| Fall of Herat | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of 2021 Taliban offensive of the War in Afghanistan (2001-2021) of the war on terror of the Afghan conflict | |||||||
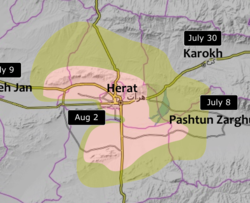 Situation on 7 August Pink: Controlled by the government Grey: Controlled by the Taliban Green: Unclear | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
(Taliban commander) (Taliban commander) (Taliban commander) | (Former Governor of Herat) (Governor of Herat) (Deputy interior minister of Herat) (Herat Provincial Council Chairman) (NDS Chief for Herat) (207th Corps Commander) (Commander of 1st regiment) (Commander of a Commando unit) | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| Taliban forces | Afghan National Security Forces (ANSF)
Public uprising forces | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Unknown | Thousands of government forces surrendered [2] | ||||||
Location within Afghanistan | |||||||
The Fall of Herat was a battle and subsequent capture of Herat by Taliban fighters. The attack on the city started around 28 July 2021, and ended in Taliban victory by 13 August of the same year. Several of the surrounding districts fell to the Taliban from June to mid-July, leaving only the city and two other districts in government hands by 10 July. The border crossings in Herat Province were captured by the Taliban on 9 July, raising prices of goods inside the city. Ismail Khan, former governor and warlord, led a public uprising force to assist the Afghan National Security Forces in defending the city.
Contents
- Background
- Fall of districts in Herat Province
- Ismail Khan
- Battle
- Surrender
- Aftermath
- Significance
- Effects
- Notes
- See also
- References
- External links
After fighting started in the city around the end of July, the Taliban launched a significant attack on 30 July, shutting down the Herat International Airport and temporarily taking the road leading to the airport. A few days later, some Heratis chanted "Allahu Akbar" (God is Great) in support of the government forces. The Taliban insurgents launched another significant attack on the city on 12 August, taking the city by night after a two-week siege. Fall of the city forced Ismail Khan and other top government officials to retreat to the provincial airport and the army corps headquarters outside the city. The next day Ismail Khan and other senior security officials including a deputy for the interior ministry, an army corps commander and an intelligence director, along with thousands of government forces, surrendered to the Taliban. [2]


