
The Windover Archeological Site is a Middle Archaic archaeological site and National Historic Landmark in Brevard County near Titusville, Florida, United States on the central east coast of the state. Windover is a muck pond where skeletal remains of 168 individuals were found buried in the peat at the bottom of the pond. The skeletons were well preserved because of the peat. In addition, remarkably well-preserved brain tissue has been recovered from 91 skulls from the site. DNA from the brain tissue has been sequenced. The collection of human skeletal remains and artifacts recovered from Windover Pond represent among the largest finds of each type from the Archaic Period. It is considered one of the most important archeological sites ever excavated.

The Weeden Island cultures are a group of related archaeological cultures that existed during the Late Woodland period of the North American Southeast. The name for this group of cultures was derived from the Weedon Island site in Old Tampa Bay in Pinellas County.

The Jaega were Native Americans living in a chiefdom of the same name, which included the coastal parts of present-day Martin County and northern Palm Beach County, Florida at the time of initial European contact, and until the 18th century. The name Jobé, or Jové, has been identified as a synonym of Jaega, a sub-group of the Jaega, or a town of the Jaega.
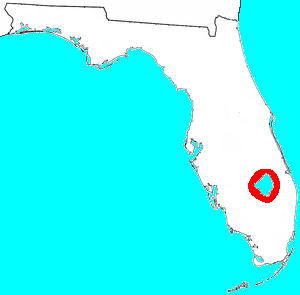
The Mayaimi were Native American people who lived around Lake Mayaimi in the Belle Glade area of Florida from the beginning of the Common Era until the 17th or 18th century. In the languages of the Mayaimi, Calusa, and Tequesta tribes, Mayaimi meant "big water." The origin of the language has not been determined, as the meanings of only ten words were recorded before extinction. The linguist Julian Granberry states that the language of the Calusa, Mayaimi and Tequesta people is related to the Tunica language. The current name, Okeechobee, is derived from the Hitchiti word meaning "big water". The Mayaimis have no linguistic or cultural relationship with the Miami people of the Great Lakes region. The city of Miami is named after the Miami River, which derived its name from Lake Mayaimi.

Crystal River State Archaeological Site is a 61-acre (250,000 m2) Florida State Park located on the Crystal River and within the Crystal River Preserve State Park. The park is located two miles (3 km) northwest of the city of Crystal River, on Museum Point off U.S. 19/98.
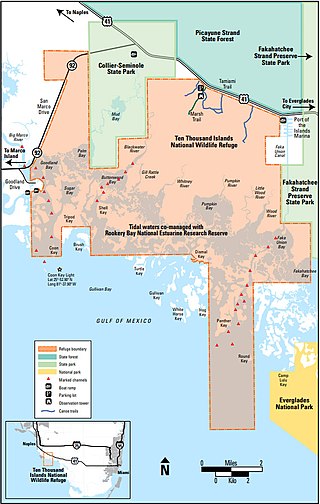
The Ten Thousand Islands are a chain of islands and mangrove islets off the coast of southwest Florida, between Cape Romano and the mouth of the Lostmans River. Some of the islands are high spots on a submergent coastline. Others were produced by mangroves growing on oyster bars. Despite the name, the islets in the chain only number in the hundreds.

Horr's Island is a significant Archaic period archaeological site located on an island in Southwest Florida formerly known as Horr's Island. Horr's Island is on the south side of Marco Island in Collier County, Florida. The site includes four mounds and a shell ring. It has one of the oldest known mound burials in the eastern United States, dating to about 3400 radiocarbon years Before Present (BP). One of the mounds has been dated to as early as 6700 BP. It was the largest known community in the southeastern United States to have been permanently occupied during the Archaic period.
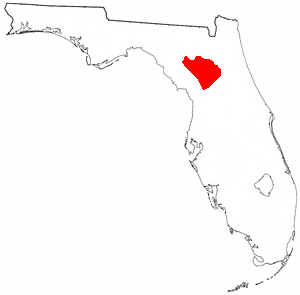
The Alachua culture is a Late Woodland Southeast period archaeological culture in north-central Florida, dating from around 600 to 1700. It is found in an area roughly corresponding to present-day Alachua County, the northern half of Marion County and the western part of Putnam County. It was preceded by the Cades Pond culture, which inhabited approximately the same area.

