| Basilodon Temporal range: Late Permian ~ | |
|---|---|
 | |
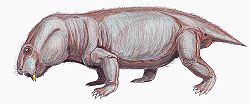
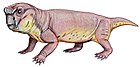
| Basilodon woodwardi | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | † Anomodontia |
| Clade: | † Dicynodontia |
| Family: | † Lystrosauridae |
| Genus: | † Basilodon Kammerer et al. 2011 |
| Type species | |
| †Basilodon woodwardi (Broom, 1921) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Basilodon is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid. [1] The type species, Basilodon woodwardi was originally named in 1921 as Dicynodon woodwardi. Fossils have been found in the Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone and Dicynodon Assemblage Zone of the Balfour Formation of the Beaufort Group in South Africa.