Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is based on several competencies intended to enhance success in their personal, professional, and social lives. These kinds of competencies develop throughout life, but they are not explicitly taught.
Training actions are offered by companies, public administrations, entities, institutions, and social agents to develop such competencies. However, these methods are not complete.
Competencies
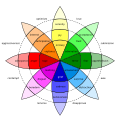
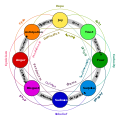
The emotional thought method proposes seven competencies. Four pertain to the self: self-knowledge, self-evaluation, emotional control, and personal motivation; and three pertain to others: knowledge of others, appreciation of others, and control of them.
- Self-knowledge includes knowledge of personal capacities, skills, personality, interests, goals, etc. It involves introspection, knowledge of skills, personal emotions, ability to apply self-criticism, and self-awareness.
- Self-evaluation requires knowledge of self and some degree of self-esteem. Self-esteem is advanced as the driving force of behaviour. This competence is the result of developing sensibility, sensuality, sexuality, optimism, happiness and self-esteem.
- Emotional control involves managing stress, fear and anxiety by developing three emotional skills: motor inhibition, self-control, and mental control.
- Personal motivation involves learning activation, productivity, quality, instrumental tools, globality, planning, culture, innovation, interests' wideness, determination and evaluation.
- Three competences in this emotional method are oriented to how to make relationships. Knowledge of others involves knowing their personality, interests, aptitudes, empathy, communication ability, social analysis, and appreciation of diversity.
- Appreciation of others involves ten abilities. They are structured in four groups:
The last competence is control of others. This competence has been criticized as not respectful of others, even to persuade others to pursue their interests. This involves the capacity to have relations, the capacity to organize groups, the capacity to solve conflicts, and leadership.
These seven competencies are developed through exercises, as much as in Hué's book, as in the TREIN project.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.