The Cades Pond culture is defined as a Middle Woodland Southeast period archaeological culture in north-central Florida, dating from around 100 to 600 CE.
The Belle Glade culture, or Okeechobee culture, is an archaeological culture that existed from as early as 1000 BCE until about 1700 CE in the area surrounding Lake Okeechobee and in the Kissimmee River valley in the Florida Peninsula.
The Caloosahatchee culture is an archaeological culture on the Gulf coast of Southwest Florida that lasted from about 500 to 1750 AD. Its territory consisted of the coast from Estero Bay to Charlotte Harbor and inland about halfway to Lake Okeechobee, approximately covering what are now Charlotte, Lee, and Collier counties. At the time of first European contact, the Caloosahatchee culture region formed the core of the Calusa domain.
The Glades culture is an archaeological culture in southernmost Florida that lasted from about 500 BCE until shortly after European contact. Its area included the Everglades, the Florida Keys, the Atlantic coast of Florida north through present-day Martin County and the Gulf coast north to Marco Island in Collier County. It did not include the area around Lake Okeechobee, which was part of the Belle Glade culture.
The Yent Mound (8FR5) is a Santa Rosa-Swift Creek culture archaeological site located on Alligator Harbor west of St. Teresa, Florida. It is on the east side of County Road 370, approximately 2.5 miles from the junction of U.S. Route 98. On May 24, 1973, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

Mount Royal (8PU35) is a U.S. archaeological site close to where the St. Johns River exits from Lake George in Putnam County, Florida. It is located three miles (5 km) south of Welaka, in the Mount Royal Airpark, off County Road 309 on the eastern bank of the St. Johns River. The site consists of a large sand mound and several nearby middens.
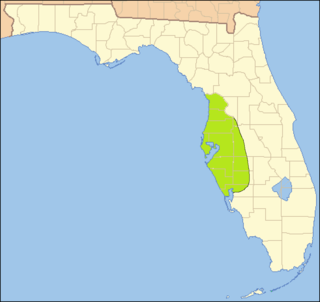
The Safety Harbor culture was an archaeological culture practiced by Native Americans living on the central Gulf coast of the Florida peninsula, from about 900 CE until after 1700. The Safety Harbor culture is defined by the presence of Safety Harbor ceramics in burial mounds. The culture is named after the Safety Harbor site, which is close to the center of the culture area. The Safety Harbor site is the probable location of the chief town of the Tocobaga, the best known of the groups practicing the Safety Harbor culture.
Fort Center is an archaeological site in Glades County, Florida, United States, a few miles northwest of Lake Okeechobee. It was occupied for more than 2,000 years, from 450 BCE until about 1700 CE. The inhabitants of Fort Center may have been cultivating maize centuries before it appeared anywhere else in Florida.

The Manasota culture was an archaeological culture that was practiced on the central Gulf coast of the Florida peninsula from about 500 BCE until about 900, when it developed into the Safety Harbor culture. From about 300 to 700 the Manasota culture adopted the ceremonial ceramics and burial practices of the Weeden Island cultures of northern Florida and adjacent Alabama and Georgia.
J.W. Corbett Wildlife Management Area is a protected area of 60,348 acres of land in Florida. It is located east of Lake Okeechobee, 25 miles northwest of West Palm Beach. It includes Big Mound City and is connected to DuPuis Management Area.
The Lawrence E. Will Museum, governed by the Glades Historical Society, is a museum of local history located in Belle Glade, Florida.
Tony's Mound (8HN3) is a prehistoric to historic period archaeological site located on Dixie Dyke Road, south of Clewiston in Hendry County, Florida. Tony's Mound is one of two monumental earthwork complexes built in southern Florida by the Glade cultures around 1000 BCE using unique and distinct sand ridges, causeways and mounds. The other site is Big Mound City, twenty-five miles to the northeast in Palm Beach County. The ritual complex was first described in print by Ross Allen in the 1948. Aerial photography showed a site consisting of nine raised causeways radiating from an immense plaza and central flat mound/midden on privately owned land used for cattle ranching.












