Garfield Park is a 184-acre (0.74 km2) urban park located in the East Garfield Park neighborhood on Chicago's West Side. It was designed as a pleasure ground by William LeBaron Jenney in the 1870s and is the oldest of the three original parks developed by the West Side parks commission on the Chicago park and boulevard plan. It is home to the Garfield Park Conservatory, one of the largest plant conservatories in the United States. It is also the park furthest west in the Chicago park and boulevard system.

Parks in Chicago include open spaces and facilities, developed and managed by the Chicago Park District. The City of Chicago devotes 8.5% of its total land acreage to parkland, which ranked it 13th among high-density population cities in the United States in 2012. Since the 1830s, the official motto of Chicago has been Urbs in horto, Latin for "City in a garden" for its commitment to parkland. In addition to serving residents, a number of these parks also double as tourist destinations, most notably Lincoln Park, Chicago's largest park, visited by over 20 million people each year, is one of the most visited parks in the United States. Notable architects, artists and landscape architects have contributed to the 570 parks, including Daniel Burnham, Frederick Law Olmsted, Jens Jensen, Dwight Perkins, Frank Gehry, and Lorado Taft.

Fuller Park is the 37th of Chicago's 77 community areas. Located on the city's South Side, it is 5 miles (8.0 km) from the Loop. It is named for a small park also known as Fuller Park within the neighborhood, which is in turn named for Melville Weston Fuller, a Chicago attorney who was the Chief Justice of the United States between 1888 and 1910.

The South Shore Cultural Center, in Chicago, Illinois, is a cultural facility located at 71st Street and South Shore Drive, in the city's South Shore neighborhood. It encompasses the club facility, grounds, and beach of the former South Shore Country Club, which in the 1970s became part of the public Chicago Park District.

Portage Park is a 36-acre (15 ha) park in the Portage Park community area of Chicago, Illinois on the National Register of Historic Places. The park stretches from Irving Park Road on the south to Berteau Avenue between Central and Long Avenues. The largest public park on Chicago's Northwest Side, it has many recreational facilities including six tennis courts, two playgrounds, a slab for in-line skating, a bike path, a nature walk, five baseball fields, two combination football/soccer fields and two fieldhouses— one housing a gymnasium and the other a cultural arts building. The park also has an Olympic-size pool featuring a large deck for sunning, misting sprays, as well as an interactive water play area with slide and diving boards in addition to a smaller heated pool. Plans are currently underway for the development of a new, 6,500-square-foot (600 m2) senior center at Portage Park.

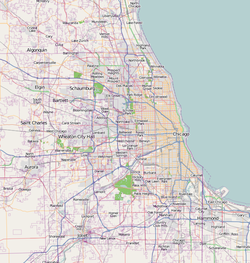
Indian Boundary Park is a 13-acre (5.3 ha) urban park in the West Ridge neighborhood of North Side, Chicago, Illinois.

Pulaski Park is a park in the West Town neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. It was founded in 1912, and was named after American Revolutionary War hero Casimir Pulaski.

Austin Town Hall Park is a park at 5610 W. Lake Street in the Austin neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. The site was formerly used for the town hall of Cicero Township. The Austin subdivision of Cicero was annexed to the City of Chicago in 1899, and the town hall site eventually became part of the Chicago Park District. The park's fieldhouse, designed by Michaelsen and Rognstad in the 1920s, is influenced largely by Philadelphia's Independence Hall.

Kosciuszko Park is a park located at 2732 N. Avers Ave. Situated along the northern boundary of Chicago's Logan Square community area at Diversey, it is heavily frequented by residents of Avondale and is considered to be part of Jackowo.

Sherman Park is a sixty-acre park in the New City neighborhood of South Side, Chicago.

Julia C. Lathrop Homes is a Chicago Housing Authority (CHA) public housing project located along the line between the Lincoln Park and North Center neighborhoods on the north side of Chicago, Illinois, United States. It is bordered by the neighborhoods of Bucktown and Roscoe Village. Completed in 1938 by the Public Works Administration, Lathrop Homes was one of the first Chicago public housing projects. Lathrop Homes was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2012 and is currently undergoing restoration. Lathrop Homes consists of two-story brick row houses and three- and four-story apartment buildings separated by landscaped courtyards and linked by small archways in a campus-like arrangement. There are a total of 925 units on 35.5 acres of land.

Edison Park is a park located in Edison Park community in Chicago, Illinois.

The Shedd Park Fieldhouse is the historic fieldhouse in Shedd Park, a public park in the South Lawndale community area of Chicago, Illinois. John G. Shedd, for whom the park and fieldhouse are named, gave the city the land for the park. The Prairie School building was designed by William Drummond and built in 1917. The brown brick building features limestone trim. A Prairie School gymnasium designed by Michaelsen and Rognstad was added to the building in 1928.

