Related Research Articles

Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical ancient Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one body of classical architecture. Roman architecture flourished in the Roman Republic and to an even greater extent under the Empire, when the great majority of surviving buildings were constructed. It used new materials, particularly Roman concrete, and newer technologies such as the arch and the dome to make buildings that were typically strong and well engineered. Large numbers remain in some form across the former empire, sometimes complete and still in use today.

An entablature is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave, the frieze, and the cornice. The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to classical architecture:

In ancient Greek and Roman architecture, a peristyle is a continuous porch formed by a row of columns surrounding the perimeter of a building or a courtyard. Tetrastoön is a rarely used archaic term for this feature. The peristyle in a Greek temple is a peristasis. In the Christian ecclesiastical architecture that developed from the Roman basilica, a courtyard peristyle and its garden came to be known as a cloister.

In ancient Rome, the domus was the type of town house occupied by the upper classes and some wealthy freedmen during the Republican and Imperial eras. It was found in almost all the major cities throughout the Roman territories. The modern English word domestic comes from Latin domesticus, which is derived from the word domus. Along with a domus in the city, many of the richest families of ancient Rome also owned a separate country house known as a villa. Many chose to live primarily, or even exclusively, in their villas; these homes were generally much grander in scale and on larger acres of land due to more space outside the walled and fortified city.
This page is a glossary of architecture.

Cavaedium or atrium are Latin names for the principal room of an ancient Roman house, which usually had a central opening in the roof (compluvium) and a rainwater pool (impluvium) beneath it. The cavaedium passively collected, filtered, stored, and cooled rainwater. It also daylit, passively cooled and passively ventilated the house.

Opus reticulatum is a facing used for concrete walls in Roman architecture from about the first century BCE to the early first century CE. They were built using small pyramid shaped tuff, a volcanic stone embedded into a concrete core. Reticulate work was also combined with a multitude of other building materials to provide polychrome colouring and other facings to form new techniques. Opus reticulatum was generally used in central and southern Italy with the exception being its rare appearance in Africa and Jericho. This was because of tuff's wider availability and ease of local transport in central Italy and Campania compared to other regions.

The Pompeian Styles are four periods which are distinguished in ancient Roman mural painting. They were originally delineated and described by the German archaeologist August Mau (1840–1909) from the excavation of wall paintings at Pompeii, which is one of the largest groups of surviving Roman frescoes.

Opus sectile is a form of pietra dura popularized in the ancient and medieval Roman world where materials were cut and inlaid into walls and floors to make a picture or pattern. Common materials were marble, mother of pearl, and glass. The materials were cut in thin pieces, polished, then trimmed further according to a chosen pattern. Unlike tessellated mosaic techniques, where the placement of very small uniformly sized pieces forms a picture, opus sectile pieces are much larger and can be shaped to define large parts of the design.

The House of the Faun, constructed in the 2nd century BC during the Samnite period, was a grand Hellenistic palace that was framed by peristyle in Pompeii, Italy. The historical significance in this impressive estate is found in the many great pieces of art that were well preserved from the ash of the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. It is one of the most luxurious aristocratic houses from the Roman Republic, and reflects this period better than most archaeological evidence found even in Rome itself.

The House of Loreius Tiburtinus is renowned for well-preserved art, mainly in wall-paintings as well as its large gardens.

The House of Menander is one of the richest and most magnificent houses in ancient Pompeii in terms of architecture, decoration and contents, and covers a large area of about 1,800 square metres (19,000 sq ft) occupying most of its insula. Its quality means the owner must have been an aristocrat involved in politics, with great taste for art.

The Domus Transitoria was Roman emperor Nero's first palace damaged or destroyed by the Great Fire of Rome in 64 AD, and then extended by his Domus Aurea.

The House of Sallust was an elite residence (domus) in the ancient Roman city of Pompeii and among the most sumptuous of the city.

The House of the Silver Wedding is the name given to the archaeological remains of a Roman house in Pompeii, buried in the ash from the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. The house was excavated in 1893 and was named after the silver wedding anniversary of Umberto I of Italy and Margherita of Savoy, which took place in that year.
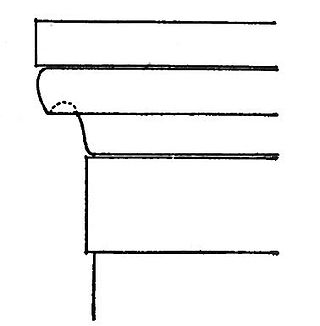
An anta capital is the crowning portion of an anta, the front edge of a supporting wall in Greek temple architecture. The anta is generally crowned by a stone block designed to spread the load from the superstructure (entablature) it supports, called an "anta capital" when it is structural, or sometimes "pilaster capital" if it is only decorative as often during the Roman period.

The mosaics of Delos are a significant body of ancient Greek mosaic art. Most of the surviving mosaics from Delos, Greece, an island in the Cyclades, date to the last half of the 2nd century BC and early 1st century BC, during the Hellenistic period and beginning of the Roman period of Greece. Hellenistic mosaics were no longer produced after roughly 69 BC, due to warfare with the Kingdom of Pontus and the subsequently abrupt decline of the island's population and position as a major trading center. Among Hellenistic Greek archaeological sites, Delos contains one of the highest concentrations of surviving mosaic artworks. Approximately half of all surviving tessellated Greek mosaics from the Hellenistic period come from Delos.

The House of the Prince of Naples is a Roman domus (townhouse) located in the ancient Roman city of Pompeii near Naples, Italy. The structure is so named because the Prince and Princess of Naples attended a ceremonial excavation of selected rooms there in 1898.

The House of the Small Fountain, aka House of the Second Fountain or House of the Landscapes, is located in the Roman city of Pompeii and, with the rest of Pompeii, was preserved by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in or after October 79 CE. It is located on the Via di Mercurio, a street running north from the Arch of Caligula, at its crossroads with Via delle Terme, and Via della Fortuna, to Pompeii's fortification tower XI in the northwest part of the city. The street is named after a public fountain at VI.8.24 with a relief of the god, Mercury. Insula 8 is on the west side of the street. The house is named after a mosaic fountain adorned with shells at the rear of its peristyle. The property is immediately adjacent to the House of the Large Fountain, a structure with an even larger mosaic fountain adorned with shells and marble sculptures of theatrical masks excavated earlier in 1826. So the size difference between the fountains was used to distinguish the two structures.
References
- Tuck, Steven L. (2010). Pompeii: Daily Life in an Ancient Roman City. Chantilly, Virginia: The Great Courses.