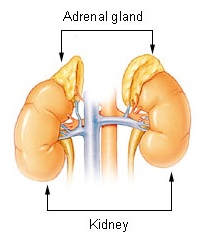
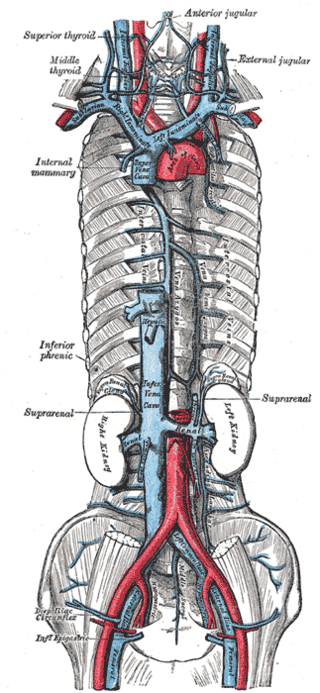
The adrenal glands are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.
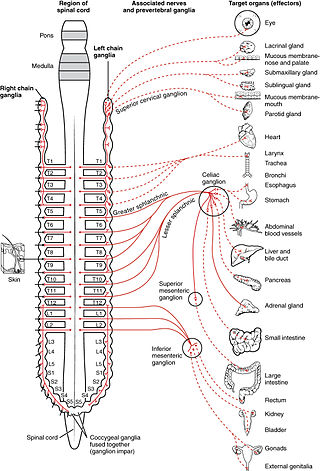
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.

In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the distal transverse colon to the upper part of the anal canal. The regions supplied by the IMA are the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and part of the rectum.
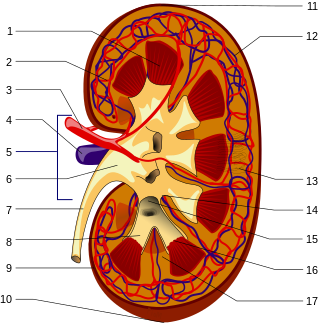
The renal circulation supplies the blood to the kidneys via the renal arteries, left and right, which branch directly from the abdominal aorta. Despite their relatively small size, the kidneys receive approximately 20% of the cardiac output.
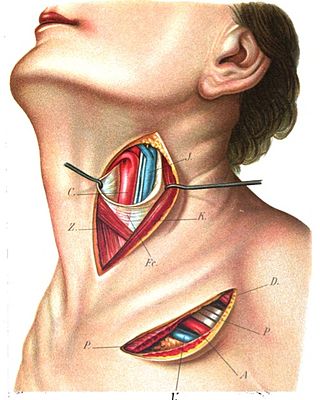
The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.

The suprarenal veins are two in number:
The inferior phrenic veins drain the diaphragm and follow the course of the inferior phrenic arteries;

The inferior phrenic artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the abdominal cavity which represents the main source of arterial supply to the diaphragm. Each artery usually arises either from the coeliac trunk or the abdominal aorta, however, their origin is highly variable and the different sites of origin are different for the left artery and right artery. The superior suprarenal artery is a branch of the inferior phrenic artery.

The inferior thyroid artery is an artery in the neck. It arises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and longus colli muscle. It then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the vessel.

The middle suprarenal artery is a paired artery in the abdomen. It is a branch of the aorta. It supplies the adrenal gland.
The inferior labial artery arises near the angle of the mouth as a branch of the facial artery; it passes upward and forward beneath the triangularis and, penetrating the orbicularis oris, runs in a tortuous course along the edge of the lower lip between this muscle and the mucous membrane.

The inferior suprarenal artery is a paired artery that supplies the adrenal gland. It usually originates at the trunk of the renal artery before its terminal division, but with many common variations. It supplies the adrenal gland parenchyma, the ureter, and the surrounding cellular tissue and muscles.

The phrenic plexus accompanies the inferior phrenic artery to the diaphragm, some filaments passing to the suprarenal gland.

The superior suprarenal artery is an artery in the abdomen. It is a branch of the inferior phrenic artery, itself a branch of the aorta. It supplies the adrenal gland.
Suprarenal artery may refer to:
The inferior hypophysial artery is an artery in the head. It is a branch of the cavernous carotid artery, itself from the internal carotid artery. It supplies the posterior pituitary of the pituitary gland.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:














