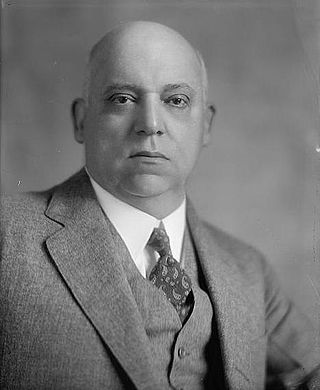John Crepps Wickliffe Beckham was an American attorney and politician who served as the 35th governor of Kentucky and a United States senator from Kentucky. He was the state's first popularly-elected senator after the passage of the Seventeenth Amendment.

James Bennett McCreary was an American lawyer and politician from Kentucky. He represented the state in both houses of the U.S. Congress and served as its 27th and 37th governor. Shortly after graduating from law school, he was commissioned as the only major in the 11th Kentucky Cavalry, serving under Confederate Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan during the American Civil War. He returned to his legal practice after the war. In 1869, he was elected to the Kentucky House of Representatives where he served until 1875; he was twice chosen Speaker of the House. At their 1875 nominating convention, state Democrats chose McCreary as their nominee for governor, and he won an easy victory over Republican John Marshall Harlan. With the state still feeling the effects of the Panic of 1873, most of McCreary's actions as governor were aimed at easing the plight of the state's poor farmers.

The Kentucky General Assembly, also called the Kentucky Legislature, is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Kentucky. It comprises the Kentucky Senate and the Kentucky House of Representatives.

Ruby Laffoon was an American attorney and politician who served as the 43rd Governor of Kentucky from 1931 to 1935. A Kentucky native, at age 17, Laffoon moved to Washington, D.C., to live with his uncle, U.S. Representative Polk Laffoon. He developed an interest in politics and returned to Kentucky, where he compiled a mixed record of victories and defeats in elections at the county and state levels. In 1931, he was chosen as the Democratic gubernatorial nominee by a nominating convention, not a primary, making him the only Kentucky gubernatorial candidate to be chosen by a convention after 1903. In the general election, he defeated Republican William B. Harrison by what was then the largest margin of victory in Kentucky gubernatorial history.

Keen Johnson was an American politician who served as the 45th Governor of Kentucky, serving from 1939 to 1943; being the only journalist to have held that office. After serving in World War I, Johnson purchased and edited the Elizabethtown Mirror newspaper. He revived the struggling paper, sold it to a competitor and used the profits to obtain his journalism degree from the University of Kentucky in 1922. After graduation, he became editor of The Anderson News, and in 1925, he accepted an offer to co-publish and edit the Richmond Daily Register.
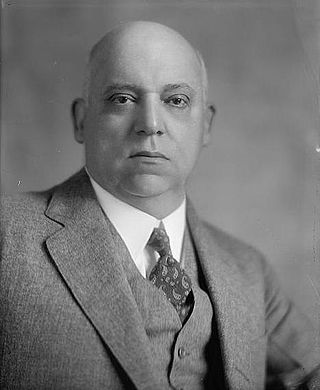
Augustus Owsley Stanley I was an American politician from Kentucky. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as the 38th governor of Kentucky and also represented the state in both the U.S. House of Representatives and the U.S. Senate. From 1903 to 1915, Stanley represented Kentucky's 2nd congressional district in the House of Representatives, where he gained a reputation as a progressive reformer. Beginning in 1904, he called for an antitrust investigation of the American Tobacco Company, claiming they were a monopsony that drove down prices for the tobacco farmers of his district. As a result of his investigation, the Supreme Court of the United States ordered the breakup of the American Tobacco Company in 1911. Stanley also chaired a committee that conducted an antitrust investigation of U.S. Steel, which brought him national acclaim. Many of his ideas were incorporated into the Clayton Antitrust Act.

John Young Brown was an American politician from the U.S. Commonwealth of Kentucky who represented the state in the United States House of Representatives and served as its 31st governor. Brown was elected to the House of Representatives for three non-consecutive terms, each of which was marred by controversy. He was first elected in 1859, despite his own protests that he was not yet twenty-five years old, the minimum age set by the Constitution for serving in the legislature. The voters of his district elected him anyway, but he was not allowed to take his seat until the Congress' second session, after he was of legal age to serve. After moving to Henderson, Kentucky, Brown was elected from that district in 1866. On this occasion, he was denied his seat because of alleged disloyalty to the Union during the Civil War. Voters in his district refused to elect another representative, and the seat remained vacant throughout the term to which Brown was elected. After an unsuccessful gubernatorial bid in 1871, Brown was again elected to the House in 1872 and served three consecutive terms. During his final term, he was officially censured for delivering a speech excoriating Massachusetts Representative Benjamin F. Butler. The censure was later expunged from the congressional record.

