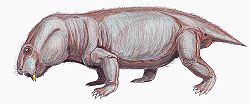
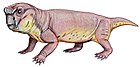
| Interpresosaurus Temporal range: Late Permian | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | † Anomodontia |
| Clade: | † Dicynodontia |
| Family: | † Elphidae |
| Subfamily: | † Elphinae |
| Genus: | † Interpresosaurus Kurkin, 2001 |
| Species: | †I. blomi |
| Binomial name | |
| †Interpresosaurus blomi Kurkin, 2001 | |
Interpresosaurus ("mediator lizard" [1] ) is a genus of dicynodont from the Late Permian (Changhsingian) Vyazniki Assemblage of Russia. [1] The type and only species, Interpresosaurus blomi, is known from a single fragmentary skull, PIN 3584/1. [2]