Lombok is an island in West Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia. It forms part of the chain of the Lesser Sunda Islands, with the Lombok Strait separating it from Bali to the west and the Alas Strait between it and Sumbawa to the east. It is roughly circular, with a "tail" to the southwest, about 70 kilometres across and a total area of about 4,738.65 square kilometres. The provincial capital and largest city on the island is Mataram.

Soekarno–Hatta International Airport, abbreviated SHIA or Soetta, formerly legally called Jakarta Cengkareng Airport, is the primary airport serving the Jakarta metropolitan area on the island of Java in Indonesia. Named after the first president and vice-president of Indonesia, Sukarno and Mohammad Hatta, the airport is located at Benda, Tangerang and Cengkareng, West Jakarta, which is about 20 km northwest of Central Jakarta. Together with Halim Perdanakusuma International Airport, they served over 80 million passengers in 2019.

Mataram is the capital of the Indonesian province of West Nusa Tenggara. The city is surrounded on all the landward sides by West Lombok Regency and lies on the western side of the island of Lombok, Indonesia. It is also the largest city of the province, and had a population of 402,843 at the 2010 Census and 429,651 at the 2020 Census.

Sultan Aji Muhammad Sulaiman Sepinggan International Airport, also known as Sepinggan Airport, is an international airport serving the city of Balikpapan and adjacent areas of East Kalimantan, located in Kalimantan, Indonesia. The airport began its new operational phase on 6 August 1997, with new building and runway structure, replacing old structure on the same site. The airport is operated by PT. Angkasa Pura I, which has an area of 300 hectares.

AdisutjiptoInternational Airport is an airport serving the Yogyakarta area on the island of Java, Indonesia. It was formerly the principal airport serving this area. The airport is in the Sleman Regency, in the Yogyakarta Special Region, on the northeast outskirts of the city, near the Prambanan historic temple site. The airport is about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) from the city center.

Kualanamu International Airport is an international airport serving Medan, Indonesia, and other parts of North Sumatra. It is located in the Deli Serdang Regency, 23 km east of downtown Medan. Kualanamu is the third-largest airport in Indonesia after Jakarta Soekarno–Hatta and Bandung Kertajati, and the fifth busiest airport in Indonesia as of 2018, as well as the first Indonesian airport to receive four stars by Skytrax.

Sultan Syarif Kasim II International Airport, is an international airport that serves the city of Pekanbaru, Riau, Indonesia. The airport is often referred to as SSK II, SSK or Sultan Syarif Qasim II International Airport, and formerly known as Simpang Tiga Airport. The namesake of the airport is Sultan Syarif Kasim II, the last sultan of Siak and an Indonesian National Hero. The airport serves flights to and from several cities and towns in Indonesia and some countries such as Malaysia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Saudi Arabia.

Sultan Mahmud Badaruddin II International Airport is an international airport serving the city of Palembang, South Sumatra and surrounding areas. It is located in the region KM.10 Talang Betutu District. It is named after Sultan Mahmud Badaruddin, the last Sultan of Palembang.

Selaparang Airport(IATA: AMI, ICAO: WADA), was the sole airport serving the island of Lombok and the city of Mataram, the capital of the province of West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia until its closure on 30 September 2011. The IATA code AMI came from the nearby port of Ampenan, now a part of Mataram. The airport was operated by PT. Angkasa Pura 1 (PERSERO). The new Lombok International Airport operated under the IATA code AMI until late November 2011, toward the end of the month the IATA code LOP was formally listed for the new airport and was slowly being transitioned by the airlines operating to Lombok.

Husein Sastranegara International Airport is an airport in Bandung, West Java, Indonesia. It is located within the city and 2.4 km from Bandung Central train station. The site occupies an area of 145 hectares and serves the area of civil aviation in the south western region of Java. The airfield is cojoined with the Husein Sastranegara air force base of the Indonesian Air Force.

Syamsudin Noor International Airport is an international airport serving Banjarmasin in South Kalimantan of Indonesia. It is located in the district of Landasan Ulin, 10 kilometers south-west of Banjarbaru, about 25 km north from the center of the city of Banjarmasin, capital and the largest city of Kalimantan. The airport served more than 5.3 million passengers in 2017.

Angkasa Pura is the name used by two separate state enterprises of the Indonesian Ministry of State Owned Enterprises responsible for the management of airports in Indonesia. The two companies are PT Angkasa Pura I and PT Angkasa Pura II. Angkasa Pura I has its head office in Kemayoran, Jakarta, while Angkasa Pura II has its head office at Soekarno-Hatta International Airport in Tangerang, Banten.

Yogyakarta International Airport is an international airport located at Temon district of Kulon Progo Regency, in Java, Indonesia. The airport is situated around 45 kilometers from the city of Yogyakarta, which serves the Yogyakarta Special Region, as well as nearby Central Javan cities such as Purworejo, Kebumen, Cilacap and Magelang. It is the largest and one of the three only airports in the Yogyakarta Special Region, the other being Adisutjipto International Airport which is located closer to the Yogyakarta city center and Gading Airfield in Wonosari, Gunung Kidul Regency. The airport serves flights to and from several cities and towns in Indonesia and some international destinations such as Malaysia and Singapore.

West Lombok Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok and the administrative capital is the town of Gerung. The regency covers an area of 1,053.92 km2 and had a population of 599,609 at the 2010 Census and 721,481 at the 2020 Census.

East Lombok Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok, of which it comprises the eastern third ; the administrative capital is the town of Selong. The Regency covers an area of 1,605.55 km2 and had a population of 1,105,582 at the 2010 Census and 1,325,240 at the 2020 Census.

Central Lombok Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok and the capital is Praya. It covers an area of 1,208.39 km2, and had a population of 859,309 at the 2010 Census and 1,034,859 at the 2020 Census.
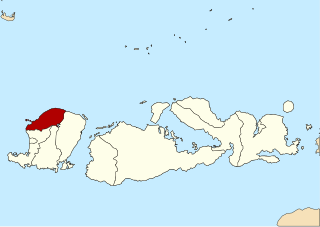
Lombok Utara Regency' is a Regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok and the capital is Tanjung situated on the north coast of the island. The regency covers an area of 809.53 km2 and had a population of 199,904 at the 2010 Census and 247,400 at the 2020 Census.

Banyuwangi International Airport, is an airport at Blimbingsari, which serves Banyuwangi city and surrounding area in East Java, Indonesia. The airport was formerly known as Blimbingsari Airport. It was opened for operations in December 2010. The airport is termed as the First Green Airport of Indonesia. The Airport is managed by PT Angkasa Pura II (Persero), after being handed over by the Ministry of Transportation on 22 December 2017.

I Gusti Ngurah Rai International Airport, is the main airport in Bali, located 13 km south of Denpasar. Ngurah Rai is the second busiest airport in Indonesia after Soekarno–Hatta International Airport. In 2018, the airport served 23,779,178 passengers. The airport has category IX and is capable of serving wide-body aircraft including the Boeing 747-8 and Airbus A380.
Kediri International Airport is an airport currently under construction at Kediri, which is situated approximately 120 kilometers southwest of Surabaya city, and will serve Kediri, Blitar and Nganjuk regency of East Java, Indonesia. The goal to develop the airport was made to boost economic growth in the southern part of East Java province, as well as to supplement operation of Juanda International Airport. The airport is expected to be operational by 2022 and could become an international airport in future.