Related Research Articles

Abgar V, called Ukkāmā meaning "the Black", was the King of Osroene with his capital at Edessa.
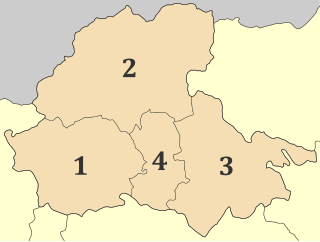
Pella is one of the regional units of Greece, in the geographic region of Macedonia. It is part of the Region of Central Macedonia. It is named after the ancient city of Pella, the capital of ancient Macedonia and the birthplace of Alexander the Great. The capital of Pella is Edessa with a population of 19,036 inhabitants according to the census of 2011, while the largest city and industrial and commercial center is Giannitsa with 29,789 inhabitants. Other centers are the towns Krya Vrisi, Aridaia and Skydra.

Osroene, also spelled Osroëne and Osrhoene and sometimes known by the name of its capital city, Edessa, was a historical kingdom in Upper Mesopotamia, which was ruled by the Abgarid dynasty of Arab origin. Generally allied with the Parthians, the Kingdom of Osroene enjoyed semi-autonomy to complete independence from the years of 132 BC to AD 214. Though ruled by a dynasty of Arab origin, the kingdom's population was mainly Aramean with a Greek and Parthian admixture. In addition, though Arab cults were attested at Edessa, the city's cultural setting was fundamentally Aramaic alongside strong Parthian influences.

The County of Edessa was one of the Crusader states in the 12th century. Its seat was the city of Edessa.

Edessa was a city in Upper Mesopotamia, founded on an earlier site by Seleucus I Nicator ca. 302 BC. It was also known as Antiochia on the Callirhoe from the 2nd century BC. It was the capital of the semi-independent kingdom of Osroene from c. 132 BC and fell under direct Roman rule in ca. 242. It became an important early centre of Syriac Christianity.

Central Macedonia is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the geographical and historical region of Macedonia. With a population of almost 1.9 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.
Jacob of Edessa was one of the most distinguished of Syriac writers.
Matthew of Edessa was an Armenian historian in the 12th century from the city of Edessa. Matthew was the superior abbot of Karmir Vank', near the town of Kessoun, east of Marash (Germanicia), the former seat of Baldwin of Boulogne. He relates much about the Bagratuni Kingdom of Armenia, the early Crusades, and the battles between Byzantines and Arabs for the possession of parts of northern Syria and eastern Asia Minor. Byzantine authors such as Joannes Zonaras and Anna Comnena were well versed in their particular spheres, but uninformed regarding Edessa and neighboring lands which are treated by Matthew.
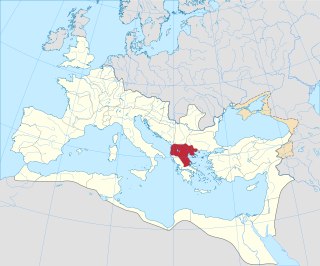
The Roman province of Macedonia was officially established in 146 BC, after the Roman general Quintus Caecilius Metellus defeated Andriscus of Macedon, the last self-styled King of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia in 148 BC, and after the four client republics established by Rome in the region were dissolved. The province incorporated the former kingdom of Macedonia with the addition of Epirus, Thessaly, and parts of Illyria, Paeonia and Thrace. This created a much larger administrative area, to which the name of 'Macedonia' was still applied.

Edessa, until 1923 Vodena, is a city in northern Greece and the capital of the Pella regional unit, in the Central Macedonia region of Greece. It was also the capital of the defunct province of the same name.

Mandritsa is a village in southernmost Bulgaria, part of Ivaylovgrad municipality, Haskovo Province. It is known as the only Albanian village in Bulgaria. As of 14 December 2006, Mandritsa has a population of 75. It lies at 41°23′N26°8′E, 93 m above sea level.

Edessaikos Football Club is a football club based in Edessa, Greece currently playing in the Gamma Ethniki. Edessaikos was founded in 1959.

European route E86 is a road part of the International E-road network. It begins in Krystallopigi, Greece and ends in Gefyra, Greece.
Giannitsa Province was one of the three provinces of Pella Prefecture of Greece. It was the largest province from the other two Edessa and Almopia and the base is the city of Giannitsa. It occupied the eastern part of the prefecture. It belongs to the Region of Central Macedonia. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipality Pella, and the municipal unit Meniida. It was abolished in 2006.

Proastiakos Thessaloniki, or Thessaloniki Suburban Railway, is a two-line Proastiakos commuter rail service connecting Thessaloniki's New Railway Station with Edessa/Florina and Larissa. It is operated using Siemens Desiro multiple units ran by the TrainOSE, the passenger railway subsidiary of the Hellenic Railways Organisation.

The Edessa railway station is the railway station of Edessa in Central Macedonia, Greece. Built in the early 1890s under Ottoman rule, when the town was called Vodena, the station is located north of the city on the Thessaloniki–Bitola railway. It is still housed in the original station building. There is no footbridge over the lines, so passengers must walk across the rails.

Neokosmos Grigoriadis was a Greek Army general, notable for his involvement in the Greek Resistance during World War II as a leading member of the left-wing National Liberation Front (EAM).

The Acts of Thaddeus is a Greek document written between 544 and 944 CE which purports to describe correspondence between King Abgar V of Edessa and Jesus, which results in Jesus' disciple Thaddeus going to Edessa.
The 1992–93 season of the Balkans Cup club tournament was the 27th season of the competition. It was won by Greek side Edessaikos in the final against Bulgarian Etar Veliko Tarnovo for their first title in the competition.
Mar Paul, usually known as Paul of Edessa or Paul of Cyprus, was the Byzantine Syriac Orthodox metropolitan of Edessa who was forced to abandon his see between about 602 and 629, when it fell under the Sasanian Empire. He was an important translator of Greek theological works into Syriac. He should not be confused with the Bishop Paul of Edessa who died in 526.
References
- ↑ "Detailed census results 1991" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. (39 MB)(in Greek and French)
| This Central Macedonia location article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |