
The Rhode Island House of Representatives is the lower house of the Rhode Island General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Rhode Island, the upper house being the Rhode Island Senate. It is composed of 75 members, elected to two-year terms from 75 districts of equal population. The Rhode Island General Assembly does not have term limits. The House meets at the Rhode Island State Capitol in Providence.

Herbert Warren Ladd was the 40th and 42nd Governor of Rhode Island for two terms: 1889–90 and 1891–92.

The 1912–13 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. They were the last U.S. Senate elections before the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, establishing direct elections for all Senate seats. Senators had been primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1912 and 1913, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. Some states elected their senators directly even before passage of Seventeenth Amendment. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.

John William Davis was a United States Democratic politician, who served as the 38th and 41st Governor of Rhode Island.
Since the Great Depression, Rhode Island politics have been dominated by the Rhode Island Democratic Party, and the state is considered part of the Democrats' "Blue Wall." Democrats have won all but four presidential elections since 1928, with the exceptions being 1952, 1956, 1972, and 1984. The Rhode Island Republican Party, although virtually non-existent in the Rhode Island General Assembly, has remained competitive in gubernatorial elections, having won one as recently as 2006. Until 2014, Democrats had not won a gubernatorial election in the state since 1992, and it was not until 2018 that they won one by double digits. The Rhode Island General Assembly has continuously been under Democratic control since 1959.

The 1890–91 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1890 and 1891, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.

The 1840–41 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1840 and 1841, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1802–03 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1802 and 1803, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1862–63 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, occurring during the American Civil War. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1862 and 1863, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 2014 United States Senate election in Rhode Island was held on November 4, 2014, to elect a member of the United States Senate from the State of Rhode Island, concurrently with the election of the governor of Rhode Island, as well as other elections to the United States Senate in other states and elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections.
Teresa Ann Tanzi is an American politician and a Democratic member of the Rhode Island House of Representatives representing District 34 since January 2011. Outside of working in government, Tanzi also works as a realtor.

John 'Jay' Gustav Edwards IV is an American politician and a Democratic member of the Rhode Island House of Representatives representing District 70 since January 2009. On March 25, 2014, Rep. Edwards was elected House Majority Whip by the House Democratic Caucus when Nicholas Mattiello became Speaker in 2014. Prior to that he had served as the Senior Deputy Majority Leader under Speaker Gordon Fox. In 2021, after Joe Shekarchi was elected speaker, Edwards was appointed Majority Floor Manager and replaced as Majority Whip by Katherine Kazarian. Edwards serves on the House Finance, House Oversight, House Municipal Government and House Labor Committees. In September 2014, Edwards became a CSG Henry Toll Fellow.
Joseph M. McNamara is an American politician and a Democratic member of the Rhode Island House of Representatives representing District 19 since January 2003. McNamara served consecutively from January 1995 until January 2003 in the District 29 seat.
John J. DeSimone is an American politician, a former Democratic member of the Rhode Island House of Representatives who represented House District 6 from January 1993 until January 2003 and District 5 from January 2003 to January 2017. DeSimone was narrowly defeated in the 2016 Democratic primary by progressive candidate Marcia Ranglin-Vassell, ending his 24 year tenure in the General Assembly.
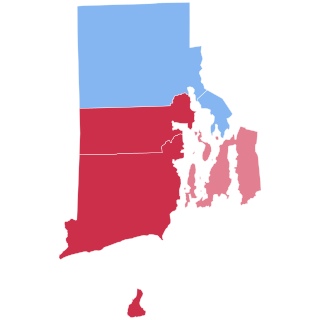
The 1928 United States presidential election in Rhode Island took place on November 6, 1928, as part of the 1928 United States presidential election which was held throughout all contemporary 48 states. Voters chose five representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1890 Rhode Island gubernatorial election was held on April 2, 1890. Democratic nominee John W. Davis defeated incumbent Republican Herbert W. Ladd with 48.76% of the vote.

The 1889 Rhode Island gubernatorial election was held on April 3, 1889. Democratic nominee John W. Davis received 49.38% of the vote and the Republican nominee Herbert W. Ladd 39.13%. With no candidate attaining a majority of the vote it was decided by the Rhode Island General Assembly. In the same election, the Republican Party had won a small majority in the legislature and selected Ladd as governor.
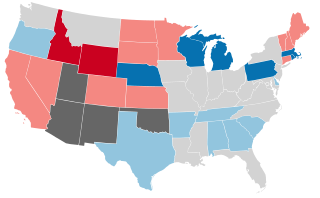
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1890, in 27 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1890.
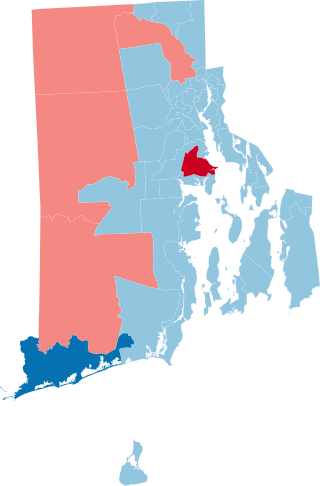
The 2022 Rhode Island State Senate elections took place on November 8, 2022. Primary elections were held on September 13, 2022. Rhode Island voters elected state senators in all 38 seats of the Senate. State senators serve two-year terms in the Rhode Island Senate.
















