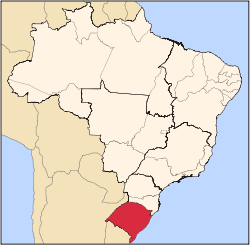
Rio Grande do Sul is a state in the southern region of Brazil. It is the fifth-most populous state and the ninth-largest by area. Located in the southernmost part of the country, Rio Grande do Sul is bordered clockwise by Santa Catarina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Uruguayan departments of Rocha, Treinta y Tres, Cerro Largo, Rivera, and Artigas to the south and southwest, and the Argentine provinces of Corrientes and Misiones to the west and northwest. The capital and largest city is Porto Alegre. The state has the highest life expectancy in Brazil, and the crime rate is relatively low compared to the Brazilian national average. The state has 5.4% of the Brazilian population and it is responsible for 6.6% of the Brazilian GDP.

Caxias do Sul is a city in Rio Grande do Sul, Southern Brazil, situated in the state's mountainous Serra Gaúcha region. It was established by Italian immigrants on June 20, 1890. Today it is the second largest city in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. In 2020, the population of Caxias do Sul was estimated at 517,451 people, many of whom are of Italian and German descent. The demonym of the citizens of Caxias do Sul is Caxiense.
Talian, or Brazilian Venetian, or Vêneto is a Venetian dialect spoken primarily in the Serra Gaúcha region in the northeast of the state of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil. It is also spoken in other parts of Rio Grande do Sul, as well as in parts of Espírito Santo and of Santa Catarina.

The Brazil socio-geographic division is a slightly different division than the Brazilian Division by Regions. It separates the country into three different and distinctive regions:

The South Region of Brazil is one of the five regions of Brazil. It includes the states of Paraná, Rio Grande do Sul, and Santa Catarina, and covers 576,409.6 square kilometres (222,553.0 sq mi), being the smallest region of the country, occupying only about 6.76% of the territory of Brazil. Its whole area is smaller than that of the state of Minas Gerais, in Southeast Brazil, for example or the whole metropolitan France.

Bento Gonçalves is a municipality located in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Created in 1875, it is one of the centers of the Italian immigration in Brazil. It is also known as the 'wine capital of Brazil' due to its vineyards and wine production. In 2020, its estimated population was 121,803 inhabitants.

The Serra Gaúcha is a cultural region comprising the mountainous areas in the northeastern portion of Rio Grande do Sul state in southern Brazil. Most of its inhabitants are of German and Italian ancestry. Consequently, the cities in the Serra Gaúcha reflect German and Italian influences through their architecture, gastronomy, and culture. Geographically, it is part of the Serra Geral mountain range.

Caminhos da Colônia, Portuguese for "Colony Pathway", is a scenic tourist route of four settlements in the Serra Gaúcha in the state of Rio Grande do Sul in southern Brazil. The 35 km route runs between the cities of Caxias do Sul, Flores da Cunha, Otávio Rocha and the old settlement of Santa Justina which never developed into a city like the other three.

Polish Brazilians refers to Brazilians of full or partial Polish ancestry who are aware of such ancestry and remain connected, to some degree, to Polish culture, or Polish-born people permanently residing in Brazil. Also, a Polish Brazilian may have one Polish parent.

Portuguese is the official and national language of Brazil being widely spoken by most of the population. Brazil is the most populous Portuguese-speaking country in the world, with its lands comprising the majority of Portugal's former colonial holdings in the Americas.

Barra Mansa is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Rio de Janeiro.

Arvorezinha is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It literally means "small tree".

Ivorá is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. According to the 2022 census by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), the municipality has a population of 1.929 inhabitants.
Nova Bassano is a municipality and a city in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, south Brazil.

Guaporé is a Brazilian municipality located in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. It is the state's greatest jewelry and lingerie producer, ranking second in the country. The city was mainly colonized by Italian immigrants in the 19th century and still retains their traditions. The name comes from the Guaraní language and its meaning is disputed, most likely being Desert Valley.

Italian Brazilians are Brazilians of full or partial Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Brazil during the Italian diaspora, or more recent Italian-born people who've settled in Brazil. Italian Brazilians are the largest number of people with full or partial Italian ancestry outside Italy, with São Paulo being the most populous city with Italian ancestry in the world. Nowadays, it is possible to find millions of descendants of Italians, from the southeastern state of Minas Gerais to the southernmost state of Rio Grande do Sul, with the majority living in São Paulo state. Small southern Brazilian towns, such as Nova Veneza, have as much as 95% of their population of Italian descent.
Viticulture in Paraná is an agricultural economic activity that aims at the production of grapes and their destination for the manufacture of wines and beverages in the state of Paraná, Brazil.

Nova Milano is a historic site and the seat of the fourth district of the Brazilian municipality of Farroupilha, considered the birthplace of Italian colonization in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. Originally the headquarters of the Caxias Colony, a pavilion was set up there in 1875 to welcome the immigrants who were waiting to be placed in the colonies in the region. In 1876 the colonial headquarters was transferred to Campo dos Bugres, but Nova Milano, on the margins of a very busy road, became a village, and in 1902 became the headquarters of the third district of Caxias. The arrival of railroads in 1910 determined a reorganization in the road and economic structure of the region, harming the growth of Nova Milano, which in 1934 was incorporated to the new municipality of Farroupilha as its fourth district, remaining until today with mainly rural characteristics.

Italian immigration in Rio Grande do Sul was a process in which Italians emigrated to the southern state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, through both private and government initiatives.

The Região da Uva e Vinho is a Brazilian tourist zone located in the northeast of the state of Rio Grande do Sul. It encompasses municipalities with the highest grape and wine production in the country. This condition has turned the region into one of the most important tourist hubs in Rio Grande do Sul, attracting hundreds of thousands of tourists from Rio Grande do Sul, other Brazilian states, and even other countries.