Cubane is a synthetic hydrocarbon compound with the formula C8H8. It consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substance, cubane is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons and a member of the prismanes. It was first synthesized in 1964 by Philip Eaton and Thomas Cole. Before this work, Eaton believed that cubane would be impossible to synthesize due to the "required 90 degree bond angles". The cubic shape requires the carbon atoms to adopt an unusually sharp 90° bonding angle, which would be highly strained as compared to the 109.45° angle of a tetrahedral carbon. Once formed, cubane is quite kinetically stable, due to a lack of readily available decomposition paths. It is the simplest hydrocarbon with octahedral symmetry.
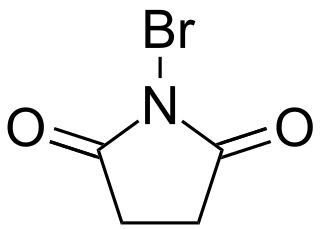
N-Bromosuccinimide or NBS is a chemical reagent used in radical substitution, electrophilic addition, and electrophilic substitution reactions in organic chemistry. NBS can be a convenient source of Br•, the bromine radical.

The Bamford–Stevens reaction is a chemical reaction whereby treatment of tosylhydrazones with strong base gives alkenes. It is named for the British chemist William Randall Bamford and the Scottish chemist Thomas Stevens Stevens (1900–2000). The usage of aprotic solvents gives predominantly Z-alkenes, while protic solvent gives a mixture of E- and Z-alkenes. As an alkene-generating transformation, the Bamford–Stevens reaction has broad utility in synthetic methodology and complex molecule synthesis.

In inorganic nomenclature, a manganate is any negatively charged molecular entity with manganese as the central atom. However, the name is usually used to refer to the tetraoxidomanganate(2−) anion, MnO2−
4, also known as manganate(VI) because it contains manganese in the +6 oxidation state. Manganates are the only known manganese(VI) compounds.
Adams' catalyst, also known as platinum dioxide, is usually represented as platinum(IV) oxide hydrate, PtO2•H2O. It is a catalyst for hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis in organic synthesis. This dark brown powder is commercially available. The oxide itself is not an active catalyst, but it becomes active after exposure to hydrogen whereupon it converts to platinum black, which is responsible for reactions.
The Carroll rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in organic chemistry and involves the transformation of a β-keto allyl ester into a α-allyl-β-ketocarboxylic acid. This organic reaction is accompanied by decarboxylation and the final product is a γ,δ-allylketone. The Carroll rearrangement is an adaptation of the Claisen rearrangement and effectively a decarboxylative allylation.
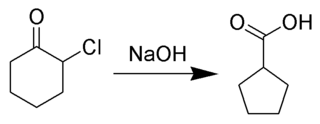
The Favorskii rearrangement is principally a rearrangement of cyclopropanones and α-halo ketones that leads to carboxylic acid derivatives. In the case of cyclic α-halo ketones, the Favorskii rearrangement constitutes a ring contraction. This rearrangement takes place in the presence of a base, sometimes hydroxide, to yield a carboxylic acid, but usually either an alkoxide base or an amine to yield an ester or an amide, respectively. α,α'-Dihaloketones eliminate HX under the reaction conditions to give α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Note that trihalomethyl ketone substrates will result in haloform and carboxylate formation via the haloform reaction instead.

Chloroplatinic acid (also known as hexachloroplatinic acid) is an inorganic compound with the formula [H3O]2[PtCl6](H2O)x (0 ≤ x ≤ 6). A red solid, it is an important commercial source of platinum, usually as an aqueous solution. Although often written in shorthand as H2PtCl6, it is the hydronium (H3O+) salt of the hexachloroplatinate anion (PtCl2−
6). Hexachloroplatinic acid is highly hygroscopic.

Tricyclobutabenzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of a benzene core with three cyclobutane rings fused onto it. This compound and related compounds are studied in the laboratory because they are often displaying unusual conformations and because of their unusual reactivity. Tricyclobutabenzenes are isomers of radialenes and form an equilibrium with them.

The Finkelstein reaction, named after the German chemist Hans Finkelstein, is a type of SN2 reaction that involves the exchange of one halogen atom for another. It is an equilibrium reaction, but the reaction can be driven to completion by exploiting the differential solubility of various halide salts, or by using a large excess of the desired halide.

