
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Portugal, Spain and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain, it is considered to overlap with the Spanish War of Independence.

The Battle of Toulouse took place on April 10, 1814, just four days after Napoleon's surrender of the French Empire to the Sixth Coalition, marking one of the final conflicts of the Napoleonic Wars. Having pushed the demoralised and disintegrating French Imperial armies out of Spain in a difficult campaign the previous autumn, the Allied British-Portuguese and Spanish army under the Duke of Wellington pursued the war into southern France in the spring of 1814.

Maximilien Sébastien Foy was a French Army officer and politician.

The Battle of the Pyrenees was a large-scale offensive launched on 25 July 1813 by Marshal Nicolas Jean de Dieu Soult from the Pyrénées region on Emperor Napoleon's order, in the hope of relieving French garrisons under siege at Pamplona and San Sebastián. After initial success the offensive ground to a halt in the face of increased allied resistance under the command of Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington. Soult abandoned the offensive on 30 July and headed toward France, having failed to relieve either garrison.

The Battle of Sorauren was part of a series of engagements in late July 1813 called the Battle of the Pyrenees in which a combined British and Portuguese force under Sir Arthur Wellesley held off Marshal Soult's French forces attempting to relieve Pamplona.

The Battle of Nivelle took place in front of the river Nivelle near the end of the Peninsular War (1808–1814). After the Allied siege of San Sebastian, Wellington's 80,000 British, Portuguese and Spanish troops were in hot pursuit of Marshal Soult who had 60,000 men to place in a 20-mile perimeter. After the Light Division, the main British army was ordered to attack and the 3rd Division split Soult's army in two. By two o'clock, Soult was in retreat and the British in a strong offensive position. Soult had lost another battle on French soil and had lost 4,500 men to Wellington's 5,500.
Manuel Alberto Freire de Andrade y Armijo was a Spanish cavalry officer and general officer during the Peninsular War, and later Defense Minister.
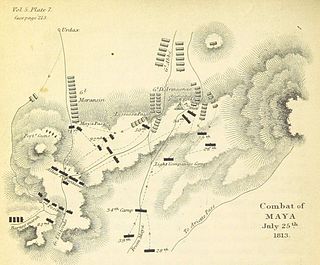
The Battle of Maya saw an Imperial French corps led by Jean-Baptiste Drouet, Comte d'Erlon attack the British 2nd Division under William Stewart at the Maya Pass in the western Pyrenees. Despite being surprised, the outnumbered British soldiers fought stoutly, inflicting greater losses on the French than they suffered themselves. By the afternoon, the French gained the upper hand and were pressing forward, but the late arrival of a brigade from the British 7th Division stabilized the situation. The British forces slipped away under the cover of night and the French did not pursue effectively. The Peninsular War battle at Maya was part of the Battle of the Pyrenees, which ended in a significant Anglo-Allied victory.

The Battle of Roncesvalles took place between French and Anglo-Portuguese forces during the Peninsular War (1808–1814).

The siege of San Sebastián, part of the Peninsular War, Allied forces under the command of Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington failed to capture the city in a siege. However in a second siege the Allied forces under Thomas Graham captured the city of San Sebastián in northern Basque Country from its French garrison under Louis Emmanuel Rey. During the final assault, the British and Portuguese troops rampaged through the town and razed it to the ground.

At the siege of Burgos, from 19 September to 21 October 1812, the Anglo-Portuguese Army led by General Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington tried to capture the castle of Burgos from its French garrison under the command of General of Brigade Jean-Louis Dubreton. The French repulsed every attempt to seize the fortress, resulting in Wellington's withdrawal. The siege took place during the Peninsular War, part of the Napoleonic Wars. Burgos is located about 210 kilometres (130 mi) north of Madrid.

In the Battle of the Bidasoa on 7 October 1813 the Allied army of Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington wrested a foothold on French soil from Nicolas Soult's French army. The Allied troops overran the French lines behind the Bidassoa River on the coast and along the Pyrenees crest between the Bidasoa and La Rhune (Larrun). The nearest towns to the fighting are Irun on the lower Bidassoa and Bera on the middle Bidasoa. The battle occurred during the Peninsular War, part of the wider Napoleonic Wars.

The Battle of Bayonne, the last major battle of the Peninsular War, ensued when the French garrison of Bayonne led by General of Division Pierre Thouvenot launched a sortie against a besieging force of British, Portuguese, and Spanish troops commanded by Lieutenant General John Hope. It was fought after unofficial news of the abdication of French emperor Napoleon on 4 April had reached the opposing forces. Thouvenot's reasons for initiating the sortie are not clear; there was apparently nothing for the French to gain by fighting. After initial success for the French, Allied forces drove them back inside Bayonne with heavy losses on both sides.

Eloi Charlemagne Taupin became a French soldier before the French Revolution and was killed in 1814 leading his division in battle against the British and the Spanish in southern France. After fighting in the French Revolutionary Wars, he was promoted to command an infantry regiment at the beginning of the First French Empire. He led the unit during the War of the Third Coalition in 1805. The following year he fought in the War of the Fourth Coalition. The year 1808 found him at Zaragoza in Spain where he was wounded. In 1809 he led a brigade during the War of the Fifth Coalition at Gefrees.

Antoine Louis Popon de Maucune led a French division against the British in 1811–1813 during the Peninsular War. He is referred to as Maucune in English-language sources. He joined the pioneer corps of the French army in 1786 and was a lieutenant by the time the French Revolutionary Wars broke out. He fought in the north in 1792 and in the Alps in 1793. Afterward he served in Italy through 1801. During this period, he fought at Arcole in 1796 and at Trebbia, Novi and Genola in 1799. He was appointed to command the 39th Line Infantry Demi-Brigade and led it in the 1800 campaign.

In the Battle of Tordesillas, Battle of Villa Muriel or Battle of Palencia between 25 and 29 October 1812, a French army led by Joseph Souham pushed back an Anglo-Portuguese-Spanish army commanded by Arthur Wellesley, Marquess Wellington. After its failed Siege of Burgos, the 35,000-man Allied army withdrew to the west, pursued by Souham's 53,000 French soldiers. On 23 October, French cavalry defeated the Allied rear guard in the Battle of Venta del Pozo. The Allies pulled back behind the Pisuerga and Carrión Rivers and took up a defensive position.

In the siege of Pamplona, a Spanish force led by Captain General Henry O'Donnell and later Major General Carlos de España blockaded an Imperial French garrison under the command of General of Brigade Louis Pierre Jean Cassan. At first, troops under Arthur Wellesley, Marquess Wellington surrounded the city, but they were soon replaced by Spanish units. In late July 1813, Marshal Nicolas Soult attempted to relieve the city but his operation failed in the Battle of the Pyrenees. Cassan capitulated to the Spanish after the French troops in the city were reduced to starvation. The surrender negotiations were marred by French bluffs to blow up the fortifications and Spanish threats to massacre the garrison, neither of which occurred. Pamplona is located on the Arga River in the province of Navarre in northern Spain. The siege occurred during the Peninsular War, part of the Napoleonic Wars.
In the Battles of San Millán and Osma two divisions of the Allied army of Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington clashed with two divisions of King Joseph Bonaparte's Imperial French army in northeast Spain. "extremely punishing couple of miniature battles at Osma and San Millan which ruined Maucune's division and sent the Army of ... There were in fact two armies involved in the campaign of 1813 " "Contact was, however, inevitable and on 18 June there was a sharp fight at the small village of San Millan, when the Light ... The French tried to make a stand at Osma the same day, but this was effortlessly beaten back and with it went .."

The Battle of Tolosa saw a British-Portuguese-Spanish column led by Thomas Graham attempt to cut off a retreating Franco-Italian force under Maximilien Sébastien Foy. Assisted by Antoine Louis Popon de Maucune's division, which fortuitously appeared, the French parried Graham's initial attacks then slipped away when threatened with envelopment. The town of Tolosa is located about 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of San Sebastián. The clash occurred during the Peninsular War, part of the wider Napoleonic Wars.

The campaign in south-west France in late 1813 and early 1814 was the final campaign of the Peninsular War. An allied army of British, Portuguese and Spanish soldiers under the command of Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington fought a string of battles against French forces under the command of Marshal Jean de Dieu Soult, from the Iberian Peninsula across the Pyrenees and into south-west France ending with the capture of Toulouse and the besieging of Bayonne.



