William Sylvester Taylor was an American politician who was the 33rd Governor of Kentucky. He was initially declared the winner of the disputed gubernatorial election of 1899, but the Kentucky General Assembly, dominated by the Democrats, reversed the election results, giving the victory to his Democratic opponent, William Goebel. Thus, Taylor served only 50 days as governor.

Flemon Davis "Flem" Sampson was the 42nd Governor of Kentucky, serving from 1927 to 1931. He graduated from Valparaiso University in 1894, and opened a law practice in Barbourville, Kentucky. He formed a political alliance with future Representatives Caleb Powers and John Robsion, both prominent Republicans in the eastern part of the state. By 1916, he was serving on the Kentucky Court of Appeals and had previously served as a county judge and circuit court judge. In 1923, he was elevated to chief justice of the Court of Appeals. He served until 1927, when he became the Republican gubernatorial nominee.

William Jason Fields was an American politician from the U.S. state of Kentucky. Known as "Honest Bill from Olive Hill", he represented Kentucky's Ninth District in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1911 to 1923, resigning to become the state's 41st governor.

Augustus Everett Willson was an American politician and the 36th Governor of Kentucky. Orphaned at the age of twelve, Willson went to live with relatives in New England. This move exposed him to such authors as Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Oliver Wendell Holmes, and James Russell Lowell, who were associates of his older brother, poet Forceythe Willson. He was also afforded the opportunity to attend Harvard University, where he earned an A.B. in 1869 and an A.M. in 1872. After graduation, he secured a position at the law firm of future Supreme Court justice John Marshall Harlan. Willson and Harlan became lifelong friends, and Willson's association with Harlan deepened his support of the Republican Party.

William Justus Goebel was an American Democratic politician who served as the 34th governor of Kentucky for four days, having been sworn in on his deathbed a day after being shot by an assassin. Goebel is the only sitting state governor in United States history to die by assassination.

Thomas Stockdale Rhea (1871–1946) was a Democratic politician from the U.S. Commonwealth of Kentucky. He served as Kentucky State Treasurer in 1912 and was state highway commissioner in the administration of Governor Ruby Laffoon. Known as "The Sage of Russellville" or "The Gray Fox", Rhea was a powerful Democratic political boss in the state. He was an unsuccessful candidate for governor in 1935, losing to A. B. "Happy" Chandler in the Democratic primary.

Parker Watkins ("Wat") Hardin was a politician from the U.S. state of Kentucky. From 1879 to 1888, he served as Attorney General of Kentucky. He was an unsuccessful candidate for Governor of Kentucky in 1891, 1895 and 1899.
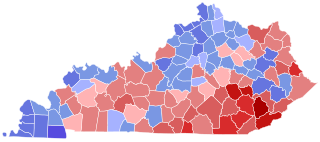
The 1899 Kentucky gubernatorial election was held on November 7, 1899, to choose the 33rd governor of Kentucky. The incumbent, Republican William O'Connell Bradley, was term-limited and unable to seek re-election.
Taylor v. Beckham, 178 U.S. 548 (1900), was a case heard before the Supreme Court of the United States on April 30 and May 1, 1900, to decide the outcome of the disputed Kentucky gubernatorial election of 1899. The litigants were Republican gubernatorial candidate William S. Taylor and Democratic lieutenant gubernatorial candidate J. C. W. Beckham. In the November 7, 1899, election, Taylor received 193,714 votes to Democrat William Goebel's 191,331. This result was certified by a 2–1 decision of the state's Board of Elections. Goebel challenged the election results on the basis of alleged voting irregularities, and the Democrat-controlled Kentucky General Assembly formed a committee to investigate Goebel's claims. Goebel was shot on January 30, 1900, one day before the General Assembly approved the committee's report declaring enough Taylor votes invalid to swing the election to Goebel. As he lay dying of his wounds, Goebel was sworn into office on January 31, 1900. He died on February 3, 1900, and Beckham ascended to the governorship.

William O'Connell Bradley was an American politician from the state of Kentucky. He served as the 32nd Governor of Kentucky and was later elected by the state legislature as a U.S. senator from that state. The first Republican to serve as governor of Kentucky, Bradley became known as the father of the Republican Party in Kentucky.

Morris Burke Belknap, also known as Colonel Morris Burke Belknap, was an American businessman from Louisville, Kentucky.

Samuel Wilber Hager was an American politician who served as the 14th Kentucky State Treasurer from 1900 to 1904, and Kentucky State Auditor from 1904 to 1908. He was the Democratic party's nominee for governor of Kentucky in 1907, but lost the race. He subsequently owned a newspaper while remaining involved in politics. Hager died in 1918.

The 1900 Kentucky gubernatorial special election was held on November 6, 1900. Incumbent Democratic governor J. C. W. Beckham was elected to complete William Goebel's term with 49.88% of the vote.