Design
For 1958, Chevrolet models were redesigned longer, lower, and heavier than their 1957 predecessors. The first ever production Chevrolet big block V8, the 348 cu in (5,700 cc), was now an option. Chevrolet's design for the year fared better than its other GM offerings, and lacked the overabundance of chrome found on Pontiacs, Oldsmobiles, Buicks and Cadillacs. Complementing Chevrolet's front design was a broad grille and quad headlights that helped simulate a 'Baby Cadillac'; the wagon's tail received a fan-shaped alcove on both side panels, similar to the sedan's, but wagons housed single tail lights instead of dual (triple on Impala) to accommodate the tailgate.
Despite being a recession year, sales increased and overtook Ford, which held the top position in 1957) and the Bel Air the most popular Chevrolet model. The Nomad station wagon name also reappeared in 1958 when the vehicle became as the premium four-door Chevrolet station wagon, rather than the two-door designs of the 1955-57 Nomads.
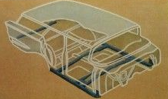
A new dash was used. [1] The value of a drag coefficient for 1958 Chevy wagons is estimated by a-c, is Cd = 0.6. [2] The Delray-based Yeoman was the lowest version and featured minimal interior and exterior trim and limited options.

The Chevrolet Impala is a full-size car that was built by Chevrolet for model years 1958 to 1985, 1994 to 1996, and 2000 to 2020. The Impala was Chevrolet's popular flagship passenger car and was among the better-selling American-made automobiles in the United States.

The Chevrolet Chevelle is a mid-sized automobile that was produced by Chevrolet in three generations for the 1964 through 1978 model years. Part of the General Motors (GM) A-body platform, the Chevelle was one of Chevrolet's most successful nameplates. Body styles included coupes, sedans, convertibles, and station wagons. The "Super Sport" versions were produced through the 1973 model year and Lagunas from 1973 through to 1976.

The Chevrolet Biscayne was a series of full-size cars produced by the American manufacturer Chevrolet between 1958 and 1975. Named after a show car displayed at the 1955 General Motors Motorama, the Biscayne was the least expensive model in the Chevrolet full-size car range. The absence of most exterior and fancy interior trimmings remained through the life of the series, as the slightly costlier Chevrolet Bel Air offered more interior and exterior features at a price significantly lower than the top-of-the-line Impala and Caprice.

The Chevrolet Caprice is a full-sized automobile produced by Chevrolet in North America for the 1965 to 1996 model years. Full-size Chevrolet sales peaked in 1965 with over a million sold. It was the most popular car in the U.S. in the 1960s and early 1970s, which, during its lifetime, included the Biscayne, Bel Air, and Impala.

The Chevrolet Bel Air is a full-size car produced by Chevrolet for the 1950–1981 model years. Initially, only the two-door hardtops in the Chevrolet model range were designated with the Bel Air name from 1950 to 1952. With the 1953 model year, the Bel Air name was changed from a designation for a unique body shape to a premium level of trim applied across a number of body styles. The Bel Air continued with various other trim level designations, and it had gone from a mid-level trim car to a budget fleet sedan when U.S. production ceased in 1975. Production continued in Canada, for its home market only, through the 1981 model year.

The Pontiac Catalina is a full-size, junior series automobile produced by Pontiac from 1950 to 1981. Initially, the name was a trim line on hardtop body styles, first appearing in the 1950 Chieftain Eight and DeLuxe Eight lines. In 1959, it became a separate model as the "entry-level" full-size Pontiac.

The Chevrolet El Camino is a coupé utility vehicle that was produced by Chevrolet between 1959–60 and 1964–1987. Unlike a standard pickup truck, the El Camino was adapted from the standard two-door Chevrolet station wagon platform and integrated the cab and cargo bed into the body.

The Chevrolet Delray, named after the Delray neighborhood of Detroit, Michigan, debuted in 1954 as an optional trim level on two-door models of Chevrolet's mid-range 210 series of cars. In 1958, it became a distinct series of its own at the bottom of Chevrolet's lineup, and added a four-door sedan, and sedan delivery, but it only remained in production for that model year.

