
Traralgon is a town located in the east of the Latrobe Valley in the Gippsland region of Victoria, Australia and the most populous city in the City of Latrobe and the region. The urban population of Traralgon at the 2021 census was 26,907. It is the largest and fastest growing city in the greater Latrobe Valley area, which has a population of 77,168 at the 2021 Census and is administered by the City of Latrobe.

Morwell is a town in the Latrobe Valley area of Gippsland, in South-Eastern Victoria, Australia approximately 152 km (94 mi) east of Melbourne.

The Latrobe Valley is an inland geographical district and urban area of the Gippsland region in the state of Victoria, Australia. The traditional owners are the Brayakaulung of the Gunai nation. The district lies east of Melbourne and nestled between the Strzelecki Ranges to the south and the Baw Baw Ranges, part of the Great Dividing Range, to the north. Mount St Phillack is the highest peak to the north of the Latrobe Valley, due north of Moe. The highest peak to the south is Mt Tassie, south of Traralgon.
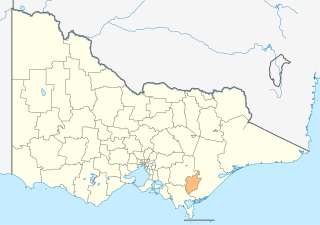
The City of Latrobe is a local government area in the Gippsland region in eastern Victoria, Australia, located in the eastern part of the state. It covers an area of 1,426 square kilometres (551 sq mi) and in June 2018 had a population of 75,211. It is primarily urban with the vast majority of its population living within the four major urban areas of Moe, Morwell, Traralgon, and Churchill, and other significant settlements in the LGA include Boolarra, Callignee, Glengarry, Jeeralang, Newborough, Toongabbie, Tyers, Yallourn North and Yinnar. It was formed in 1994 from the amalgamation of the City of Moe, City of Morwell, City of Traralgon, Shire of Traralgon, and parts of the Shire of Narracan and Shire of Rosedale. The Yallourn Works Area was added in 1996. When formed, the municipality was called the Shire of La Trobe, but on 6 April 2000, it adopted its current name.

Dandenong railway station is the junction for the Cranbourne and Pakenham lines in Victoria, Australia. It serves the south-eastern Melbourne suburb of the same name, and opened on 8 October 1877.
The Gippsland V/Line rail service is a passenger service operated by V/Line in Victoria, Australia between Melbourne and the Gippsland region including the regional cities of Moe, Morwell, Traralgon, Sale and Bairnsdale. It operates along the Gippsland railway line.

Tynong railway station is located on the Gippsland line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the town of Tynong, and it opened on 12 February 1880.

Warragul railway station is located on the Gippsland line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the town of Warragul, and it opened on 1 March 1878 as Warrigal. It was renamed Warragul on 1 May 1879.

Moe railway station is located on the Gippsland line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the town of Moe, and it opened on 1 March 1878.

Morwell railway station is located on the Gippsland line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the town of Morwell, and it opened on 1 June 1877.
Mirboo North is a town in Victoria, Australia, located 150 kilometres (93 mi) east of Melbourne, with a population of 1,697. It is in the South Gippsland Shire local government area.

Moe is a town in the Latrobe Valley in the Gippsland region of Victoria, Australia. It is approximately 130 kilometres east of the central business district of Melbourne, 45 kilometres due south of the peak of Mount Baw Baw in the Great Dividing Range and features views of the Baw Baw Ranges to the north and Strzelecki Ranges to the south.

Traralgon railway station is located on the Gippsland line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the city of Traralgon, and it opened on 1 June 1877.

The Gippsland League is an Australian rules football and netball league in the Gippsland region of Victoria, Australia. It is considered the only AFL Victoria major league in Gippsland.

The Shire of Narracan was a local government area about 120 kilometres (75 mi) east-southeast of Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria, Australia. The shire covered an area of 2,300 square kilometres (888.0 sq mi), and existed from 1878 until 1994.

The Warragul Football and Netball Club, nicknamed the Gulls, is an Australian rules football and netball club based in the city of the same name in the state of Victoria.
The Noojee railway line is a closed railway line in Victoria, Australia. Branching off from the Gippsland line at Warragul station, it was built to service the timber industry in the upper Latrobe River area, transporting timber as well as providing a general goods and passenger service to townships in the area. The final section of the line between Neerim South and Noojee traversed increasingly hilly terrain and featured a number of large timber trestle bridges. Extensively and repeatedly damaged by bushfires over the years, the line was closed in the 1950s and dismantled. The last remaining large trestle bridge on the line has been preserved and has become a popular local tourist attraction.

The Moe Football Netball Club, nicknamed the Lions, is an Australian rules football and netball club based at Ted Summerton Reserve in the town of Moe, Victoria. The club teams currently compete in the Gippsland Football League.
























