| Bronze-tailed comet | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Clade: | Strisores |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Trochilidae |
| Tribe: | Lesbiini |
| Genus: | Polyonymus Heine, 1863 |
| Species: | P. caroli |
| Binomial name | |
| Polyonymus caroli (Bourcier, 1847) | |
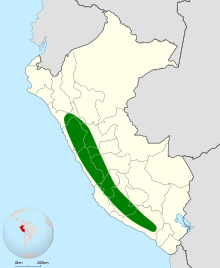 | |
The bronze-tailed comet (Polyonymus caroli) is a species of hummingbird in the "coquettes", tribe Lesbiini of subfamily Lesbiinae. It is endemic to Peru. [3] [4]