The tert-butyloxycarbonyl protecting group or tert-butoxycarbonyl protecting group is an acid-labile protecting group used in organic synthesis.

Orotidine 5′-phosphate decarboxylase or orotidylate decarboxylase is an enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis. It catalyzes the decarboxylation of orotidine monophosphate (OMP) to form uridine monophosphate (UMP). The function of this enzyme is essential to the de novo biosynthesis of the pyrimidine nucleotides uridine triphosphate, cytidine triphosphate, and thymidine triphosphate. OMP decarboxylase has been a frequent target for scientific investigation because of its demonstrated extreme catalytic efficiency and its usefulness as a selection marker for yeast strain engineering.
The Hammick reaction, named after Dalziel Hammick, is a chemical reaction in which the thermal decarboxylation of α-picolinic acids in the presence of carbonyl compounds forms 2-pyridyl-carbinols.
In organic chemistry, a homologation reaction, also known as homologization, is any chemical reaction that converts the reactant into the next member of the homologous series. A homologous series is a group of compounds that differ by a constant unit, generally a methylene group. The reactants undergo a homologation when the number of a repeated structural unit in the molecules is increased. The most common homologation reactions increase the number of methylene units in saturated chain within the molecule. For example, the reaction of aldehydes or ketones with diazomethane or methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine to give the next homologue in the series.
Alcohol oxidation is a collection of oxidation reactions in organic chemistry that convert alcohols to aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters where the carbon carries a higher oxidation state. The reaction mainly applies to primary and secondary alcohols. Secondary alcohols form ketones, while primary alcohols form aldehydes or carboxylic acids.

The Birch reduction is an organic reaction that is used to convert arenes to 1,4-cyclohexadienes. The reaction is named after the Australian chemist Arthur Birch and involves the organic reduction of aromatic rings in an amine solvent with an alkali metal and a proton source. Unlike catalytic hydrogenation, Birch reduction does not reduce the aromatic ring all the way to a cyclohexane.
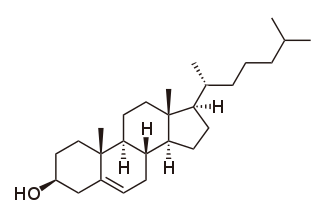
Cholesterol total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule cholesterol and is considered a great scientific achievement. The research group of Robert Robinson with John Cornforth published their synthesis in 1951 and that of Robert Burns Woodward with Franz Sondheimer in 1952. Both groups competed for the first publication since 1950 with Robinson having started in 1932 and Woodward in 1949. According to historian Greg Mulheirn the Robinson effort was hampered by his micromanagement style of leadership and the Woodward effort was greatly facilitated by his good relationships with chemical industry. Around 1949 steroids like cortisone were produced from natural resources but expensive. Chemical companies Merck & Co. and Monsanto saw commercial opportunities for steroid synthesis and not only funded Woodward but also provided him with large quantities of certain chemical intermediates from pilot plants. Hard work also helped the Woodward effort: one of the intermediate compounds was named Christmasterone as it was synthesized on Christmas Day 1950 by Sondheimer.
Decarboxylative cross coupling reactions are chemical reactions in which a carboxylic acid is reacted with an organic halide to form a new carbon-carbon bond, concomitant with loss of CO2. Aryl and alkyl halides participate. Metal catalyst, base, and oxidant are required.
Mucobromic acid is an organic compound that consists of a dibrominated alkene with aldehyde and carboxylic acid functional groups. It easily tautomerizes to a furanone hemiacetal form. This compound, and the analogous mucochloric acid, form the group of known mucohalic acids. The bromide appears to behave similarly to the more heavily studied chloride.

Diethyl acetamidomalonate (DEAM) is a derivative of malonic acid diethyl ester. Formally, it is derived through the acetylation of ester from the unstable aminomalonic acid. DEAM serves as a starting material for racemates including both, natural and unnatural α-amino acids or hydroxycarboxylic acids. It is also usable as a precursor in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly in the cases of active ingredients like fingolimod, which is used to treat multiple sclerosis.












