
A railcar is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach, with a driver's cab at one or both ends. Some railway companies, such as the Great Western, termed such vehicles "railmotors".

Lilydale railway station is a commuter railway station and the terminus of the Lilydale line, serving the north-eastern Melbourne suburb of Lilydale in Victoria, Australia. Lilydale is an elevated premium station, featuring an island platform with two faces. It opened on 1 December 1882, with the current terminus station and stabling provided in 2022.

Yarra Glen is the city-end terminus of the Yarra Valley Railway, which operates over part of the former Healesville railway line.

Tarrawarra was a station on the former Healesville line between Yarra Glen and Healesville stations, in Victoria, Australia. The station opened in 1889 and closed along with the line in December 1980. In the 1970s, timetables showed that the station was a flag stop because of the small number of passengers using the station.

Healesville is a railway station in Victoria, Australia. Formerly the terminus of the Healesville railway line, it is currently the principal station of the heritage Yarra Valley Railway. A temporary station was built on the site in 1888–1889 when the railway line was extended from Lilydale to Healesville. The current station was built in 1903 and is now listed with Heritage Victoria.
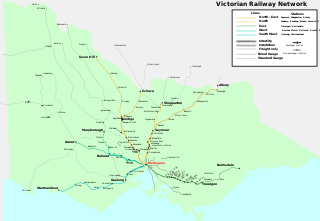
Rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria is provided by a number of railway operators who operate over the government-owned railway lines. The network consists of 2,357 km of Victorian broad gauge lines, and 1,912 km of standard gauge freight and interstate lines; the latter increasing with gauge conversion of the former. Historically, a few experimental 762 mm gauge lines were built, along with various private logging, mining and industrial railways. The rail network radiates from the state capital, Melbourne, with main interstate links to Sydney and to Adelaide, as well as major lines running to regional centres, upgraded as part of the Regional Fast Rail project.

The Lilydale to Warburton Rail Trail is a walking, cycling and horse-riding track in eastern Victoria, Australia. It runs a distance of 40 km (25 mi) between Lilydale and Warburton, along the former Warburton railway line in the Yarra Valley.

The Yarra Valley Railway is a heritage railway operating on a section of the former Healesville railway which operated between Lilydale and Healesville in the Yarra Valley area northeast of Melbourne, Australia.

The Warburton railway line just outside Melbourne, Australia, was a railway branching off from the Healesville line at the present terminus, Lilydale.
The South Gippsland railway line is a partially closed railway line in Victoria, Australia. It was first opened in 1892, branching from the Orbost line at Dandenong, and extending to Port Albert. Much of it remained open until December 1994. Today, only the section between Dandenong and Cranbourne remains open for use. The section of the line from Nyora to Leongatha was used by the South Gippsland Tourist Railway until it ceased operations in 2016. The section from Nyora to Welshpool, with extension trail to Port Welshpool and a portion of the former line at Koo Wee Rup, have been converted into the Great Southern Rail Trail.
The South Gippsland Railway was a tourist railway located in South Gippsland, Victoria, Australia. It controlled a section of the former South Gippsland railway line between Nyora and Leongatha, and operated services from Leongatha to Nyora, via Korumburra, the journey taking about 65 minutes.
Railmotor is a term used in the United Kingdom and elsewhere for a railway lightweight railcar, usually consisting of a railway carriage with a steam traction unit, or a diesel or petrol engine, integrated into it.

The steam rail motors (SRM) were self-propelled carriages operated by the Great Western Railway in England and Wales from 1903 to 1935. They incorporated a steam locomotive within the body of the carriage.

The Gulflander is a passenger train operated by Queensland Rail on the isolated Normanton to Croydon line in the Gulf Country of northern Queensland, Australia.

The Diesel Electric Rail Motor (DERM) was a type of railmotor operated by the Victorian Railways in Australia.
The MT type carriages were railmotor trailers, used on the Victorian Railways (VR) in Australia.
The New Deal for Country Passengers was a timetable introduced on 4 October 1981 in Victoria, Australia which revolutionised the provision of country passenger railway services in that state. Thirty-five little-used passenger stations were closed, rolling stock utilisation was improved, and new rolling stock introduced. The timetable and associated service changes resulted in an average patronage growth of 8.7% per year, from 3 million in 1981 to 5.6 million passengers in 1990/91.

The family of Walker railmotors were a type of diesel railcar operated by the Victorian Railways in Australia.

Creamy Kate is a former New South Wales Government Railways railmotor, numbered 38. It is an evolution of the CPH rail motor class.