The Ford Fairlane is an automobile model that was sold between the 1955 and 1970 model years by Ford in North America. Taking its name from the Dearborn, Michigan estate of Henry Ford, the Fairlane nameplate was used for seven different generations of vehicles. Through its production, the model line would be marketed in a wide variety of body styles, including two-door and four-door sedans, two-door and four-door hardtops, station wagons, and both traditional and retractable-hardtop convertibles.

The Chevrolet Brookwood is a series of full-size station wagons produced by Chevrolet from 1958 to 1961, and again from 1969 to 1972. It debuted in 1958 as Chevrolet's mid-range model in its station wagon lineup, positioned between the less expensive Yeoman and more luxurious Nomad station wagons. After the Yeoman was discontinued in 1959, the Brookwood was subsequently demoted to entry-level status, before going out of production altogether in 1961. It made a brief reappearance from 1969 and 1972, once again as the least-expensive wagon in Chevrolet's lineup.

The 1957 Chevrolet is a car that was introduced by Chevrolet in September 1956 for the 1957 model year. It was available in three series models: the upscale Bel Air, the mid-range Two-Ten, and the One-Fifty. A two-door station wagon, the Nomad, was produced as a Bel Air model. An upscale trim option called the Delray was available for Two-Ten 2-door sedans. It is a popular and sought after classic car. These vehicles are often restored to their original condition and sometimes modified. The car's image has been frequently used in toys, graphics, music, movies, and television. The '57 Chevy, as it is often known, is an auto icon.

Chevrolet Nomad is a nameplate used by Chevrolet in North America from the 1950s to the 1970s, applied largely to station wagons. Three different Nomads were produced as a distinct model line, with Chevrolet subsequently using the name as a trim package.

The Chevrolet One-Fifty was the economy/fleet model of the Chevrolet car from 1953 until 1957. It took its name by shortening the production series number (1500) by one digit in order to capitalize on the numerical auto name trend of the 1950s. The numerical designation "150" was also sporadically used in company literature. It replaced the Styleline Special model available in previous years. This model was dropped following the 1957 model year and replaced by the Delray.
The Chevrolet Kingswood was a 4-door station wagon produced by Chevrolet in 1959 and 1960, and again from 1969 to 1972 built on the GM B Body platform.

The 1955 Ford is an automobile which was produced by Ford in the United States for the 1955 model year and, in revised form, for the 1956 model year. A new design would be offered in 1957.

The Chevrolet 210 or Two-Ten is a midrange car from Chevrolet that was marketed from 1953 until 1957. It took its name by shortening the production series number 2100 by one digit in order to capitalize on the 1950s trend toward numerical auto names. The numerical designation "210" was also sporadically used in company literature. It replaced the Styleline DeLuxe model available in previous years. The 210 was discontinued after the 1957 model year to be replaced by the Biscayne.
The Chevrolet Parkwood was a station wagon built by Chevrolet from 1959 to 1961. As the station wagon equivalent of the Bel Air passenger car series, it represented the middle member of the Chevrolet station wagon lineup of those years, above the lowest-priced Brookwood models, but below the luxury-leader Nomad.

The fifth generation of the Chevrolet Impala is a line of full-size cars produced by Chevrolet from the 1971 to 1976 model years. The largest generation of the model line, the fifth-generation Impala grew to a 121.5-inch wheelbase

The Chevrolet Impala (fourth generation) are full-size automobiles produced by Chevrolet for the 1965 through 1970 model years. The 1965 Impala was all new, while the 1967 and 1969 models featured new bodies on the same redesigned perimeter frame introduced on the 1965 models. All Impalas of this generation received annual facelifts as well, distinguishing each model year. Throughout the early 1960s, Chevrolet's basic body designs became increasingly subtle, while the bright trim that was part of the Impala package added more than a touch of luxury to the look. The same pattern was followed in the interiors, where the best materials and equipment Chevrolet had to offer were displayed. In short, the Impala was on its way to becoming a kind of junior-grade Cadillac, which, for both the company and its customers, was just fine.

The Chevrolet Van or Chevy Van is a range of vans that was manufactured by General Motors from the 1964 to 1996 model years. Introduced as the successor for the rear-engine Corvair Corvan/Greenbrier, the model line also replaced the panel van configuration of the Chevrolet Suburban. The vehicle was sold both in passenger van and cargo van configurations as well as a cutaway van chassis that served as the basis for a variety of custom applications.