries recognize it.










