Related Research Articles
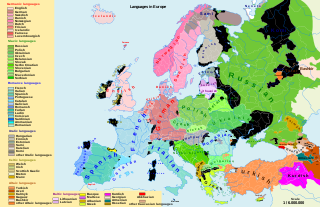
There are over 250 languages indigenous to Europe, and most belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. The three largest phyla of the Indo-European language family in Europe are Romance, Germanic, and Slavic; they have more than 200 million speakers each, and together account for close to 90% of Europeans.
Bozo is a Mande language spoken by the Bozo people of the Inner Niger Delta in Mali. For Fishing, many Bozo are also found in other West African countries where there are Rivers and Dams, such as Nigeria, Burkina Faso and the Ivory Coast. According to the 2000 census, the Bozo people number about 132,100. Bozo is considered a dialect cluster, but there is a quite a bit of diversity. Ethnologue recognises four languages on the basis of requirements for literacy materials. Bozo is part of the northwestern branch of the Mande languages; the closest linguistic relative is Soninke, a major language spoken in the northwestern section of southern Mali, in eastern Senegal, and in southern Mauritania. The Bozo often speak one or more regional languages such as Bambara, Fula, or Western Songhay. The language is tonal, with three lexical tones.
The Magar language or Magar ḍhuṭ is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken mainly in Nepal, southern Bhutan, and in Darjeeling, Assam and Sikkim, India, by the Magar people. It is divided into two groups and further dialect divisions give distinct tribal identity. In Nepal 810,000 people speak the language. Despite Magars not having a state for its own country the Magar language is an additional official language in Gandaki Province, Nepal and the Indian state of Sikkim.

Tamang is a term used to collectively refer to a dialect cluster spoken mainly in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang and other Tamang languages varies between 81% and 63%. For comparison, the lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese is estimated at 89%.
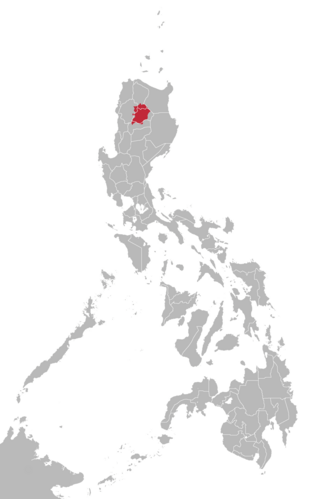
Kalinga is a dialect continuum of Kalinga Province in the Philippines, spoken by the Kalinga people, alongside Ilocano. The Banao Itneg variety is not one of the neighboring Itneg languages.

Ifugao or Batad is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in the northern valleys of Ifugao, Philippines. It is a member of the Northern Luzon subfamily and is closely related to the Bontoc and Kankanaey languages. It is a dialect continuum, and its four main varieties—such as Tuwali—are sometimes considered separate languages.

Bontoc (Bontok) is the native language of the indigenous Bontoc people of the Mountain Province, in the northern part of the Philippines.
The Mnong language belongs to the Austro-Asiatic language family. It is spoken by the different groups of Mnong in Vietnam and a Pnong group in Cambodia.
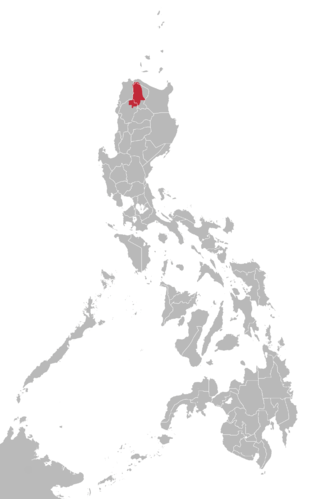
Isnag is a language spoken by around 40,000 Isnag people of Apayao Province in the Cordillera Administrative Region in the northern Philippines. Around 85% of Isnag are capable of reading the Isnag language. Many Isnag speakers also speak Ilocano.

Bhujel, also called Bujhyal, is a Chepangic language of Greater Magaric Branch spoken in central Nepal. It is a semi-tonal language, employing a complex array of affixes. It is believed that their original homeland was Nisi-Buji area of Baglung. In addition, Bhujel term is also the clan name of various ethnic groups including Brahmin, Chhetri & Magar. Bhujel people normally are with Mongoloid features rather than with Caucasoid features. Due to the social structure & social development, This term has been the identity of many other ethnic people too.
Fali comprises two languages spoken in northern Cameroon. Included in Greenberg's Adamawa languages, it was excluded from that family by Boyd (1989). Roger Blench suspects it may represent one of the earlier lineages to have branched off the Atlantic–Congo stock.
Tusya, also spelled Tusiã, Tusian, Toussian and also known as Wín, is a language of Burkina Faso that is of uncertain affiliation within Niger-Congo. It may be a Gur language.
Baram is a critically endangered Sino-Tibetan language spoken in Nepal. Speakers are shifting to Nepali. Dialects are Dandagaun and Mailung.
Moklen is an Austronesian language spoken on the western coast of southern Thailand. It is related to but distinct from the Moken language of Myanmar and southern Thailand. Unlike Moken, it is not spoken in Myanmar.
Guiyang Miao, also known as Guiyang Hmong, is a Miao language of China. It is named after Guiyang, Guizhou, though not all varieties are spoken there. The endonym is Hmong, a name it shares with the Hmong language.
Agusan is a Manobo language of northeastern Mindanao in the Philippines.
Lohorung, also spelled Lorung, Lohrung or Loharung, is a Kirati language of eastern Nepal. It has been described by George van Driem.
Kutang, also known as Kutang Ghale,Kuke, and Kukay, is a minor Tibeto-Burman language of Nepal. Anthropologist Geoff Childs notes that "the term Kukay literally means "Language of Kutang," but it has a double meaning in that the first syllable - ku, for Kutang - is a homonym of the first sylllbe of the Tibetan word for their, kuma. Therefore, Kukay is also interpreted to mean "stolen language," since it incorporates words and phrases from several neighboring languages, including Tibetan."
Lawa is a Mon–Khmer language of Thailand. There are two distinct varieties or dialects of Lawa, considered to be separate languages; their names in the Ethnologue are Eastern Lawa and Western Lawa. They are spoken in Lawa villages in the provinces of Mae Hong Son and Chiang Mai in Northern Thailand.

Itneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
References
- ↑ Northern at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Southern at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
