Talian, or Brazilian Venetian, or Vêneto is a Venetian dialect spoken primarily in the Serra Gaúcha region in the northeast of the state of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil. It is also spoken in other parts of Rio Grande do Sul, as well as in parts of Espírito Santo and of Santa Catarina.
Lagoa may refer to the following:
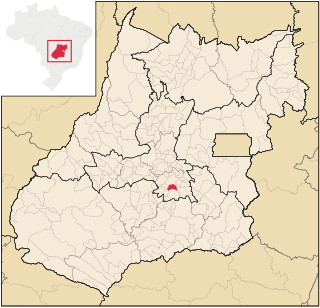
Aparecida de Goiânia is a city and municipality in central Goiás, Brazil. It is the second largest city in the state and the third largest industrial center, with a GDP of 11.980.984 billion reais in 2018.

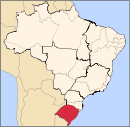
The Serra Gaúcha is a cultural region comprising the mountainous areas in the northeastern portion of Rio Grande do Sul state in southern Brazil. Most of its inhabitants are of German and Italian ancestry. Consequently, the cities in the Serra Gaúcha reflect German and Italian influences through their architecture, gastronomy, and culture. Geographically, it is part of the Serra Geral mountain range.

Cabeceiras is a municipality in east-central Goiás state, Brazil. It is fast becoming a major producer of agricultural products using center pivot irrigation.

Portuguese is the official and national language of Brazil being widely spoken by most of the population. Brazil is the most populous Portuguese-speaking country in the world, with its lands comprising the majority of Portugal's former colonial holdings in the Americas.

Nova Prata is a municipality in the mountainous Serra Gaúcha region of Rio Grande do Sul, in southern Brazil. It is in the Guapore micro-region of the Nordeste Rio-Grandense meso-region of the state.

Caçapava do Sul is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, located on the banks of the Camaquã River. As of 2020, the city has an estimated population of 33,548. It was the 2nd capital of the Piratini Republic from 1839 to 1840.

Turuçu is a Brazilian municipality in the southeastern part of the state of Rio Grande do Sul. It is nicknamed the National Capital of the Chili Pepper. The population is 3,423 in an area of 253.64 km2. The name comes from a local Native American language. It lies close to the Lagoa dos Patos, a lagoon connected with the Atlantic Ocean.

André da Rocha is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is surrounded by the municipalities Nova Prata, Protásio Alves, and Guabiju.

Antônio Prado is a municipality located in the Serra Gaúcha regionin The city is in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It boasts the largest collection of architectural heritage designated by IPHAN related to Italian colonization in Brazil. Its population is estimated at 13,045 people.

Flores da Cunha is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is the largest producer of wines inside Brazil. The Venetian language in its Brazilian form Talian is co-official with Portuguese in Flores da Cunha.

Lagoa Vermelha is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. As of 2020, the estimated population was 27,778.

Machadinho is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It was raised to municipality status in 1959, the area being taken out of the municipality of Lagoa Vermelha. As of 2020, the estimated population was 5,427.

Muitos Capões is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It was raised to municipality status in 1992, the area being taken out of the municipalities of Vacaria, Lagoa Vermelha and Esmeralda. As of 2020, the estimated population was 3,173.
Nova Bassano is a municipality and a city in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, south Brazil.
Lagoa do Itaenga is a municipality located in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. Located 78 km from Recife, capital of the state of Pernambuco. As of 2020, it has an estimated population of 21,460.

Bom Jesus do Araguaia is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil.

The Microregion of Frederico Westphalen was one of the Microregions of the Rio Grande do Sul state, in Brazil. It belonged to the mesoregion of the Noroeste Rio-Grandense. Its population was estimated by the IBGE to be of 175,391 in 2005, divided in 27 municipalities. Its total area is 5,182.529 km². The IBGE has since discontinued the microregion system for population tracking, replacing it with the term "immediate geographic region".

The Região da Uva e Vinho is a Brazilian tourist zone located in the northeast of the state of Rio Grande do Sul. It encompasses municipalities with the highest grape and wine production in the country. This condition has turned the region into one of the most important tourist hubs in Rio Grande do Sul, attracting hundreds of thousands of tourists from Rio Grande do Sul, other Brazilian states, and even other countries.