The Produce Terminal Cold Storage Company Building is a historic refrigerated warehouse at 1550 South Blue Island Avenue in the Near West Side neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. Built in 1928–29, the warehouse was the largest cold storage facility in Chicago when it opened. As Chicago was a major shipping and transportation hub, refrigerated storage played a key role in preserving perishable goods so they could be sold year-round. Architects H. Peter Henschien, a designer of refrigerated facilities, and Robert J. McLaren designed the Art Deco building. The top two stories of the eleven-story building feature extensive terra cotta and tile ornamentation, including chevrons, Egyptian-inspired colonettes, and a dentillated cornice with cymatium molding. In addition to its extensive refrigerated space, the interior plan also included processing and office space, improving efficiency and lowering costs for the building's tenants.

Trumbull Park is a public park at 2400 E. 105th Street in the South Deering neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. The South Park Commission opened the park in 1907 as part of its efforts to bring parks to dense immigrant neighborhoods with little green space. The park's fieldhouse and other facilities were not completed until the 1910s; around this time, the park was officially named for Lyman Trumbull, a United States senator from Illinois who co-wrote the Thirteenth Amendment. While the park and its facilities were designed in-house by the South Park Commission, they were inspired by the designs of landscape architects the Olmsted Brothers and architecture firm D. H. Burnham and Company used in many of the South Park Commission's other parks. The fieldhouse in particular has a Beaux-Arts design which calls back to Burnham's work for the 1893 Columbian Exposition.

Fuller Park is a public park at 331 W. 45th Street in the neighborhood of the same name in Chicago, Illinois, United States. The park was one of several built by the South Park Commission in the early 20th century to provide parks in dense and poor South Side Chicago neighborhoods which lacked them. While most of the South Park Commission parks opened in the mid-1900s, work on Fuller Park did not begin until 1910 due to a dispute over its location, and its facilities gradually opened over the next four years. The park was named for Melville Fuller, an Illinois native and former Chief Justice of the United States. The South Park Commission designed the park's landscape in a similar style to their earlier parks, which had been designed by the Olmsted Brothers; D. H. Burnham and Company designed its buildings, as they had for the earlier parks. The park originally included a Beaux-Arts fieldhouse, a gymnasium, a bathhouse, a grandstand, and a running track and walking paths. Fuller Park was first settled by Irish immigrants in the later 1860s after the Union Stock Yards opened on Christmas Day 1865. This area became a part of the Lake Township area and after the Great Chicago Fire of 1871 and the opening of the Lake Shore & Michigan Southern Railroad the area flourished into a community.

Davis Square is a public park located between 44th and 45th Streets and Marshfield and Hermitage Avenues in the New City community area of Chicago, Illinois. The park opened in 1905 as one of the initial parks in the South Park Commission's plan to build parks in the dense, poor neighborhoods of Chicago's South Side. It was named for Nathan Smith Davis, a Chicago physician and one of the founders of the American Medical Association. As they did for most of the South Park Commission's parks, the Olmsted Brothers designed Davis Square's landscape, while D. H. Burnham and Company designed its facilities. The park initially included a Beaux-Arts styled fieldhouse, a swimming pool and pool house, baseball fields, and walking paths.

Cornell Square is a public park at 1809 W. 50th Street in the New City community area of Chicago, Illinois. Opened in 1905, the park was one of many planned by the South Park Commission to provide parks in dense, poor South Side neighborhoods. The park was named for Paul Cornell, one of the Commission's board members. As with the South Park Commission's other early parks, landscape architects the Olmsted Brothers designed the park's layout while D. H. Burnham and Company designed its facilities. The park originally included a fieldhouse with gymnasium facilities, a swimming pool, athletic fields, and walking paths. The fieldhouse has a Beaux-Arts design and includes a painting of Ezra Cornell, the founder of Cornell University and Paul Cornell's cousin.

Grand Crossing Park is a public park at 7655 S. Ingleside Avenue in the Greater Grand Crossing neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. Opened in 1915, the park was planned by the South Park Commission, which was responsible for adding several parks in dense, poor South Side neighborhoods. While the South Park Commission designed the park and its facilities in-house, its designs were heavily influenced by the work of the Olmsted Brothers and D. H. Burnham and Company in its earlier parks. The park originally included a Beaux-Arts fieldhouse, a swimming pool, outdoor gymnasiums, a baseball field, tennis courts, and running and walking paths. The fieldhouse includes indoor gymnasiums, meeting rooms, and a series of murals titled An Allegory of Recreation.
The Charles Warrington Earle School is a historic school building at 6121 S. Hermitage Avenue in the West Englewood neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. Opened in 1897, the school was one of many built to serve Chicago's growing student population in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, a result of compulsory education laws and an influx of European immigrants to the city. School board architect William August Fiedler designed the Renaissance Revival school; his plan was typical of Progressive Era school designs, which focused on improving the layout, lighting, and ventilation of schools. Though the school was built to serve six hundred students, settlement in West Englewood outpaced its capacity, and in 1900 the school board doubled the school's size with an addition. The school served Chicago students for over a century before closing along with over fifty other public schools in 2013.