
The putamen is a round structure located at the base of the forebrain (telencephalon). The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. It is also one of the structures that comprise the basal nuclei. Through various pathways, the putamen is connected to the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, the claustrum, and the thalamus, in addition to many regions of the cerebral cortex. A primary function of the putamen is to regulate movements at various stages and influence various types of learning. It employs GABA, acetylcholine, and enkephalin to perform its functions. The putamen also plays a role in degenerative neurological disorders, such as Parkinson's disease.

The striatum, or corpus striatum, is a nucleus in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia.

The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. Substantia nigra is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of neuromelanin in dopaminergic neurons. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.

The basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates, including humans, which are situated at the base of the forebrain and top of the midbrain. There are some differences in the basal ganglia of primates. Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion.
In neuroanatomy, a nucleus is a cluster of neurons in the central nervous system, located deep within the cerebral hemispheres and brainstem. The neurons in one nucleus usually have roughly similar connections and functions. Nuclei are connected to other nuclei by tracts, the bundles (fascicles) of axons extending from the cell bodies. A nucleus is one of the two most common forms of nerve cell organization, the other being layered structures such as the cerebral cortex or cerebellar cortex. In anatomical sections, a nucleus shows up as a region of gray matter, often bordered by white matter. The vertebrate brain contains hundreds of distinguishable nuclei, varying widely in shape and size. A nucleus may itself have a complex internal structure, with multiple types of neurons arranged in clumps (subnuclei) or layers.

The globus pallidus also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rodents as the entopeduncular nucleus. It is part of the telencephalon, but retains close functional ties with the subthalamus in the diencephalon – both of which are part of the extrapyramidal motor system. The globus pallidus is a major component of the basal ganglia, with principal inputs from the striatum, and principal direct outputs to the thalamus and the substantia nigra. The latter is made up of similar neuronal elements, has similar afferents from the striatum, similar projections to the thalamus, and has a similar synaptology. Neither receives direct cortical afferents, and both receive substantial additional inputs from the intralaminar thalamus.

The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. The internal capsule contains both ascending and descending axons, going to and coming from the cerebral cortex. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.
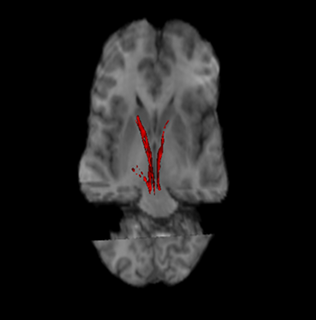
The nigrostriatal pathway is a bilateral dopaminergic pathway in the brain that connects the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) in the midbrain with the dorsal striatum in the forebrain. It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain, and is critical in the production of movement as part of a system called the basal ganglia motor loop. Dopaminergic neurons of this pathway release dopamine from axon terminals that synapse onto GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons (SPNs), located in the striatum.

The indirect pathway, sometimes known as the indirect pathway of movement, is a neuronal circuit through the basal ganglia and several associated nuclei within the central nervous system (CNS) which helps to prevent unwanted muscle contractions from competing with voluntary movements. It operates in conjunction with the direct pathway.

The lentiform nucleus, or lenticular nucleus, comprises the putamen and the globus pallidus within the basal ganglia. With the caudate nucleus, it forms the striatum. It is a large, lens-shaped mass of gray matter just lateral to the internal capsule.

The subthalamus or prethalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its most prominent structure is the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamus connects to the globus pallidus, a basal nucleus of the telencephalon.

The basal ganglia form a major brain system in all species of vertebrates, but in primates there are special features that justify a separate consideration. As in other vertebrates, the primate basal ganglia can be divided into striatal, pallidal, nigral, and subthalamic components. In primates, however, there are two pallidal subdivisions called the external globus pallidus (GPe) and internal globus pallidus (GPi). Also in primates, the dorsal striatum is divided by a large tract called the internal capsule into two masses named the caudate nucleus and the putamen—in most other species no such division exists, and only the striatum as a whole is recognized. Beyond this, there is a complex circuitry of connections between the striatum and cortex that is specific to primates. This complexity reflects the difference in functioning of different cortical areas in the primate brain.

Medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons, are a special type of GABAergic inhibitory cell representing 95% of neurons within the human striatum, a basal ganglia structure. Medium spiny neurons have two primary phenotypes : D1-type MSNs of the direct pathway and D2-type MSNs of the indirect pathway. Most striatal MSNs contain only D1-type or D2-type dopamine receptors, but a subpopulation of MSNs exhibit both phenotypes.
Premovement neuronal activity in neurophysiological literature refers to neuronal modulations that alter the rate at which neurons fire before a subject produces movement. Through experimentation with multiple animals, predominantly monkeys, it has been shown that several regions of the brain are particularly active and involved in initiation and preparation of movement. Two specific membrane potentials, the bereitschaftspotential, or the BP, and contingent negative variation, or the CNV, play a pivotal role in premovement neuronal activity. Both have been shown to be directly involved in planning and initiating movement. Multiple factors are involved with premovement neuronal activity including motor preparation, inhibition of motor response, programming of the target of movement, closed-looped and open-looped tasks, instructed delay periods, short-lead and long-lead changes, and mirror motor neurons.

The ventral lateral nucleus (VL) is a nucleus in the ventral nuclear group of the thalamus.

The external globus pallidus combines with the internal globus pallidus (GPi) to form the globus pallidus, an anatomical subset of the basal ganglia. Globus pallidus means "pale globe" in Latin, indicating its appearance. The external globus pallidus is the segment of the globus pallidus that is relatively further (lateral) from the midline of the brain.

The internal globus pallidus and the external globus pallidus (GPe) make up the globus pallidus. The GPi is one of the output nuclei of the basal ganglia. The GABAergic neurons send their axons to the ventral anterior nucleus (VA) and the ventral lateral nucleus (VL) in the dorsal thalamus, to the centromedian complex, and to the pedunculopontine complex.

Basal ganglia disease is a group of physical problems that occur when the group of nuclei in the brain known as the basal ganglia fail to properly suppress unwanted movements or to properly prime upper motor neuron circuits to initiate motor function. Research indicates that increased output of the basal ganglia inhibits thalamocortical projection neurons. Proper activation or deactivation of these neurons is an integral component for proper movement. If something causes too much basal ganglia output, then the ventral anterior (VA) and ventral lateral (VL) thalamocortical projection neurons become too inhibited, and one cannot initiate voluntary movement. These disorders are known as hypokinetic disorders. However, a disorder leading to abnormally low output of the basal ganglia leads to reduced inhibition, and thus excitation, of the thalamocortical projection neurons which synapse onto the cortex. This situation leads to an inability to suppress unwanted movements. These disorders are known as hyperkinetic disorders.

Blocq's disease was first considered by Paul Blocq (1860–1896), who described this phenomenon as the loss of memory of specialized movements causing the inability to maintain an upright posture, despite normal function of the legs in the bed. The patient is able to stand up, but as soon as the feet are on the ground, the patient cannot hold himself upright nor walk; however when lying down, the subject conserved the integrity of muscular force and the precision of movements of the lower limbs. The motivation of this study came when a fellow student Georges Marinesco (1864) and Paul published a case of parkinsonian tremor (1893) due to a tumor located in the substantia nigra.

The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop is a system of neural circuits in the brain. The loop involves connections between the cortex, the basal ganglia, the thalamus, and back to the cortex. It is of particular relevance to hyperkinetic and hypokinetic movement disorders, such as Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease, as well as to mental disorders of control, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), and Tourette syndrome.














