
Crotonogyne is a shrub of the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae) first described as a genus in 1864. It is native to western and central Africa. It is dioecious.

The Guinean forests of West Africa is a biodiversity hotspot designated by Conservation International, which includes the belt of tropical moist broadleaf forests along the coast of West Africa, running from Sierra Leone and Guinea in the west to the Sanaga River of Cameroon in the east. The Dahomey Gap, a region of savanna and dry forest in Togo and Benin, divides the Guinean forests into the Upper Guinean forests and Lower Guinean forests.

Moloney's mimic bat is a species of vesper bat. It can be found in Benin, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, Mozambique, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, and Zambia. It is found in subtropical or tropical dry, moist, montane, or mangrove forests and in savanna.

Fraser's sunbird or the scarlet-tufted sunbird, is a species of bird in the family Nectariniidae. It is found in Angola, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Mali, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, Togo, and Uganda.

Palisota is a genus of plant in family Commelinaceae, first described in 1828. It is native to sub-Saharan Africa.
Podococcus is a genus of palms found in tropical Africa. It includes two recognized species:

Laccosperma is a clustering genus of flowering plant in the family palm found in tropical Africa. Poorly studied and rarely cultivated, they are closely related to the genus Eremospatha and with it form a tribe in the Calameae characterized by dyads of hermaphrodite flowers. The genus name combines the Greek words for "reservoir" and "seed".

Cercestis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. The species in this genus are all climbers and are native to Africa. At intervals along the stem they produce long leafless shoots called flagella. Many of the species in Cersestis show signs of fenestration.

Culcasia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to tropical Africa. Most of its species are climbers and resemble Cercestis, except that they do not produce flagella.
- Culcasia angolensisWelw. ex Schott - western + central Africa from Senegal to Angola
- Culcasia annetiiNtépé-Nyamè - Ivory Coast, Cameroon, Liberia
- Culcasia bosiiNtépé-Nyamè - Cameroon, Gabon, Congo-Brazzaville
- Culcasia brevipetiolataBogner - Gabon
- Culcasia caudataEngl. - Zaïre
- Culcasia dinklageiEngl - western + central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre
- Culcasia ekongoloiNtépé-Nyamè - central Africa from Nigeria to Zaïre
- Culcasia falcifoliaEngl. - central Africa from Gabon east to Tanzania and south to Mozambique
- Culcasia glandulosaHepper - Ivory Coast, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Congo-Brazzaville
- Culcasia insulanaN.E.Br. - Zaïre, Cameroon, Gulf of Guinea Islands
- Culcasia lanceolataEngl. - Cameroon, Gabon
- Culcasia libericaN.E.Br. - Ivory Coast, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Togo
- Culcasia linearifoliaBogner - Cameroon, Gabon
- Culcasia loukandensisPellegr - Cameroon, Gabon, Congo-Brazzaville, Zaïre, Central African Republic
- Culcasia mannii(Hook.f.) Engl. - Cameroon, Gabon, Congo-Brazzaville, Nigeria, Equatorial Guinea
- Culcasia obliquifoliaEngl. - Cameroon, Gabon
- Culcasia orientalisMayo - Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, Zambia
- Culcasia panduriformisEngl. & K.Krause - Cameroon, Gabon
- Culcasia parvifloraN.E.Br. - western + central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre
- Culcasia rotundifoliaBogner - Gabon
- Culcasia sanagensisNtépé-Nyamè - Cameroon
- Culcasia scandensP.Beauv. - western + central Africa from Liberia to Angola
- Culcasia seretiiDe Wild - western + central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre
- Culcasia simiarumNtépé-Nyamè - western Africa from Ivory Coast to Cameroon
- Culcasia striolataEngl. - western + central Africa from Liberia to Congo-Brazzaville
- Culcasia tenuifoliaEngl. - western + central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre
- Culcasia yangambiensisLouis & Mullend. - Congo-Brazzaville, Zaïre

Ancistrorhynchus is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family Orchidaceae. It contains 16 species native to tropical Africa.
Cuviera is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae native to tropical Africa. It was originally described by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1807 and is named after the French naturalist Georges Cuvier.
Aulacocalyx is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is found in tropical Africa.

Euxanthe eurinome, the common forest queen, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Senegal, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, the Central African Republic, Uganda, Kenya and Ethiopia. The habitat consists of lowland evergreen forests and dry and degraded forests.

Cymothoe fumana, the scalloped yellow glider, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The habitat consists of forests.

Craterispermum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It contains 16 species that occur in tropical Africa and Seychelles. It is the only genus in the tribe Craterispermeae, of which the divergence time is estimated at 34.8 million years ago.

Eresiomera isca, the common pearly, is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It is found in Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, Bioko, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The habitat consists of forests and swamp forests.
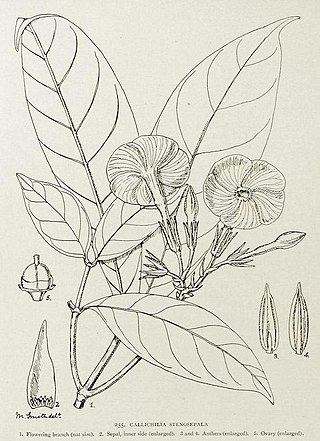
Callichilia is a genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae, native to tropical Africa.

Pleiocarpa is a genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1876. It is native to tropical Africa from Senegal to Tanzania and south to Zimbabwe. As of August 2013 the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families recognises 6 species:
- Pleiocarpa bicarpellataStapf - Cabinda, Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya
- Pleiocarpa brevistylaOmino - Gabon
- Pleiocarpa muticaBenth. - Ghana, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Nigeria, Cameroon, Gabon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo
- Pleiocarpa picralimoides(Pichon) Omino - Cabinda, Republic of the Congo, Gabon
- Pleiocarpa pycnantha(K.Schum) Stapf - widespread across most of tropical Africa
- Pleiocarpa rostrataBenth. - Nigeria, Cameroon, Gabon
- Pleiocarpa camerunensis(K.Schum. ex Hallier f.) Stapf = Hunteria camerunensisK.Schum. ex Hallier f.
- Pleiocarpa hockiiDe Wild. - Acokanthera oppositifolia(Lam.) Codd
- Pleiocarpa simii(Stapf) Stapf ex Hutch. & Dalziel = Hunteria simii(Stapf) H.Huber

Aristolochia macrocarpa, synonym Pararistolochia macrocarpa, is a species of flowering plant in the family Aristolochiaceae native to west and west-central tropical Africa.
Gambeya is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Sapotaceae.
















